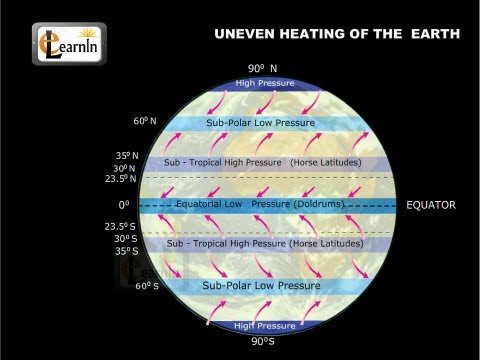
How does atmosphere respond to uneven solar heating? The uneven heating causes temperature differences, which in turn cause air currents (wind) to develop, which then move heat from where there is more heat (higher temperatures) to where there is less heat (lower temperatures).
Q. Is most responsible for the uneven heating?
Answer Expert Verified. The answer would be convection currents. Convection happens when atoms with a lot of heat energy in a liquid or gas transfer and get the room of particles with fewer heat energy. Heat energy is transported from hot places to cooler places by convection.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is most responsible for the uneven heating?
- Q. How does the uneven heating of Earth influence the movement of fluid?
- Q. What factors contribute to the uneven heating of Earth by the sun quizlet?
- Q. What is the composition of the atmosphere?
- Q. How does solar heating vary with latitude?
- Q. Where does the sun hit the earth most directly?
- Q. What latitude receives the most direct sunlight?
- Q. What latitude appears to have the sun hitting at a 90 degree angle?
- Q. How many times each year does the sun pass through your zenith if you live on the equator?
- Q. What is the position of sun rays on June 21st?
- Q. Does Sun stay still?
Q. How does the uneven heating of Earth influence the movement of fluid?
Earth receives more solar radiation at the equator than it does at the poles; this uneven distribution of heat creates pressure differences, which in turn cause the movement of air, or wind. Earth’s rotation causes fluids — both air and water — to be deflected to the side as they move across our planet’s surface.
Q. What factors contribute to the uneven heating of Earth by the sun quizlet?
what factors contribute to the uneven heating of the earth by the sun? The eastwards rotation of Earth on its axis deflects the moving air or water (or any moving object that has mass) away from its initial course. This deflection is called the Corliosis effect. You just studied 8 terms!
Q. What is the composition of the atmosphere?
Composition of air Nitrogen — 78 percent. Oxygen — 21 percent. Argon — 0.93 percent. Carbon dioxide — 0.04 percent.
Q. How does solar heating vary with latitude?
When the sun’s rays strike Earth’s surface near the equator, the incoming solar radiation is more direct (nearly perpendicular or closer to a 90˚ angle). At higher latitudes, the angle of solar radiation is smaller, causing energy to be spread over a larger area of the surface and cooler temperatures.
Q. Where does the sun hit the earth most directly?
During the summer solstice, the Sun shines most directly on the Tropic of Cancer, 23.5 degrees north of the equator, giving its most direct energy on Earth to the Northern Hemisphere.
Q. What latitude receives the most direct sunlight?
0° latitude
Q. What latitude appears to have the sun hitting at a 90 degree angle?
Since the Earth’s axis is tilted 23.5 degrees, then on this particular day, the Sun’s rays are striking the Earth directly at a latitude approximately 23.5 degrees north of the equator (that is, the Sun’s rays are coming in at an angle of 90 degrees here; this is the subsolar point).
Q. How many times each year does the sun pass through your zenith if you live on the equator?
Once or twice each year, people who live at lower latitudes (within 23.5 degrees of the equator) can see the sun reach the zenith, an imaginary point directly overhead.
Q. What is the position of sun rays on June 21st?
On June 21-22, the Sun’s perpendicular rays (witnessed by 90o position of sun at noon) shine down at 23.5o N latitude (Tropic of Cancer). b. From June to September 21, the Sun’s perpendicular rays migrate from 23.5o N latitude to the equator (0o latitude).
Q. Does Sun stay still?
Yes, the Sun rotates! The Sun is the center of our solar system, but it doesn’t stay in one place.