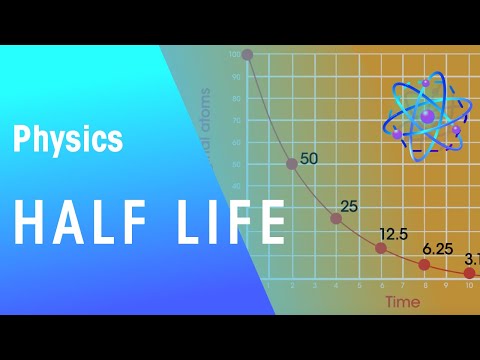
Q. How does radioactivity change each half life?
Half-life, in radioactivity, the interval of time required for one-half of the atomic nuclei of a radioactive sample to decay (change spontaneously into other nuclear species by emitting particles and energy), or, equivalently, the time interval required for the number of disintegrations per second of a radioactive …
Q. Does the half life of a radioactive isotope increase as the radioactive isotope ages?
The rate at which a radioactive isotope decays is measured in half-life. The term half-life is defined as the time it takes for one-half of the atoms of a radioactive material to disintegrate….After this reading this section you will be able to do the following:
Table of Contents
- Q. How does radioactivity change each half life?
- Q. Does the half life of a radioactive isotope increase as the radioactive isotope ages?
- Q. How does half life relate to radioactive decay?
- Q. What is a half life of a radioactive isotope?
- Q. What is the shortest lived isotope of carbon?
- Q. What does the 13 mean in carbon-13?
- Q. Is carbon 12 or carbon-14 radioactive?
- Q. How long does it take for half of a sample of carbon 14 to break down?
- Q. How long does it take for 50% of a specific amount of carbon-14 to decay?
- Q. Which of the following has the longest half life?
- Q. What material has the shortest half life?
- Q. What is the shortest lived element?
- Q. Does gold have a half life?
- Q. Is gold a toxic metal?
- Q. Is Gold-197 stable?
- Q. Why is gold-197 stable?
- Q. What is the normal phase for gold?
| Radioisotope | Half-life |
|---|---|
| Uranium-238 | 4.5 billion years |
Q. How does half life relate to radioactive decay?
The decay of radioactive elements occurs at a fixed rate. The half-life of a radioisotope is the time required for one half of the amount of unstable material to degrade into a more stable material. After ten half-lives, less than one-thousandth of the original activity will remain.
Q. What is a half life of a radioactive isotope?
The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the amount of time it takes for one-half of the radioactive isotope to decay. The half-life of a specific radioactive isotope is constant; it is unaffected by conditions and is independent of the initial amount of that isotope.
Q. What is the shortest lived isotope of carbon?
In total, there are 15 known isotopes of carbon and the shortest-lived of these is 8C, which decays through proton emission and alpha decay, and has a half-life of 1.98739 x 10−21 seconds.
Q. What does the 13 mean in carbon-13?
Carbon-13 (13C): The carbon isotope whose nucleus contains six protons and seven neutrons. This gives an atomic mass of 13 amu. seven neutrons, resulting in an atomic mass of 13 amu.
Q. Is carbon 12 or carbon-14 radioactive?
Radiocarbon dating uses carbon isotopes. Most carbon on Earth exists as the very stable isotope carbon-12, with a very small amount as carbon-13. Carbon-14 is an unstable isotope of carbon that will eventually decay at a known rate to become carbon-12. Carbon-14 is considered a radioactive isotope of carbon.
Q. How long does it take for half of a sample of carbon 14 to break down?
5,730 years
Q. How long does it take for 50% of a specific amount of carbon-14 to decay?
6000 years
Q. Which of the following has the longest half life?
Bismuth-209 (209Bi) is the isotope of bismuth with the longest known half-life of any radioisotope that undergoes α-decay (alpha decay). It has 83 protons and a magic number of 126 neutrons, and an atomic mass of 208.9803987 amu (atomic mass units).
Q. What material has the shortest half life?
Uranium-234 has the shortest half-life of them all at 245,500 years, but it occurs only indirectly from the decay of U-238. In comparison, the most radioactive element is polonium. It has a half-life of a mere 138 days.
Q. What is the shortest lived element?
The shortest-lived isotope of Ununtrium has a half life of only 0.24 milliseconds. Little is known about element 113 and its isotopes and possible compounds. The most stable isotope is Uut-286, which has a half life of 20 seconds.
Q. Does gold have a half life?
Gold (79Au) has one stable isotope, 197Au, and 36 radioisotopes, with 195Au being the most stable with a half-life of 186 days.
Q. Is gold a toxic metal?
In its metallic form, gold is not toxic, which is why we can eat ice cream with gold flakes. However, some natural gold compounds will break down in the body releasing gold ions, which can have toxic effects on living organisms.
Q. Is Gold-197 stable?
Gold has 41 known isotopes, ranging from gold-170 to gold-210. Only one of these, gold-197, is stable, the rest are radioactive. A stable isotope has no experimentally detected nuclear decays. Isotopes which undergo these decays are referred to as radioactive, or radioisotopes.
Q. Why is gold-197 stable?
Stable isotopes of the heavier elements (top right of the graph) have more neutrons than protons. For example, Gold-197 is stable. It contains 79 protons and 118 neutrons. Hence the line begins to curve upwards, away from N = Z.
Q. What is the normal phase for gold?
Solid