To obtain a 3 percent margin of error at a 90 percent level of confidence requires a sample size of about 750. For a 95 percent level of confidence, the sample size would be about 1,000. Determining the margin of error at various levels of confidence is easy.
Q. What is the sample size necessary for a 90% confidence level?
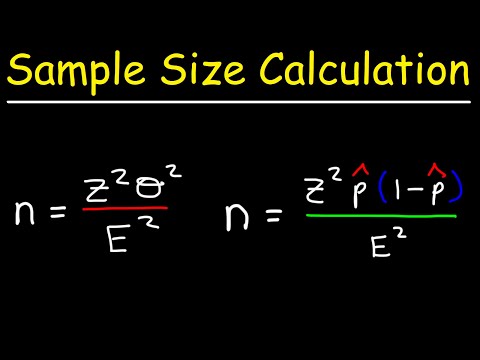
Example 11 Find the minimum sample size required to estimate the proportion to within three percentage points, at 90% confidence. Solution: Confidence level 90% means that α=1−0.90=0.10 so α∕2=0.05.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the sample size necessary for a 90% confidence level?
- Q. How do you find the 90 confidence interval for a proportion?
- Q. What is the Z * value for a 95% confidence interval?
- Q. What is the value of z * For a 90% confidence interval?
- Q. How do you find the Z-score on a calculator for confidence interval?
- Q. What is the margin of error for a 95% confidence interval?
- Q. What is the meaning of 95% confidence interval?
- Q. How do you calculate the critical value?
- Q. What is a critical value in statistics?
- Q. What is the positive critical value?
- Q. How do you calculate the critical region?
- Q. What is the critical region?
- Q. How do you find the null hypothesis?
- Q. How do you find the level of significance?
- Q. What does 5% significance level mean?
- Q. How do you interpret independent t test results in SPSS?
Q. How do you find the 90 confidence interval for a proportion?
Because you want a 95% confidence interval, your z*-value is 1.96. Take the square root to get 0.0499. The margin of error is, therefore, plus or minus 1.96 ∗ 0.0499 = 0.0978, or 9.78%….How to Determine the Confidence Interval for a Population Proportion.
| Confidence Level | z*-value |
|---|---|
| 80% | 1.28 |
| 90% | 1.645 (by convention) |
| 95% | 1.96 |
| 98% | 2.33 |
Q. What is the Z * value for a 95% confidence interval?
1.96
Q. What is the value of z * For a 90% confidence interval?
Checking Out Statistical Confidence Interval Critical Values
| Confidence Level | z*– value |
|---|---|
| 85% | 1.44 |
| 90% | 1.64 |
| 95% | 1.96 |
| 98% | 2.33 |
Q. How do you find the Z-score on a calculator for confidence interval?
Therefore, a z-interval can be used to calculate the confidence interval.
- Step 1: Go to the z-interval on the calculator. Press [STAT]->Calc->7.
- Step 2: Highlight STATS. Since we have statistics for the sample already calculated, we will highlight STATS at the top.
- Step 3: Enter Data.
- Step 4: Calculate and interpret.
Q. What is the margin of error for a 95% confidence interval?
You need to input a confidence level in the margin of error calculator….How to calculate margin of error.
| Desired confidence level | z-score |
|---|---|
| 80% | 1.28 |
| 85% | 1.44 |
| 90% | 1.65 |
| 95% | 1.96 |
Q. What is the meaning of 95% confidence interval?
A 95% confidence interval is a range of values (upper and lower) that you can be 95% certain contains the true mean of the population.
Q. How do you calculate the critical value?
In statistics, critical value is the measurement statisticians use to calculate the margin of error within a set of data and is expressed as: Critical probability (p*) = 1 – (Alpha / 2), where Alpha is equal to 1 – (the confidence level / 100).
Q. What is a critical value in statistics?
In hypothesis testing, a critical value is a point on the test distribution that is compared to the test statistic to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. If the absolute value of your test statistic is greater than the critical value, you can declare statistical significance and reject the null hypothesis.
Q. What is the positive critical value?
Think of the mean as a “mirror”. We know that the critical value at the mean is zero. Every critical value to the left of the mean is negative. Every critical value to the right of the mean is positive.
Q. How do you calculate the critical region?
If the level of significance is α = 0.10, then for a one tailed test the critical region is below z = -1.28 or above z = 1.28. For a two tailed test, use α/2 = 0.05 and the critical region is below z = -1.645 and above z = 1.645.
Q. What is the critical region?
A critical region, also known as the rejection region, is a set of values for the test statistic for which the null hypothesis is rejected. i.e. if the observed test statistic is in the critical region then we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis.
Q. How do you find the null hypothesis?
H0: The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0….An appropriate alternative hypothesis is:
- p = 0.20.
- p > 0.20.
- p < 0.20.
- p ≤ 0.20.
Q. How do you find the level of significance?
To find the significance level, subtract the number shown from one. For example, a value of “. 01” means that there is a 99% (1-. 01=.
Q. What does 5% significance level mean?
The significance level, also denoted as alpha or α, is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. For example, a significance level of 0.05 indicates a 5% risk of concluding that a difference exists when there is no actual difference.
Q. How do you interpret independent t test results in SPSS?
- Data Set-Up. Your data should include two variables (represented in columns) that will be used in the analysis.
- Run an Independent Samples t Test. To run an Independent Samples t Test in SPSS, click Analyze > Compare Means > Independent-Samples T Test.
- Example: Independent samples T test when variances are not equal.