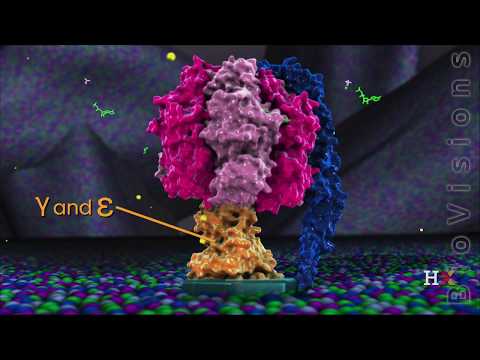
Q. How many protons does it take to make 1 ATP?
four
Q. How does ATP synthase produce ATP?
ATP synthase is an enzyme that directly generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) during the process of cellular respiration. ATP synthase forms ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate (Pi) through oxidative phosphorylation, which is a process in which enzymes oxidize nutrients to form ATP.
Table of Contents
- Q. How many protons does it take to make 1 ATP?
- Q. How does ATP synthase produce ATP?
- Q. How many protons are required for the conversion of ADP to ATP?
- Q. Does ATP synthase pump protons?
- Q. How fast does ATP synthase spin?
- Q. Which step makes the most ATP?
- Q. Does ATP synthase break down ATP?
- Q. What causes the ATP synthase rotor to spin?
- Q. What is the role of ATP synthase?
- Q. What must be transported to pass an electron?
- Q. How does 1 NADH produce 3 ATP?
- Q. Is glucose used to make ATP?
- Q. How is glucose turned to ATP?
- Q. How is glucose broken down into ATP?
- Q. How do we make ATP?
- Q. Do plants still use oxygen in order to produce ATP?
- Q. How does a plant use ATP?
- Q. How many ATP does fermentation cost?
- Q. What reactants of ATP must be available in the cell in order to produce ATP?
Q. How many protons are required for the conversion of ADP to ATP?
Thus, since just over 5 kcal/mol of free energy is made available, the passage of at least two, and more likely three or four, protons is essential for the synthesis of each molecule of ATP from ADP and Pi.
Q. Does ATP synthase pump protons?
The same process takes place in the mitochondria, where ATP synthase is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane and the F1-part projects into the mitochondrial matrix. The consumption of ATP by ATP-synthase pumps proton cations into the matrix.
Q. How fast does ATP synthase spin?
about 130 revolutions per second
Q. Which step makes the most ATP?
electron transport chain
Q. Does ATP synthase break down ATP?
This is why the intact ATP synthase is also called the FoF1-ATPase. When the F1-ATPase is isolated in vitro, it catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi (which is why it is called the F1-ATPase).
Q. What causes the ATP synthase rotor to spin?
The Fo rotor spins in response to proton (H+) flow down a concentration gradient across the membrane. This rotation causes the central stalk (axle) to rotate, altering the conformation of components of the F1 base, driving the synthesis of ATP.
Q. What is the role of ATP synthase?
The function of ATP synthase is to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) in the F1 sector. This is possible due to energy derived from a gradient of protons which cross the inner mitochondrial membrane from the intermembrane space into the matrix through the Fo portion of the enzyme.
Q. What must be transported to pass an electron?
The electrons are passed through a series of redox reactions, with a small amount of free energy used at three points to transport hydrogen ions across a membrane. This process contributes to the gradient used in chemiosmosis. The end products of the electron transport chain are water and ATP.
Q. How does 1 NADH produce 3 ATP?
For every pair of electrons transported to the electron transport chain by a molecule of NADH, between 2 and 3 ATP are generated. For each pair of electrons transferred by FADH2, between 1 and 2 ATP are generated. As a result, between 1 and 2 ATP are generated from these NADH.
Q. Is glucose used to make ATP?
The energy to make ATP comes from glucose. Cells convert glucose to ATP in a process called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration: process of turning glucose into energy In the form of ATP. Before cellular respiration can begin, glucose must be refined into a form that is usable by the mitochondrion.
Q. How is glucose turned to ATP?
During cellular respiration, glucose, in the presence of oxygen, is converted into carbon dioxide and water. The process can be summarized as: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water. During this process, the energy stored in glucose is transferred to ATP.
Q. How is glucose broken down into ATP?
During glycolysis, a glucose molecule with six carbon atoms is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, each of which contains three carbon atoms. For each molecule of glucose, two molecules of ATP are hydrolyzed to provide energy to drive the early steps, but four molecules of ATP are produced in the later steps.
Q. How do we make ATP?
Most of the ATP in cells is produced by the enzyme ATP synthase, which converts ADP and phosphate to ATP. ATP synthase is located in the membrane of cellular structures called mitochondria; in plant cells, the enzyme also is found in chloroplasts.
Q. Do plants still use oxygen in order to produce ATP?
This last step requires oxygen, and therefore is called aerobic respiration. Thus, the final result of cellular respiration is that the plant consumes glucose and oxygen and produces carbon dioxide, water, and ATP energy molecules. The plant needs energy all of the time.
Q. How does a plant use ATP?
The ATP and NADPH then enter the Calvin cycle and fuel the synthesis of molecules that eventually become sugar molecules. These sugar molecules can then be sent to the plant cell’s mitochondrion to undergo cell respiration, which produces even more ATP that can be used to fuel the plant cell’s many complex processes.
Q. How many ATP does fermentation cost?
Fermentation is less efficient at using the energy from glucose: only 2 ATP are produced per glucose, compared to the 38 ATP per glucose nominally produced by aerobic respiration.
Q. What reactants of ATP must be available in the cell in order to produce ATP?
What reactants of ATP must be available in the cell in order to produce ATP? In order to make ATP, the cell must have ADP and P, available.