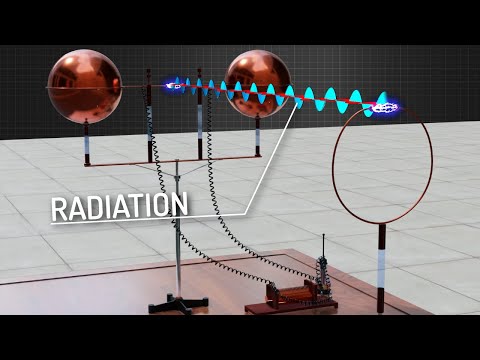
Q. How electromagnetic oscillations are generated?
Electromagnetic waves are created by oscillating charges (which radiate whenever accelerated) and have the same frequency as the oscillation. Since the electric and magnetic fields in most electromagnetic waves are perpendicular to the direction in which the wave moves, it is ordinarily a transverse wave.
Q. What are oscillators used for?
Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating current (AC) signal. They are widely used in many electronic devices ranging from simplest clock generators to digital instruments (like calculators) and complex computers and peripherals etc.
Table of Contents
- Q. How electromagnetic oscillations are generated?
- Q. What are oscillators used for?
- Q. Why do electromagnetic waves oscillate?
- Q. What are the types of oscillators?
- Q. What is the principle of an oscillator?
- Q. What do you mean by oscillators?
- Q. What is the other name for oscillator?
- Q. Which is the best oscillator?
- Q. What is oscillation in simple words?
- Q. What is the formula of oscillation?
- Q. What is a period of oscillation?
- Q. What is Oscillation give two examples?
- Q. What is a full oscillation?
- Q. What is difference between oscillation and vibration?
- Q. What is wave and oscillation?
- Q. Is a wave and oscillation?
- Q. What are 4 parts of a wave?
- Q. What is the least dangerous radiation?
- Q. Can radiation be felt?
- Q. What does dying of radiation feel like?
- Q. What are the symptoms of radiation?
- Q. What is Oscillator and how it works?
- Q. Why do oscillators need positive feedback?
- Q. What is the value of frequency of horizontal oscillator?
- Q. What is the function of vertical oscillator?
- Q. What is horizontal deflection?
- Q. What is horizontal circuit?
- Q. What is a deflection circuit?
- Q. What is hot transistor?
- Q. What is vertical IC on a TV?
- Q. What causes horizontal line on CRT TV?
- Q. Do transistors get hot?
- Q. What causes transistor to overheat?
- Q. What is hot in CRT TV?
- Q. What is a vertical transistor?
- Q. Why does horizontal output transistor keep blowing?
Q. Why do electromagnetic waves oscillate?
A charge oscillates. It creates a changing electric field, which induces changing magnetic field which in turn induces changing electric field, and so on. This whole phenomenon spreads out in space and that is called as ‘Electromagnetic radiations’. So, you see, the radiations themselves do not oscillate.
Q. What are the types of oscillators?
Types of Oscillators: Common oscillator technology variations
- Crystal Oscillators.
- SAW oscillators.
- MEMS Oscillators.
- Voltage-controlled oscillators.
- Voltage-controlled oscillators can operate at higher frequencies but are much less stable than other oscillator signals.
Q. What is the principle of an oscillator?
There are many types of electronic oscillators, but they all operate according to the same basic principle: an oscillator always employs a sensitive amplifier whose output is fed back to the input in phase. Thus, the signal regenerates and sustains itself. This is known as positive feedback.
Q. What do you mean by oscillators?
An oscillator is a technical analysis tool that constructs high and low bands between two extreme values, and then builds a trend indicator that fluctuates within these bounds. Traders use the trend indicator to discover short-term overbought or oversold conditions.
Q. What is the other name for oscillator?
noun. ( ˈɑːsəˌleɪtɝ) Generator that produces sonic oscillations or alternating current. Synonyms. crystal oscillator heterodyne oscillator generator quartz oscillator local oscillator. stator rotor.
Q. Which is the best oscillator?
In general, momentum oscillators with a fixed range are best suited for identifying overbought and oversold conditions. These include RSI, the Stochastic Oscillator and StochRSI. RSI and the Stochastic Oscillator fluctuate between zero and one hundred, while StochRSI fluctuates between zero and one.
Q. What is oscillation in simple words?
a single swing or movement in one direction of an oscillating body. fluctuation between beliefs, opinions, conditions, etc. Physics. an effect expressible as a quantity that repeatedly and regularly fluctuates above and below some mean value, as the pressure of a sound wave or the voltage of an alternating current.
Q. What is the formula of oscillation?
The period formula, T = 2π√m/k, gives the exact relation between the oscillation time T and the system parameter ratio m/k.
Q. What is a period of oscillation?
the smallest interval of time in which a system undergoing oscillation returns to the state it was in at a time arbitrarily chosen as the beginning of the oscillation.
Q. What is Oscillation give two examples?
Most common examples for oscillation are the tides in the sea and the movement of a simple pendulum in a clock. Another example of oscillation is the movement of spring. The vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments are also examples of oscillations.
Q. What is a full oscillation?
A cycle is one complete oscillation. Note that a vibration can be a single or multiple event, whereas oscillations are usually repetitive for a significant number of cycles.
Q. What is difference between oscillation and vibration?
Oscillation is a definite distance covered by the movement about its equilibrium position, vibration is referred to the physical change brought about due to movement of the body.
