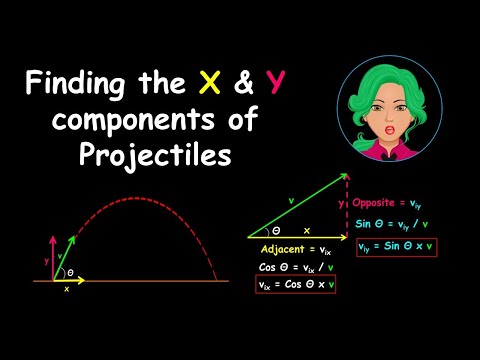
How is the horizontal component of motion affected by the vertical component of motion? It is NOT! The horizontal velocity of a projectile does not change, so if a projectile has horizontal velocity it will have the same horizontal velocity at the top of its trajectory.
Q. How is the motion of the object affected by the horizontal and vertical components of its velocity and or acceleration?
The horizontal motion of an object is unaffected by the force of gravity for relatively short displacements. This means that the horizontal velocity is constant, while the vertical velocity is accelerating. This change in angle affects the motion of the object and its velocity is no longer independent.
Table of Contents
- Q. How is the motion of the object affected by the horizontal and vertical components of its velocity and or acceleration?
- Q. How is the motion in the vertical affected by the motion in the horizontal?
- Q. How do you find the initial height of a falling object?
- Q. How do you find a falling object?
- Q. What is a measure of the change in velocity?
- Q. How do you find the time it takes for an object to hit the ground?
- Q. What is the force of an object falling?
- Q. How do you calculate the force needed to lift an object?
Q. How is the motion in the vertical affected by the motion in the horizontal?
The vertical force acts perpendicular to the horizontal motion and will not affect it since perpendicular components of motion are independent of each other. Thus, the projectile travels with a constant horizontal velocity and a downward vertical acceleration.
Q. How do you find the initial height of a falling object?
Example 2:
- An object is dropped from a height of 120 feet.
- If h is measured in feet, t is the number of seconds the object had fallen, and h0 is the initial height from which the object was dropped, then the model for the height of falling object is:
- h=−16t2+h0.
- Substitute 0 for h and 120 for h0 in the model.
Q. How do you find a falling object?
An object in free fall will still have a weight, governed by the equation W = mg , where W is the object’s weight, m is the object’s mass, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Q. What is a measure of the change in velocity?
Acceleration is a measure of the change in velocity of a moving object. It measures the rate at which velocity changes. Velocity, in turn, is a measure of the speed and direction of motion, so a change in velocity may reflect a change in speed, a change in direction, or both.
Q. How do you find the time it takes for an object to hit the ground?
Measure the distance the object will fall in feet with a ruler or measuring tape. Divide the falling distance by 16. For example, if the object will fall 128 feet, divide 128 by 16 to get 8. Calculate the square root of the Step 2 result to find the time it takes the object to fall in seconds.
Q. What is the force of an object falling?
An object that is falling through a vacuum is subjected to only one external force, the gravitational force, expressed as the weight of the object. The motion of a free falling object can be described by Newton’s second law of motion, force (F) = mass (m) times acceleration (a).
Q. How do you calculate the force needed to lift an object?
If the object is lifted straight up at constant speed, then the force needed to lift it is equal to its weight mg. The work done on the mass is then W = Fd = mgh. We define this to be the gravitational potential energy (PEg) put into (or gained by) the object-Earth system.