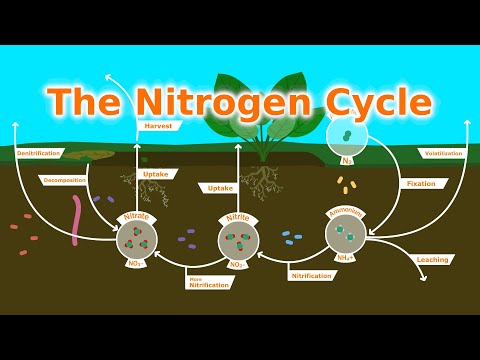
Q. How is nitrogen made available to plants?
Plants get their nitrogen from the soil and not directly from the air. From here, various microorganisms convert ammonia to other nitrogen compounds that are easier for plants to use. In this way, plants get their nitrogen indirectly from the air via microorganisms in the soil and in certain plant roots.
Q. Can we breathe nitrogen?
Nitrogen is an inert gas — meaning it doesn’t chemically react with other gases — and it isn’t toxic. But breathing pure nitrogen is deadly. That’s because the gas displaces oxygen in the lungs. Unconsciousness can occur within one or two breaths, according to the U.S. Chemical Safety and Hazard Investigation Board.
Table of Contents
- Q. How is nitrogen made available to plants?
- Q. Can we breathe nitrogen?
- Q. Can you breathe hydrogen?
- Q. How do we get nitrogen in our bodies?
- Q. Which food contains nitrogen?
- Q. What causes nitrogen deficiency in humans?
- Q. What does it mean that we eat our nitrogen?
- Q. How much of the air is made up of nitrogen?
- Q. How do humans get the nitrogen they need Brainly?
- Q. What is the importance of the carbon and nitrogen cycles to ecosystems?
- Q. Which is a key element found in all carbohydrates?
- Q. What is a key element found in co2 and glucose?
- Q. What is the formula for glucose?
- Q. What is the most common process by which nitrogen is made available to plants?
- Q. What are three processes that make nitrogen available to plants?
- Q. What process makes nitrogen available to plants and animals?
- Q. Where is nitrogen found?
- Q. What is an interesting fact about nitrogen?
- Q. Which fruit contains nitrogen?
- Q. What is the best source of nitrogen?
- Q. Does our body need nitrogen?
- Q. Is nitrogen harmful to humans?
- Q. What is the importance of nitrogen to a plant?
- Q. Why does it rain water instead of nitrogen?
- Q. Will we ever run out of drinking water?
- Q. Will we run out of water in 2050?
- Q. How much water will there be in 2050?
Q. Can you breathe hydrogen?
Inhaled hydrogen gas (H2) has been shown to have significant protective effects on ischemic organs. Clinical trials abroad have shown promise that treatment of patients suffering from stroke, cardiac arrest, or heart attacks may benefit from inhaling hydrogen gas during the early recovery period.
Q. How do we get nitrogen in our bodies?
When an organism excretes waste or dies, the nitrogen in its tissues is in the form of organic nitrogen (e.g. amino acids, DNA). Various fungi and prokaryotes then decompose the tissue and release inorganic nitrogen back into the ecosystem as ammonia in the process known as ammonification.
Q. Which food contains nitrogen?
Nitrogen-Rich Vegetables and Fruits
- Tofu and soy-based proteins.
- Beans, including lentils, garbanzo, black, pinto and kidney beans.
- Nuts such as almonds, hazelnuts and walnuts.
- Seeds, including sesame seeds.
- Peanut butter.
Q. What causes nitrogen deficiency in humans?
For example, Nitrogen deficiency of tea is identified by retarded shoot growth and yellowing of younger leaves. However, these physical symptoms can also be caused by numerous other stresses, such as deficiencies in other nutrients, toxicity, herbicide injury, disease, insect damage or environmental conditions.
Q. What does it mean that we eat our nitrogen?
We need to “eat our nitrogen” What does it mean that we “eat our nitrogen”? We get nitrogen by eating plants and animals that get it through the soil. 2. Earthworms are key organisms in the recycling of nutrients in an ecosystem.
Q. How much of the air is made up of nitrogen?
78 percent
Q. How do humans get the nitrogen they need Brainly?
Answer: Humans get the nitrogen they need by eating plants or other animals that contain nitrogen. Explanation: When organisms die, their bodies decompose bringing the nitrogen into soil on land or into ocean water. Bacteria alter the nitrogen into a form that plants are able to use.