Q. What is wave and oscillation?
A wave can be thought of as a disturbance or oscillation that travels through space-time, accompanied by a transfer of energy. The direction a wave propagates is perpendicular to the direction it oscillates for transverse waves. A wave does not move mass in the direction of propagation; it transfers energy.
Q. Is a wave and oscillation?
Waves are one of the ways in which energy may be transferred between stores. Waves can be described as oscillations , or vibrations , about a rest position. For example: The direction of these oscillations is the difference between longitudinal or transverse waves.
Q. What are 4 parts of a wave?
Wave Crest: The highest part of a wave. Wave Trough: The lowest part of a wave. Wave Height: The vertical distance between the wave trough and the wave crest. Wave Length: The distance between two consecutive wave crests or between two consecutive wave troughs.
Q. What is the least dangerous radiation?
alpha particles
Q. Can radiation be felt?
Although we cannot see or feel the presence of radiation, it can be detected and measured in the most minute quantities with quite simple radiation measuring instruments. Sunlight feels warm because our body absorbs the infra-red rays it contains.
Q. What does dying of radiation feel like?
Initial symptoms include nausea, vomiting, headache and diarrhoea. These symptoms can start within minutes or days after the exposure. People who have been exposed to high doses can also have skin damage ranging from itching to burns, blisters and ulcers. They may also have temporary hair loss.
Q. What are the symptoms of radiation?
Possible symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Diarrhea.
- Headache.
- Fever.
- Dizziness and disorientation.
- Weakness and fatigue.
- Hair loss.
- Bloody vomit and stools from internal bleeding.
Q. What is Oscillator and how it works?
An oscillator is a circuit which produces a continuous, repeated, alternating waveform without any input. Oscillators basically convert unidirectional current flow from a DC source into an alternating waveform which is of the desired frequency, as decided by its circuit components.
Q. Why do oscillators need positive feedback?
Positive feedback is used in oscillator to satisfy Barkhausen’s Criteria in order to produce sustain oscillations. Oscillator produces sinusoidal waveform without any input signal hence starting voltage is noise signal which may be due to resistor’s, power supply.
Q. What is the value of frequency of horizontal oscillator?
The horizontal oscillator circuit 51 is designed to generate a signal having a frequency within a predetermined frequency range, for example, about (maximum frequency)/(minimum frequency)≤3, i.e., to accommodate a change in the frequency of the input horizontal synchronizing signal HD within such a range, in each of …
Q. What is the function of vertical oscillator?
The oscillator that produces, under control of the vertical synchronizing signals, the sawtooth voltage waveform that is amplified to feed the vertical deflection coils on the picture tube of a television receiver. Also known as vertical oscillator.
Q. What is horizontal deflection?
A horizontal deflection hinders the ability of a motorist to drive in a straight line by creating a horizontal shift in the roadway. This shift forces a motorist to slow the vehicle in order to comfortably navigate the measure. The types of horizontal deflections described in this ePrimer are: Lateral shift. Chicane.
Q. What is horizontal circuit?
A horizontal deflection circuit makes a sawtooth current flow through a deflection coil. The current will have equal amounts of positive and negative current. The horizontal switch transistor conducts for the right hand side of the picture. The damper diode conducts for the left side of the picture.
Q. What is a deflection circuit?
[di′flek·shən ‚sər·kət] (electronics) A circuit which controls the deflection of an electron beam in a cathode-ray tube.
Q. What is hot transistor?
Each transistor is slightly different. If you try to share current from one resistor, one transistor will get more of the current, causing it to warm up, which drops the Vbe even more, which causes it to get even more current.
Q. What is vertical IC on a TV?
Overview The LA7847 is EW drive and vertical deflection output ICs for high-definition TV and CRT displays in systems that use a bus control system signal-processing IC .
Q. What causes horizontal line on CRT TV?
One horizontal line problem in CRT TV or Monitor is actually very common and the usual cause were dry joints in the vertical output IC, missing DC supply voltage to the vertical output IC, improper DC supply voltage (usually low dc supply voltage) , bad surrounding components, bad vertical output IC and etc.
Q. Do transistors get hot?
The transistor will only heat up if being over driven.. Either something is drawing too much current, you are demanding too much power, or it is being over clocked.. Normally it should only be warm, not a burning to touch feeling if you touch the transistor..
Q. What causes transistor to overheat?
There is a chance that reducing the base current will make the transistor get hotter. This is because if the transistor goes into the active region, the voltage on it will increase. True, the overall current will reduce, but with the increase in voltage, the power dissipation in the transistor will increase.
Q. What is hot in CRT TV?
There are many reasons why the horizontal output transistor (HOT) shorted in CRT Monitor. Here are the possible cause: One of the best example was the HP 17″ 7500 CRT Monitor. Not only it blow the HOT, the B+ coil and the B+ FET blown as well! Shorted or open internal capacitor in flyback transformer.
Q. What is a vertical transistor?
A new theory for vertical transistors provides visual representations of the voltages, currents, and electric potentials inside these advanced devices. Such tools were previously unavailable for vertical transistors, in which currents flow through vertical channels made of nanotubes or nanowires.
Q. Why does horizontal output transistor keep blowing?
Improper drive to horizontal output transistor (HOT). A weak drive might cause the HOT to turn on or (more likely) shut off too slowly (greatly increasing heat dissipation. Check driver and HOT base circuit components. Sometimes, the horizontal deflection is designed based on the quirks of a particular transistor.