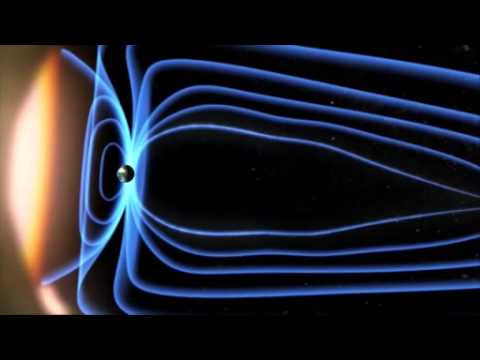
Earth’s magnetic field serves to deflect most of the solar wind, whose charged particles would otherwise strip away the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation. One stripping mechanism is for gas to be caught in bubbles of magnetic field, which are ripped off by solar winds.
Q. Why is Earth magnetic field weakening?
The forces in the core and the tilt of the magnetic axis together produce the anomaly, the area of weaker magnetism – allowing charged particles trapped in Earth’s magnetic field to dip closer to the surface.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why is Earth magnetic field weakening?
- Q. What is the major cause of the earth’s magnetic field?
- Q. Why do we need a magnetic field?
- Q. Does Earth’s electromagnetic field protect us?
- Q. How does the Earth protect us?
- Q. What is a nickname for Earth?
- Q. What phenomenon is the result of Earth’s rotation?
- Q. What would happen if there was no magnetosphere?
- Q. What happens if the magnetic field flips?
- Q. What is the average time between field reversals?
- Q. Why does the magnetic field flip?
Q. What is the major cause of the earth’s magnetic field?
The Earth’s magnetic field is mostly caused by electric currents in the liquid outer core. The Earth’s core is hotter than 1043 K, the Curie point temperature above which the orientations of spins within iron become randomized. Such randomization causes the substance to lose its magnetization.
Q. Why do we need a magnetic field?
Extending from Earth like invisible spaghetti is the planet’s magnetic field. Created by the churn of Earth’s core, this field is important for everyday life: It shields the planet from solar particles, it provides a basis for navigation and it might have played an important role in the evolution of life on Earth.
Q. Does Earth’s electromagnetic field protect us?
The magnetic field of the Earth plays a very important role in our lives, it protects us from the solar winds. These are currents of particles charged of energy emanated from the sun which emit radiation. The magnetosphere deflects the dangerous ultraviolet rays of the sun, keeping us safe from any risk.
Q. How does the Earth protect us?
It contains the oxygen that we breath as well as other important gases such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water vapor, and ozone. It protects us from the Sun’s harmful rays, burns and destroys meteors that are headed toward Earth, and it keeps our planet from having extreme temperature changes.
Q. What is a nickname for Earth?
Earth has a number of nicknames, including the Blue Planet, Gaia, Terra, and “the world” – which reflects its centrality to the creation stories of every single human culture that has ever existed.
Q. What phenomenon is the result of Earth’s rotation?
Revolution: The revolution of the Earth on its axis is important in setting up the seasons. Evidence for this is in a phenomena called parallax where nearby stars appear to shift with regards to distant stars. The direction of Earth’s revolution is in the direction of its rotation.
Q. What would happen if there was no magnetosphere?
Without the magnetosphere, the relentless action of these solar particles could strip the Earth of its protective layers, which shield us from the Sun’s ultraviolet radiation. It’s clear that this magnetic bubble was key to helping Earth develop into a habitable planet.
Q. What happens if the magnetic field flips?
During an excursion or a reversal, the magnetic field is considerably weakened and allows many more cosmic rays to reach the surface of the planet. These energetic particles from space can be damaging to life on Earth if too many reach the surface.
Q. What is the average time between field reversals?
approximately 7000 years
Q. Why does the magnetic field flip?
The reversals take place when iron molecules in Earth’s spinning outer core start going in the opposite direction as other iron molecules around them. As their numbers grow, these molecules offset the magnetic field in Earth’s core.