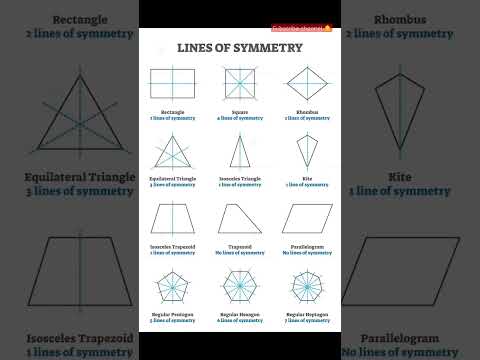
Q. How many lines of symmetry does D have?
two lines
Q. How Is height a normal distribution?
The normal distribution is essentially a frequency distribution curve which is often formed naturally by continuous variables. Height is a good example of a normally distributed variable. The average height of an adult male in the UK is about 1.77 meters. Most men are not this exact height!
Table of Contents
- Q. How many lines of symmetry does D have?
- Q. How Is height a normal distribution?
- Q. Why is normal distribution so common?
- Q. How do you read a bell curve?
- Q. How do you check for normal distribution?
- Q. Is normal distribution random?
- Q. When can we assume a normal distribution?
- Q. What is a normal distribution data set?
- Q. What is range of normal distribution?
- Q. How do you fit a normal distribution?
Q. Why is normal distribution so common?
The Normal Distribution (or a Gaussian) shows up widely in statistics as a result of the Central Limit Theorem. The Normal distribution is still the most special because: It requires the least math. It is the most common in real-world situations with the notable exception of the stock market.
Q. How do you read a bell curve?
Look at the symmetrical shape of a bell curve. The center should be where the largest portion of scores would fall. The smallest areas to the far left and right would be where the very lowest and very highest scores would fall. Read across the curve from left to right.
Q. How do you check for normal distribution?
For quick and visual identification of a normal distribution, use a QQ plot if you have only one variable to look at and a Box Plot if you have many. Use a histogram if you need to present your results to a non-statistical public. As a statistical test to confirm your hypothesis, use the Shapiro Wilk test.
Q. Is normal distribution random?
A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known.
Q. When can we assume a normal distribution?
In general, it is said that Central Limit Theorem “kicks in” at an N of about 30. In other words, as long as the sample is based on 30 or more observations, the sampling distribution of the mean can be safely assumed to be normal.
Q. What is a normal distribution data set?
A normal distribution is a common probability distribution . It is a statistic that tells you how closely all of the examples are gathered around the mean in a data set. The shape of a normal distribution is determined by the mean and the standard deviation.
Q. What is range of normal distribution?
The area under each curve is one but the scaling of the X axis is different. Note, however, that the areas to the left of the dashed line are the same. The BMI distribution ranges from 11 to 47, while the standardized normal distribution, Z, ranges from -3 to 3.
Q. How do you fit a normal distribution?
To fit a normal distribution we need to know the mean and the standard deviation. Remember that the mean of a binomial distribution is μ = np, and that the standard deviation for that distribution is σ = np(1− p). The normal distribution is continuous, whereas the binomial distribution is discrete.