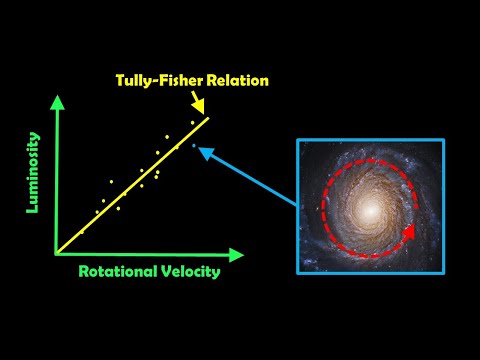
Q. How is the Tully-Fisher relation used to measure distances to galaxies?
Tully-Fisher relation is a correlation for spiral galaxies between their luminosity and how fast they are rotating. By comparing the intrinsic brightness with the apparent magnitude (what you actually observe — because the further the galaxy, the dimmer it “appears”), you can calculate its distance.
Q. What is the physical significance of the Tully-Fisher relation for spiral galaxies?
We find a new Tully–Fisher-like relation for spiral galaxies holding at different galactocentric radii. This radial Tully–Fisher relation allows us to investigate the distribution of matter in the optical regions of spiral galaxies.
Table of Contents
- Q. How is the Tully-Fisher relation used to measure distances to galaxies?
- Q. What is the physical significance of the Tully-Fisher relation for spiral galaxies?
- Q. What is the Tully-Fisher relation used for?
- Q. What three properties of a galaxy are related by the Tully-Fisher relation?
- Q. What did galaxies tend to look like in their younger age?
- Q. What is the oldest light that we can observe?
- Q. What is the salary of astronaut in India?
- Q. Is job at ISRO good?
- Q. Does ISRO give pension?
- Q. What is the salary of K Sivan?
- Q. Is ISRO a government job?
- Q. Which is the highest paid job in ISRO?
- Q. Can I do PhD while working in ISRO?
- Q. Is ISRO exam tough?
Q. What is the Tully-Fisher relation used for?
Independent of the value of the Hubble Constant, the Tully-Fisher relation can be used to measure peculiar velocities, motions of galaxies that are deviations from the linear Hubble expansion. These motions are thought to be due to the gravitational influence of over- and under-densities of matter.
Q. What three properties of a galaxy are related by the Tully-Fisher relation?
The slope, intercept and scatter of the Tully-Fisher relation (TFR; Tully & Fisher 1977) are key parameters that any successful prescription for galaxy formation and evolution must reproduce.
Q. What did galaxies tend to look like in their younger age?
Most galaxies are compressed spheres, and the team noted that younger galaxies tend to be more flattened. This is also true of less common spiral galaxies like the Milky Way. The bulge near the center contains older stars, while the flattened arms are home to younger ones. Andromeda is a spiral galaxy.
Q. What is the oldest light that we can observe?
The oldest light in the universe is the cosmic microwave background. Roughly 380,000 years after the Big Bang, protons and electrons “recombined”1 into hydrogen atoms. Before this, any photons scattered off the free electrons in the plasma filling space, and the universe was essentially opaque to light.
Q. What is the salary of astronaut in India?
The average pay scale of an Astronaut is INR 2,00,000 to 6,00,000. What are the top recruiters in India for Astronauts?
Q. Is job at ISRO good?
ISRO is a great institute in india as it is central government and launching satellites. Work experience in isro was a great thing as i can learn many things. ISRO is very good organization to work but for only sometime for contract employees not whole life. Work relaxation is there but growth is not there.
Q. Does ISRO give pension?
ISRO Salary | Benefits of Joining ISRO The organization doesn’t only provide a decent salary but also lends reputation and decent lifestyle to its employees. D- ISRO Employees are also liable for the pension after retirement.
Q. What is the salary of K Sivan?
K Sivan gets a monthly salary of Rs. 2.50 lacs per annum from ISRO. The chief of ISRO rank is equivalent to IAS and IPS . Sivan Net Worth is assumed to be around 2.5 Crores .
Q. Is ISRO a government job?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) was established in 15 August 1969 and Headquarters in Bangalore. ISRO is under the administrative control of the Department of Space, Government of India. ISRO is amongst the largest government space agencies in the world.
Q. Which is the highest paid job in ISRO?
ISRO Scientist
Q. Can I do PhD while working in ISRO?
Yes you can do PhD while working in ISRO . Sponsorship: here along with study leave with salary , even expenses for PhD shall be taken by isro.
Q. Is ISRO exam tough?
Overall Exam Analysis for ISRO Scientist/Engineer – Electronics. Exam was tough as compared to the previous year exams. No question was asked from Computer Architect and EMMI (Electronic Measurement & Measuring Instruments). Many questions were time consuming, lengthy and calculative.