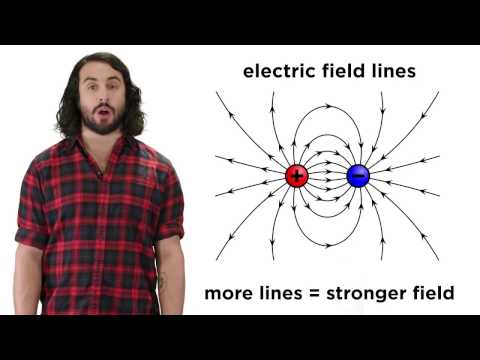
Q. How many types of electrical charges are there?
two
Q. What are the basic property of charge?
The charge is a scalar quantity as it has only magnitude and no direction. The charge is just as other fundamental properties of the system like mass. The only difference between mass and charge is that charge is both positive and negative, while mass is always positive.
Table of Contents
- Q. How many types of electrical charges are there?
- Q. What are the basic property of charge?
- Q. Why an atom has no electrical charge?
- Q. What is a charged atom called?
- Q. Why is an atom neutral?
- Q. Why can’t oxygen have 9 protons?
- Q. Are atoms that carry an electric charge?
- Q. What does it mean if an atom has an electric charge?
- Q. What is the origin of an electric charge?
- Q. What is the difference between AC and DC current electricity?
- Q. What are the 3 types of charges?
- Q. What are the 3 laws of electric charges?
- Q. What is the basic electric charge?
- Q. What are basic properties of charge?
- Q. What particle has a negative charge?
- Q. Why is there no overall charge on an atom?
- Q. How do you know if an atom is neutral?
- Q. What is the difference between positive and negative charge?
- Q. What causes charge?
- Q. What is a charged object give three examples?
- Q. Do like charges repel or attract?
- Q. What type of material Cannot be charged?
- Q. Can Insulators be charged negatively?
- Q. Do all objects get charged by rubbing?
- Q. How do airplanes get charged?
Q. Why an atom has no electrical charge?
Every atom has no overall charge (neutral). This is because they contain equal numbers of positive protons and negative electrons. These opposite charges cancel each other out making the atom neutral.
Q. What is a charged atom called?
Ion, any atom or group of atoms that bears one or more positive or negative electrical charges. Positively charged ions are called cations; negatively charged ions, anions.
Q. Why is an atom neutral?
When an atom has an equal number of electrons and protons, it has an equal number of negative electric charges (the electrons) and positive electric charges (the protons). The total electric charge of the atom is therefore zero and the atom is said to be neutral.
Q. Why can’t oxygen have 9 protons?
Oxygen has eight protons in its nucleus, and therefore eight electrons. The innermost shell of an atom can have only two electrons. So, here, there six electrons in the outer shell—two short of completion (eight total).
Q. Are atoms that carry an electric charge?
Overview of Atomic Electrical Charges Atoms, the fundamental building blocks of all molecules, consist of three types of particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Of these three subatomic particle types, two (protons and electrons) carry a net electric charge, while neutrons are neutral and have no net charge.
Q. What does it mean if an atom has an electric charge?
An entire atom becomes electrically charged when the number of electrons or protons stops being equal. The “extra” electron or proton isn’t balanced by something inside the atom anymore and begins to be attracted to the protons or electrons in other atoms.
Q. What is the origin of an electric charge?
Most electric charge is carried by the electrons and protons within an atom. Electrons are said to carry negative charge, while protons are said to carry positive charge, although these labels are completely arbitrary (more on that later). Conversely, two protons repel each other, as do two electrons.
Q. What is the difference between AC and DC current electricity?
In direct current (DC), the electric charge (current) only flows in one direction. Electric charge in alternating current (AC), on the other hand, changes direction periodically.
Q. What are the 3 types of charges?
Electric Charge
- protons are positively charged.
- electrons are negatively charged.
- neutrons have zero charge.
Q. What are the 3 laws of electric charges?
Based on the same types of experiments like the one you performed, scientists were able to establish three laws of electrical charges: Opposite charges attract each other. Like charges repel each other. Charged objects attract neutral objects.
Q. What is the basic electric charge?
Electric charge is a basic property of electrons, protons and other subatomic particles. Electrons are negatively charged while protons are positively charged. Things that have the same charge push each other away (they repel each other).
Q. What are basic properties of charge?
Q. What particle has a negative charge?
Electron
Q. Why is there no overall charge on an atom?
Q. How do you know if an atom is neutral?
Atoms are neutral if they have the same number of charged protons and electrons, balancing positive and negative charges. As long as the numbers of electron and protons are the same, the charges will balance. Sometimes atoms are more stable though when they are not perfectly electrically neutral.
Q. What is the difference between positive and negative charge?
There are two types of electric charge: positive and negative (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively). Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms.
Q. What causes charge?
An electrical charge is created when electrons are transferred to or removed from an object. Because electrons have a negative charge, when they are added to an object, it becomes negatively charged. When electrons are removed from an object, it becomes positively charged.
Q. What is a charged object give three examples?
Some examples of charged objects are free electrons floating around, Proton career bulbs, glowing tungsten, lithium ion battery, Magnetic parts, horseshoe magnet, u shaped magnets, protons. Objects can be charged by the process of conduction or convection.
Q. Do like charges repel or attract?
Like charges repel each other; unlike charges attract. Thus, two negative charges repel one another, while a positive charge attracts a negative charge. The attraction or repulsion acts along the line between the two charges. The size of the force is proportional to the value of each charge.
Q. What type of material Cannot be charged?
Insulators: materials that do NOT allow electrons to flow through them easily. Insulators can be easily charged by friction as the extra electrons gained CANNOT easily escape.
Q. Can Insulators be charged negatively?
Some insulating materials become electrically charged when they are rubbed together. A substance that gains electrons becomes negatively charged, while a substance that loses electrons becomes positively charged.
Q. Do all objects get charged by rubbing?
Answer: No,all objects does not gets charged by rubbing. Since rubbing is the process in which one body transferred its own charge to other body but the required condition is that both the body posses a property known as electro-static(Charge at rest).
Q. How do airplanes get charged?
Precipitation static is an electrical charge on an airplane caused by flying through rain, snow, ice, or dust particles. When the aircraft charge is great enough, it discharges into the surrounding air.