Q. How long does DNA replication take in human cells?
The typical human chromosome has about 150 million base pairs that the cell replicates at the rate of 50 pairs per second. At that speed of DNA replication, it would take the cell over a month to copy a chromosome. The fact that it takes only one hour is because of multiple replication origins.
Q. How are the long DNA molecules found in eukaryotes?
The long DNA molecules found in eukaryotes packed into short chromosomes by the nucleosomes packing with one another to form a thick fiber, which is shortened by a system of loops and coils.
Table of Contents
- Q. How long does DNA replication take in human cells?
- Q. How are the long DNA molecules found in eukaryotes?
- Q. How much of the original DNA strand is retained in each of the daughter Dnas?
- Q. How many DNA strands exist at the end of Semiconservative replication?
- Q. What are the 5 major steps in DNA replication?
- Q. In which type of cell is DNA circular?
- Q. What is the purpose of Okazaki fragments?
- Q. Why do Okazaki fragments exist?
- Q. Why are they called Okazaki fragments?
- Q. What happens if Okazaki fragments are not joined?
- Q. Who named Okazaki fragments?
- Q. What are Okazaki fragments Byjus?
- Q. Which of the following is true about Okazaki fragments?
- Q. What is the lagging strand in DNA replication?
- Q. What is the difference between DNA polymerase 1 and 3?
- Q. Is RNA built 5 to 3?
Q. How much of the original DNA strand is retained in each of the daughter Dnas?
At the end of the process the cell has made to identical copies of all the biological information contained on the original, parental, DNA molecule, but the two new daughter DNA molecules are “Half old” and “Half new”. Half the original DNA molecule is saved, or conserved in the daughter molecules.
Q. How many DNA strands exist at the end of Semiconservative replication?
In one model, semiconservative replication, the two strands of the double helix separate during DNA replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied; after replication, each double-stranded DNA includes one parental or “old” strand and one “new” strand.
Q. What are the 5 major steps in DNA replication?
What are the 5 steps of DNA replication in order?
- Step 1: Replication Fork Formation. Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be “unzipped” into two single strands.
- Step 2: Primer Binding. The leading strand is the simplest to replicate.
- Step 3: Elongation.
- Step 4: Termination.
Q. In which type of cell is DNA circular?
Eukaryotic chromosomes are found in a special compartment called the cell nucleus. The genomes of bacterial cells (prokaryotes ), which lack a nucleus, are typically circular DNA molecules that associate with special structures in the cell membrane.
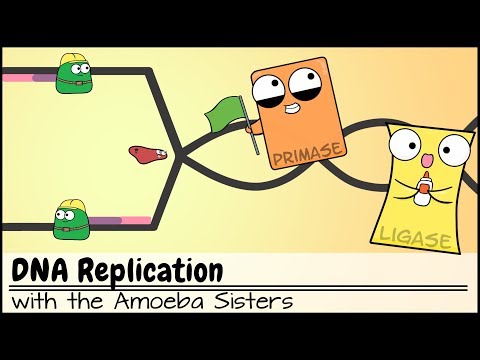
Q. What is the purpose of Okazaki fragments?
Okazaki fragments are short, newly synthesized DNA fragments that are formed on the lagging template strand during DNA replication. They are complementary to the lagging template strand, together forming short double-stranded DNA sections. Function: A building block for DNA synthesis of the lagging strand.
Q. Why do Okazaki fragments exist?
Okazaki fragments are formed on the lagging strand for the synthesis of DNA in 5′ to 3′ direction towards the replication fork. The fragments exists as replication of DNA takes place in 5′ -> 3′ direction due to the action of the DNA polymerase on the 3′- OH of the current strand to add free nucleotides.
Q. Why are they called Okazaki fragments?
Word origin: named after its discoverers, Reiji Okazaki and his wife, Tsuneko Okazaki, while studying replication of bacteriophage DNA in Escherichia coli in 1968.
Q. What happens if Okazaki fragments are not joined?
Okazaki fragments that are not ligated could cause double-strand-breaks, which cleaves the DNA. Since only a small number of double-strand breaks are tolerated, and only a small number can be repaired, enough ligation failures could be lethal to the cell.
Q. Who named Okazaki fragments?
Rollin Hotchkiss
Q. What are Okazaki fragments Byjus?
Okazaki fragments are the short sequences of deoxyribonucleotides, which are formed at the lagging strand during replication.
Q. Which of the following is true about Okazaki fragments?
Each of these primers is elongated in the 5′–>3′ direction and form discontinuous segments called Okazaki fragments which are later joined together by DNA ligase. The DNA fragment produced due to radiation are called fragments only. Option C is the correct answer.
Q. What is the lagging strand in DNA replication?
Lagging-strand replication is discontinuous, with short Okazaki fragments being formed and later linked together.
Q. What is the difference between DNA polymerase 1 and 3?
The main difference between DNA polymerase 1 and 3 is that DNA polymerase 1 is involved in the removal of primers from the fragments and replacing the gap by relevant nucleotides whereas DNA polymerase 3 is mainly involved in the synthesis of the leading and lagging strands.
Q. Is RNA built 5 to 3?
An RNA strand is synthesized in the 5′ → 3′ direction from a locally single stranded region of DNA.