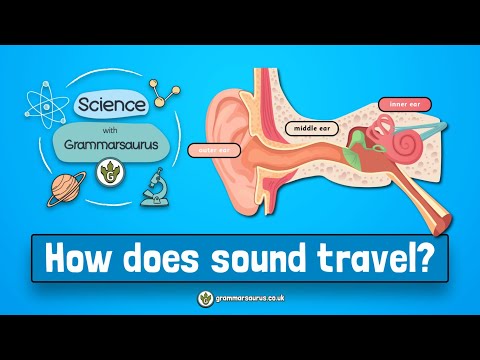
Sound travels in mechanical waves. A mechanical wave is a disturbance that moves and transports energy from one place to another through a medium. In sound, the disturbance is a vibrating object. And the medium can be any series of interconnected and interactive particles.
Q. Can sound travel through objects?
Sound waves need to travel through a medium such as solids, liquids and gases. The sound waves move through each of these mediums by vibrating the molecules in the matter. The molecules in solids are packed very tightly. Liquids are not packed as tightly.
Table of Contents
- Q. Can sound travel through objects?
- Q. What can a sound travel through?
- Q. Can we touch sound?
- Q. Can sound pass through water?
- Q. Can humans hear whale sounds above water?
- Q. What travels faster in a vacuum?
- Q. What is the 2 fastest thing in the world?
- Q. Is a tachyon real?
- Q. Is a tachyon faster than light?
- Q. Is FTL theoretically possible?
Q. What can a sound travel through?
Sound is a type of energy made by vibrations. These vibrations create sound waves which move through mediums such as air, water and wood. When an object vibrates, it causes movement in the particles of the medium. This movement is called sound waves, and it keeps going until the particles run out of energy.
Q. Can we touch sound?
Well, sound is vibration, and vibration is tactile. You can feel sound by touch. Put your hand on a piano while someone is playing. You can feel the sound vibrations through your clothing or against your skin.
Q. Can sound pass through water?
Thus sound waves travel much faster in water than they do in air. Our head itself is full of tissues that contain water and can transmit sound waves when we are underwater. When this happens, the vibrations bypass the eardrum, the part of the ear that evolved to pick up sound waves in the air.
Q. Can humans hear whale sounds above water?
Humans can only hear part of the whales’ songs. We aren’t able to hear the lowest of the whale frequencies. Humans hear low frequency sounds starting at about 100 Hz. Researchers have noted that whale songs sound very similar to the songs of hoofed animals, such as.
Q. What travels faster in a vacuum?
“Nothing can travel faster than the speed of light in a vacuum.” “Light in a vacuum always travels at the same speed.” Those additional three words in a vacuum are very important. So a vacuum would not contain any dust particles (unlike a vacuum cleaner, which is generally full of dust particles).
Q. What is the 2 fastest thing in the world?
List of animals by speed
| Rank | Animal | Maximum speed |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Peregrine falcon | 389 km/h (242 mph) 108 m/s (354 ft/s) |
| 2 | Golden eagle | 240–320 km/h (150–200 mph) 67–89 m/s (220–293 ft/s) |
| 3 | White-throated needletail swift | 169 km/h (105 mph) |
| 4 | Eurasian hobby | 160 km/h (100 mph) |
Q. Is a tachyon real?
Tachyons have never been found in experiments as real particles traveling through the vacuum, but we predict theoretically that tachyon-like objects exist as faster-than-light ‘quasiparticles’ moving through laser-like media.
Q. Is a tachyon faster than light?
A tachyon (/ˈtækiɒn/) or tachyonic particle is a hypothetical particle that always travels faster than light. Most physicists believe that faster-than-light particles cannot exist because they are not consistent with the known laws of physics.
Q. Is FTL theoretically possible?
According to the current scientific theories, matter is required to travel at slower-than-light (also subluminal or STL) speed with respect to the locally distorted spacetime region. Apparent FTL is not excluded by general relativity; however, any apparent FTL physical plausibility is currently speculative.