Q. What is the importance of the carbon and nitrogen cycles to ecosystems?
Matter is constantly cycled between living and nonliving parts of the environment. Processes like photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation allow the carbon and nitrogen cycles to regenerate needed substances by recycling Earth’s atoms.
Q. Which is a key element found in all carbohydrates?
All carbohydrates, including sugar, therefore contain the same three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Different arrangements of these elements form single units to make different types of carbohydrates. Glucose, for instance, is a single-unit carb with six carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms and six oxygen atoms.
Q. What is a key element found in co2 and glucose?
Carbon is the only possible solution in this question for the reason that the chemical formula for glucose is c6h12o6 (6, 12 and 6 underscore) and carbon dioxide is co2. Both of the chemical formula contains carbon that is why that is the main element.
Q. What is the formula for glucose?
C₆H₁₂O₆
Nitrogen in organic materials (plant residues, animal manures, sewage, soil organic matter) is present as part of proteins, amino acids and other plant and microbial materials. It becomes available to plants only after the compound is decomposed by soil microorganisms. This is called “mineralization” (Fig.
Q. What is the most common process by which nitrogen is made available to plants?
Nitrogen fixation
Q. What are three processes that make nitrogen available to plants?
Overview: The nitrogen cycle involves three major steps: nitrogen fixation, nitrification, and denitrification.
Q. What process makes nitrogen available to plants and animals?
nitrification
Q. Where is nitrogen found?
Nitrogen, the most abundant element in our atmosphere, is crucial to life. Nitrogen is found in soils and plants, in the water we drink, and in the air we breathe.
Q. What is an interesting fact about nitrogen?
Nitrogen is odorless, tasteless, and colorless gas at room temperature and pressure. Its atomic weight is 14.0067. Nitrogen gas (N2) makes up 78.1% of the volume of the Earth’s air. It’s the most common uncombined (pure) element on Earth.
Q. Which fruit contains nitrogen?
Here are the 10 best foods to boost your nitric oxide levels.
- Beets. Share on Pinterest.
- Garlic.
- Meat.
- Dark Chocolate.
- Leafy Greens.
- Citrus Fruits.
- Pomegranate.
- Nuts and Seeds.
Q. What is the best source of nitrogen?
Some organic methods of adding nitrogen to the soil include:
- Adding composted manure to the soil.
- Planting a green manure crop, such as borage.
- Planting nitrogen fixing plants like peas or beans.
- Adding coffee grounds to the soil.
Q. Does our body need nitrogen?
Your body needs nitrogen to make proteins in your muscles, skin, blood, hair, nails and DNA. You obtain nitrogen from protein-containing foods in your diet, according to the Royal Society of Chemistry.
Q. Is nitrogen harmful to humans?
High concentrations of nitrogen gas can be particularly harmful to human health. Nitrogen can displace oxygen from ambient air within an enclosed space leading to a dangerous build-up of the inert gas.
Q. What is the importance of nitrogen to a plant?
Nitrogen in Plants Nitrogen is so vital because it is a major component of chlorophyll, the compound by which plants use sunlight energy to produce sugars from water and carbon dioxide (i.e., photosynthesis). It is also a major component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins.
Q. Why does it rain water instead of nitrogen?
Lightning can provide this energy, breaking the bonds and leaving the free nitrogen atoms to combine with oxygen in the atmosphere. The resulting compounds are called nitrates, which dissolve in rainwater more readily than nitrogen gas.
Q. Will we ever run out of drinking water?
While our planet as a whole may never run out of water, it’s important to remember that clean freshwater is not always available where and when humans need it. In fact, half of the world’s freshwater can be found in only six countries. Also, every drop of water that we use continues through the water cycle.
Q. Will we run out of water in 2050?
By 2050 the U.S. could be as much as 5.7°F warmer, and extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and drought, could be more intense and occur more frequently. 120 million Americans rely on these ancient subterranean lakes for drinking water, but they’re becoming depleted.
Q. How much water will there be in 2050?
This number will increase from 33 to 58% to 4.8 to 5.7 billion by 2050. About 73% of the people affected by water scarcity presently live in Asia. In the 2010s, groundwater use globally amounted to 800 km3 per year.