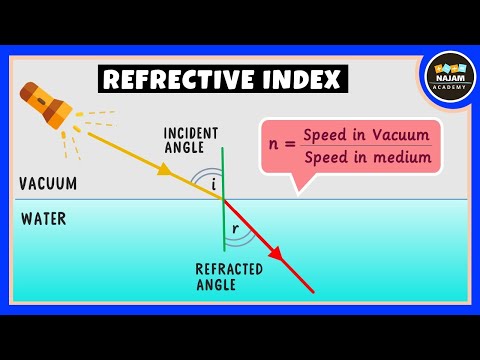
Q. How is the refractive index related with speed of light?
The refractive index of a medium (n) is equal to the speed of light (c) divided by the velocity of light through the medium (v). Rearranging the equation allows us to see the relationship regarding v. The lower the refractive index, the faster the velocity of light. Medium A has the smaller refractive index.
Q. Is the speed of light constant in general relativity?
General Relativity. In special relativity, the speed of light is constant when measured in any inertial frame. In general relativity, the appropriate generalisation is that the speed of light is constant in any freely falling reference frame (in a region small enough that tidal effects can be neglected).
Table of Contents
- Q. How is the refractive index related with speed of light?
- Q. Is the speed of light constant in general relativity?
- Q. How do you prove the speed of light is constant?
- Q. What if speed of light is not constant?
- Q. Does light change speed?
- Q. What is the slowest speed of light?
- Q. Can you speed up the speed of light?
- Q. Is it possible to slow down the speed of light?
- Q. Can anything slow the speed of light?
- Q. Why does light travel more slowly through glass?
- Q. Which medium does light travel the slowest?
- Q. Can light be slowed down by gravity?
- Q. Is gravity faster than the speed of light?
- Q. Why is light affected by gravity if it has no mass?
- Q. Can gravity exist without mass?
- Q. Why does light turn into heat?
- Q. Which object would absorb the most light and heat?
- Q. Is heat just vibration?
- Q. Does all energy eventually become heat?
- Q. Will all energy eventually become useless?
- Q. What are the 1st 2nd and 3rd laws of thermodynamics?
- Q. What does the 1st law of thermodynamics state?
Q. How do you prove the speed of light is constant?
Therefore, since the motion of a source (Maxwell’s equations), nor the motion of an observer (Michelson-Morley) lead to a RELATIVE speed of light, then the combination of these two observations leads to the conclusion of the second postulate of Einstein’s Relativity, since all relative speed between an observer and a …
Q. What if speed of light is not constant?
The speed of light is constant, or so textbooks say. But some scientists are exploring the possibility that this cosmic speed limit changes, a consequence of the nature of the vacuum of space.
Q. Does light change speed?
Light, no matter how high-or-low in energy, always moves at the speed of light, so long as it’s traveling through the vacuum of empty space. By passing that light into a non-vacuum medium, you can change its speed so long as it’s in that medium.
Q. What is the slowest speed of light?
The speed of light is normally about 186,000 miles per second, or fast enough to go around the world seven times in the wink of eye. Scientists succeeded in slowing it down to 38 mph. They did this by shooting a laser through extremely cold sodium atoms, which worked like “optical molasses” to slow the light down.
Q. Can you speed up the speed of light?
Nothing can move faster than the speed of light. Through a medium of any type — whether that’s air, water, glass, acrylic, or any gas, liquid, or solid — light travels at a measurably slower speed. Energetic particles, on the other hand, are only bound to travel slower than light in a vacuum, not light in a medium.
Q. Is it possible to slow down the speed of light?
In a vacuum like space, the speed of light is just over 186,280 miles per second. Scientists have now shown it’s possible to slow it down to zero miles per second without sacrificing its brightness, regardless of its frequency or bandwidth.
Q. Can anything slow the speed of light?
Yes, yes nothing can travel faster than light, but… When light travels through a medium other than vacuum, it will be slowed down. For instance, when light propagates through water or air, it will do so at a slower speed. For some materials such as water, light will slow down more than electrons will.
Q. Why does light travel more slowly through glass?
Electromagnetic waves simply travel slower through glass than through air. So the wave crests are closer to each other, but the light still oscillates the same number of times per second. When light goes through glass, it gets knocked around and bumps into all sorts of molecules and electrons.
Q. Which medium does light travel the slowest?
The higher the index of refraction is, the slower the speed of light is. The indexes of refraction for diamond, air and glass are, respectively, 2.42, 1.00, and approximately 1.50, depending upon the composition of the glass. Light travels slowest in diamond.
Q. Can light be slowed down by gravity?
The short answer is no, the speed of light is unchanged by gravity. In Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, space and time can be visualized as a four-dimensional construct that gets warped under the influence of gravity.
Q. Is gravity faster than the speed of light?
Kopeikin and Fomalont concluded that the speed of gravity is between 0.8 and 1.2 times the speed of light, which would be fully consistent with the theoretical prediction of general relativity that the speed of gravity is exactly the same as the speed of light.
Q. Why is light affected by gravity if it has no mass?
It might be surprising to you to hear that gravity can affect light even though light has no mass. According to general relativity, gravity is actually caused by a curving of space and time. Since light travels in a straight line through straight spacetime, the curving of spacetime causes light to follow a curved path.
Q. Can gravity exist without mass?
The only way to get gravity is with mass. The more mass, the more gravity you get. Without mass, you can’t have gravity. The force of gravity that we feel is actually just an acceleration towards the center of the Earth at 9.8 meters per second squared, or 1G.
Q. Why does light turn into heat?
When visible light is absorbed by an object, the object converts the short wavelength light into long wavelength heat. This causes the object to get warmer.
Q. Which object would absorb the most light and heat?
The more light the object absorbs, the more heat absorbed since light is energy. If you consider it a color, black absorbs the most heat. A black object absorbs all wavelengths of light and reflects none. Objects that are white, on the other hand, reflect all wavelengths of light and therefore absorb the least heat.
Q. Is heat just vibration?
It’s both: At the smallest scale, thermal energy is just kinetic energy, the energy of motion. When molecules vibrate, they’re bumping into each other—transferring kinetic energy to other molecules, which sometimes radiate this energy as heat (on a larger scale).
Q. Does all energy eventually become heat?
Does all energy eventually turn into heat? No, but some does when it’s absorbed into the energy levels of molecules. And the heat can’t all turn back to useful energy because of entropy, which disperses some of it, rendering it unable to do useful work or generate heat.
Q. Will all energy eventually become useless?
For the purposes of our little system, and most anything else, it is lost forever. The electricity made by our little turbine isn’t enough to keep the system going. It will eventually “wind down” and stop, because all of the energy will eventually become low-grade and useless.
Q. What are the 1st 2nd and 3rd laws of thermodynamics?
The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of any isolated system always increases. The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a system approaches a constant value as the temperature approaches absolute zero.
Q. What does the 1st law of thermodynamics state?
The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another.