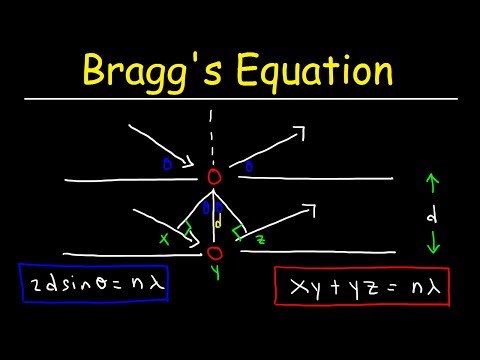
n * λ = 2 * d * sin(θ) ,
Q. What is difference between diffraction and divergence?
Diffraction is a wave effect, so it applies to laser beams as well. The divergence of a beam means the amount that the rays are spreading out. The amount that they spread out depends on the length of the waves, and the width of the beam. A narrower beam of laser light spreads out more quickly than a wider beam.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is difference between diffraction and divergence?
- Q. What does N stand for in Bragg’s law?
- Q. What is Bragg’s law and how can it be used to identify minerals?
- Q. Which of the following is based on Bragg’s law?
- Q. What is Bragg’s angle?
- Q. How does XRD determine crystal structure?
- Q. How Bragg’s law is useful in XRD?
- Q. What is diffraction condition?
- Q. What determines the intensity of the XRD peaks?
- Q. How is crystal structure determined?
- Q. Which crystal structure is the strongest?
- Q. What is the purpose of crystal lattice?
- Q. What do you understand by lattice and basis of a crystal?
- Q. What is the difference between a lattice and a crystal?
- Q. What is basis of crystal?
- Q. What is difference between lattice and basis?
- Q. What is called lattice?
- Q. What is a lattice point?
- Q. What is meant by a lattice structure?
- Q. What is Bravais lattice and structure?
- Q. Why are lattice structures strong?
Q. What does N stand for in Bragg’s law?
The reflected (glancing) angle θ, as shown by experiment, is equal to the incident angle θ. The condition for the two waves to stay in phase after both are reflected is that the path length CBD be a whole number (n) of wavelengths (λ), or nλ.
- n is the positive integer, the order,
- λ [m] is the wavelength of the X-ray,
- d [m] is the interplanar distance, the distance between consecutive layers of atoms,
- θ [rad] is the angle of the incident X-ray.
Q. What is Bragg’s law and how can it be used to identify minerals?
Bragg’s law In crystallography, the law that describes how an X-ray beam is reflected or diffracted in a crystal lattice, given by the Bragg equation nλ – 2dsinθ where n is any integer, λ is the wavelength of the incident-beam X-ray, d is the spacing between crystal planes (d spacing), and θ is the angle between the …
Q. Which of the following is based on Bragg’s law?
Explanation: Bragg’s law is a special case of Laue diffraction. It is used in X-ray crystallography, the basis of which is to identify the crystal lattice.
Q. What is Bragg’s angle?
: the small angle between an incident X-ray beam and the diffracting planes of a crystal — compare bragg’s law.
Q. How does XRD determine crystal structure?
XRD finds the geometry or shape of a molecule using X-rays. XRD techniques are based on the elastic scattering of X-rays from structures that have long range order. The X-rays get diffracted by a crystal because the wavelength of X-rays is similar to the inter-atomic spacing in the crystals.
Q. How Bragg’s law is useful in XRD?
Applications of Bragg’s Law. In X-ray diffraction (XRD) the interplanar spacing (d-spacing) of a crystal is used for identification and characterization purposes. Solving Bragg’s Equation gives the d-spacing between the crystal lattice planes of atoms that produce the constructive interference.
Q. What is diffraction condition?
When a monochromatic, collimated beam of radiation (X-rays or neutrons) is incident upon a stationary single crystal, the diffraction condition will probably be satisfied for few if any reflections, depending on a number of parameters such as the size of the unit cell, crystal mosaicity, and the energy spread of the …
Q. What determines the intensity of the XRD peaks?
Crystalline materials are characterized by the long-range orderly periodic arrangements of atoms. structure. The crystal structure describes the atomic arrangement of a material. –The atom types and positions determine the diffraction peak intensities.
Q. How is crystal structure determined?
The main technique for determining molecular structure in the gaseous and crystalline states is diffraction, electron diffraction for gases, and X-ray diffraction for crystals.
Q. Which crystal structure is the strongest?
Diamond is the hardest material known, while cubic boron nitride (BN) is the second-hardest. Silicon carbide (SiC) is very structurally complex and has at least 70 crystalline forms.
Q. What is the purpose of crystal lattice?
What is a Lattice? A lattice is an ordered array of points describing the arrangement of particles that form a crystal. The unit cell of a crystal is defined by the lattice points. The unit cell is the smallest part of a crystal that repeated regularly through translation in three dimensions creates the whole crystal.
Q. What do you understand by lattice and basis of a crystal?
The crystal structure is formed by associating every lattice point with an assembly of atoms or molecules or ions, which are identical in composition, arrangement and orientation, is called as the basis. The atomic arrangement in a crystal is called crystal structure. Thus lattice + basis = crystal structure.
Q. What is the difference between a lattice and a crystal?
Crystalline material consists of a regular repetition of a group of atoms in three dimensional space. A crystal lattice is an infinitely repeating array of points in space .
Q. What is basis of crystal?
The crystal basis is the arrangement of atoms that is particular to the mineral being considered. Each of these basis units is called a unit cell. The unit cells are repeated over and over again in three dimensions to make up a macroscopic crystal.
Q. What is difference between lattice and basis?
A lattice is a hypothetical regular and periodic arrangement of points in space. A basis is a collection of atoms in particular fixed arrangement in space. We could have a basis of a single atom as well as a basis of a complicated but fixed arrangement of hundreds of atoms.
Q. What is called lattice?
A lattice is an abstract structure studied in the mathematical subdisciplines of order theory and abstract algebra. It consists of a partially ordered set in which every two elements have a unique supremum (also called a least upper bound or join) and a unique infimum (also called a greatest lower bound or meet).
Q. What is a lattice point?
A lattice point is a point in a Cartesian coordinate system such that both its – and. -coordinates are integers. A lattice point is a point at the intersection of two or more grid lines in a regularly spaced array of points, which is a point lattice.
Q. What is meant by a lattice structure?
Lattice structures are topologically ordered, three-dimensional open-celled structures composed of one or more repeating unit cells [2,3]. These cells are defined by the dimensions and connectivity of their constituent strut elements, which are connected at specific nodes.
Q. What is Bravais lattice and structure?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after Auguste Bravais (1850), is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by: (1)
Q. Why are lattice structures strong?
Because of the strong electrostatic forces between them, it takes a great deal of energy to separate the positive and negative ions in a crystal lattice. This means that ionic compounds have high melting points and boiling points.