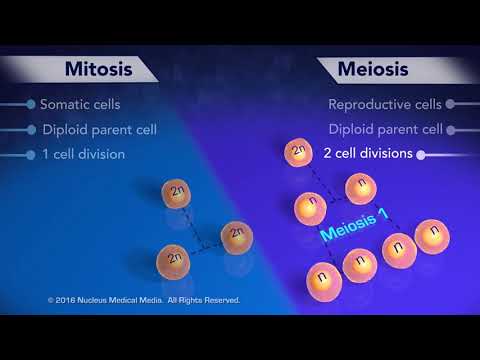
Q. How many cells are produced in mitosis versus meiosis?
Mitosis creates two identical daughter cells that each contain the same number of chromosomes as their parent cell. In contrast, meiosis gives rise to four unique daughter cells, each of which has half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Q. How many cells are produced in meiosis?
four daughter cells
The process results in four daughter cells that are haploid, which means they contain half the number of chromosomes of the diploid parent cell. Meiosis has both similarities to and differences from mitosis, which is a cell division process in which a parent cell produces two identical daughter cells.
Table of Contents
- Q. How many cells are produced in mitosis versus meiosis?
- Q. How many cells are produced in meiosis?
- Q. How many cells are produced by meiosis and cell division?
- Q. What is the comparison between mitosis and meiosis?
- Q. How many cells are produced in mitosis?
- Q. How many cells are created at the end of mitosis?
- Q. How many cells are made in mitosis?
- Q. How many cells are produced during mitosis?
- Q. How many cells are produced at the end of mitosis?
- Q. How many cells are produced at the end of meiosis I?
- Q. What type of cells are produced by meiosis and mitosis?
- Q. What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
- Q. How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
- Q. What’s the difference between mitosis and cytokinesis?
- Q. How are new gene combinations introduced in meiosis?
Q. How many cells are produced by meiosis and cell division?
four cells
Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information. These cells are our sex cells – sperm in males, eggs in females. During meiosis one cell? divides twice to form four daughter cells.
Q. What is the comparison between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis involves the division of body cells, while meiosis involves the division of sex cells. The division of a cell occurs once in mitosis but twice in meiosis. Two daughter cells are produced after mitosis and cytoplasmic division, while four daughter cells are produced after meiosis.
Q. How many cells are produced in mitosis?
two
Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells.
Q. How many cells are created at the end of mitosis?
two daughter cells
At the end of mitosis, the two daughter cells will be exact copies of the original cell. Each daughter cell will have 30 chromosomes.
Q. How many cells are made in mitosis?
During mitosis, a cell divides once to produce two daughter cells with genetic material identical to that of the original parent cell and to each other. Both haploid and diploid cells can undergo mitosis.
Q. How many cells are produced during mitosis?
Q. How many cells are produced at the end of mitosis?
Q. How many cells are produced at the end of meiosis I?
Meiosis I is responsible for creating genetically unique chromosomes. Sister chromatids pair up with their homologs and exchange genetic material with one another. At the end of this division, one parent cell produces two daughter cells, each carrying one set of sister chromatids.
Q. What type of cells are produced by meiosis and mitosis?
Mitosis produces two diploid (2n) somatic cells that are genetically identical to each other and the original parent cell, whereas meiosis produces four haploid (n) gametes that are genetically unique from each other and the original parent (germ) cell.
Q. What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Meiosis is a different type of cell division that begins with one cell that has the proper number of chromosomes and ends with four cells that have half the normal number of chromosomes (haploid cells). In a human, almost all cells undergo mitosis.
Q. How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in the formation of four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Q. What’s the difference between mitosis and cytokinesis?
The term cytokinesis refers to dividing a cell in half, while mitosis and meiosis refer to two different forms of nuclear division. Mitosis results in two nuclei that are identical to the original nucleus. Meiosis on the other hand results in four nuclei that each have ½ the chromosomes of the original cell.
Q. How are new gene combinations introduced in meiosis?
New gene combinations are introduced in a population through the genetic recombination that occurs during meiosis. Thus, unlike the two genetically identical cells produced in mitosis, the meiotic cell cycle produces four cells that are genetically different.