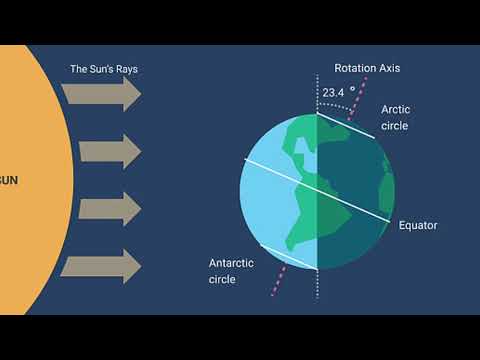
Q. How does solar intensity change with latitude?
When the sun’s rays strike Earth’s surface near the equator, the incoming solar radiation is more direct (nearly perpendicular or closer to a 90˚ angle). At higher latitudes, the angle of solar radiation is smaller, causing energy to be spread over a larger area of the surface and cooler temperatures.
Q. At what latitude is solar intensity greatest?
Latitudinal Variation. Only locations lying along one line of latitude on the surface of the Earth can receive sunlight at a 90 degree angle on a given day. All other places receive sunlight at lesser intensities. In general, the sun’s rays are the most intense at the equator and the least intense at the poles.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does solar intensity change with latitude?
- Q. At what latitude is solar intensity greatest?
- Q. What is the solar constant at the top of the atmosphere?
- Q. Where is the most latitude and solar energy on Earth?
- Q. Where is solar energy most concentrated?
- Q. Why are higher latitudes colder?
- Q. Where is insolation the highest?
- Q. Which planet has the largest solar constant?
- Q. What is the intensity of solar energy?
- Q. Where is the solar energy most concentrated?
- Q. Which part of the earth receive most light?
- Q. Which states produce the most solar energy?
- Q. What is the average amount of solar irradiance in the atmosphere?
- Q. How does latitude affect the amount of solar energy the Earth receives?
- Q. How is the radiation at the top of the atmosphere determined?
- Q. How is the Earth-atmosphere energy balance achieved?
Q. What is the solar constant at the top of the atmosphere?
1366 2 W/m2
At the top of the atmosphere, energy is received with a flux, or power density of 1366 2 W/m2, a value known as the solar constant.
Q. Where is the most latitude and solar energy on Earth?
the equator
Earth receives different amounts of solar energy at different latitudes, with the most at the equator and the least at the poles.
Q. Where is solar energy most concentrated?
The sun’s rays strike Earth’s surface most directly at the equator. This focuses the rays on a small area….
- A lot of the solar energy that reaches Earth hits the equator.
- Much less solar energy gets to the poles.
- The difference in the amount of solar energy drives atmospheric circulation.
Q. Why are higher latitudes colder?
In general, the farther from the equator an area is, the colder and snowier it will be. This is because higher-latitude regions receive less light and energy from the Sun than low-latitude, tropical areas.
Q. Where is insolation the highest?
The intensity of insolation is greatest on the equator. This is because the angle. of the sun is higher, at close to 90.
Q. Which planet has the largest solar constant?
The largest planet in our solar system by far is Jupiter, which beats out all the other planets in both mass and volume. Jupiter’s mass is more than 300 times that of Earth, and its diameter, at 140,000 km, is about 11 times Earth’s diameter.
Q. What is the intensity of solar energy?
approximately 1380 watts per square meter
Above the earth’s atmosphere, solar radiation has an intensity of approximately 1380 watts per square meter (W/m2). This value is known as the Solar Constant. At our latitude, the value at the surface is approximately 1000 W/m2 on a clear day at solar noon in the summer months.
Q. Where is the solar energy most concentrated?
Mojave Desert
The 377 MW Ivanpah Solar Power Facility, located in the Mojave Desert, is the largest CSP facility in the world, and uses three power towers. Ivanpah generated only 0.652 TWh (63%) of its energy from solar means, and the other 0.388 TWh (37%) was generated by burning natural gas.
Q. Which part of the earth receive most light?
The equator of the earth receives most of the sun’s rays. This is because it lies directly over the sun.
Q. Which states produce the most solar energy?
Related Content:
| State | Rank | Solar share of total energy production |
|---|---|---|
| California | 1 | 14.0% |
| North Carolina | 2 | 5.7% |
| Arizona | 3 | 4.6% |
| Nevada | 4 | 12.1% |
Q. What is the average amount of solar irradiance in the atmosphere?
The average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere (1361 W/m 2) represents the power per unit area of solar irradiance across the spherical surface surrounding the sun with radius equal to the distance to the Earth (1 AU ).
Q. How does latitude affect the amount of solar energy the Earth receives?
The progressive decrease in the angle of solar illumination with increasing latitude reduces the average solar irradiance by an additional one-half. The solar radiation received at Earth’s surface varies by time and latitude. This graph illustrates the relationship between latitude, time, and solar energy during the equinoxes.
Q. How is the radiation at the top of the atmosphere determined?
Irradiation at the top of the atmosphere. The distribution of solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere is determined by Earth’s sphericity and orbital parameters. This applies to any unidirectional beam incident to a rotating sphere. Insolation is essential for numerical weather prediction and understanding seasons and climate change.
Q. How is the Earth-atmosphere energy balance achieved?
The earth-atmosphere energy balance is achieved as the energy received from the Sun balances the energy lost by the Earth back into space. In this way, the Earth maintains a stable average temperature and therefore a stable climate. Using 100 units of energy from the sun as a baseline the energy balance is as follows: