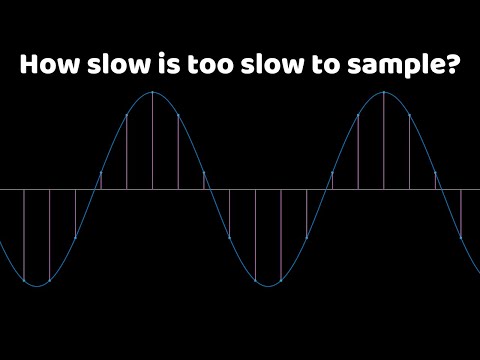
Nyquist’s theorem states that a periodic signal must be sampled at more than twice the highest frequency component of the signal. In practice, because of the finite time available, a sample rate somewhat higher than this is necessary. A sample rate of 4 per cycle at oscilloscope bandwidth would be typical.
Q. What is the minimum sampling rate for this signal?
The minimum sampling rate is often called the Nyquist rate. For example, the minimum sampling rate for a telephone speech signal (assumed low-pass filtered at 4 kHz) should be 8 KHz (or 8000 samples per second), while the minimum sampling rate for an audio CD signal with frequencies up to 22 KHz should be 44KHz.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the minimum sampling rate for this signal?
- Q. How do you find the minimum sample rate?
- Q. What is ideal sampling?
- Q. Why does aliasing occur?
- Q. What is the problem of aliasing?
- Q. What is the condition for aliasing problem?
- Q. What will happen when sampling rate is less than Nyquist rate?
- Q. Is sampling pattern which is repeated periodically?
- Q. What is the condition for the frequency sampling?
- Q. What is a sampling frequency?
- Q. Which is more vulnerable to noise?
- Q. Which modulation technique is most affected by noise?
- Q. Which is better for avoiding jamming?
- Q. Which filter is used to get the final FHSS signal?
- Q. What provides constant delay?
Q. How do you find the minimum sample rate?
MINIMUM NUMBER OF SAMPLES The sampling theorem states that a real signal, f(t), which is band-limited to f Hz can be reconstructed without error from samples taken uniformly at a rate R > 2f samples per second. This minimum sampling frequency, fs = 2f Hz, is called the Nyquist rate or the Nyquist frequency (6).
Q. What is ideal sampling?
Ideal Sampling is also known as Instantaneous sampling or Impulse Sampling. In this sampling technique the sampling function is a train of impulses and the principle used is known as multiplication principle. Here, Figure (a), represent message signal or input signal or signal to be sampled.
Q. Why does aliasing occur?
Aliasing occurs when you sample a signal (anything which repeats a cycle over time) too slowly (at a frequency comparable to or smaller than the signal being measured), and obtain an incorrect frequency and/or amplitude as a result.
Q. What is the problem of aliasing?
The aliasing effect is the appearance of jagged edges or “jaggies” in a rasterized image (an image rendered using pixels). The problem of jagged edges technically occurs due to distortion of the image when scan conversion is done with sampling at a low frequency, which is also known as Undersampling.
Q. What is the condition for aliasing problem?
Answer. Aliasing is the distortion that refers to the results that occur when the sample which is reconstructed is something different from the continuous signal which was originally there. Aliasing is referred to as temporal aliasing when it can occur in signals sampled as digital audio.
Q. What will happen when sampling rate is less than Nyquist rate?
As the sampling frequency decreases, the signal separation also decreases. When the sampling frequency drops below the Nyquist rate, the frequencies will crossover and cause aliasing.
Q. Is sampling pattern which is repeated periodically?
Explanation: Multi-order sampling is a sampling pattern in which the sampling is of different signals and which is repeated periodically.
Q. What is the condition for the frequency sampling?
The sampling theorem essentially says that a signal has to be sampled at least with twice the frequency of the original signal. Since signals and their respective speed can be easier expressed by frequencies, most explanations of artifacts are based on their representation in the frequency domain.
Q. What is a sampling frequency?
Definition: Sampling rate or sampling frequency defines the number of samples per second (or per other unit) taken from a continuous signal to make a discrete or digital signal. For some types of noise, sampling rates in excess of 48 kHz may be advantageous. For any higher sampling rates IASA recommends 96 kHz.”
Q. Which is more vulnerable to noise?
3. Which is more vulnerable to noise? Explanation: The minimum energy noise vector for 4-ary system is smaller than 2-ary system. So 4-ary system is more vulnerable to noise.
Q. Which modulation technique is most affected by noise?
Amplitude modulation methods like ASK/OOK and QAM are far more susceptible to noise so they have a higher BER for a given modulation. Phase and frequency modulation (BPSK, FSK, etc.) fare better in a noisy environment so they require less signal power for a given noise level (Fig. 7).
Q. Which is better for avoiding jamming?
Explanation: Frequency hopping spread spectrum is better for avoiding jamming.
Q. Which filter is used to get the final FHSS signal?
Band pass filter
Q. What provides constant delay?
Which provides constant delay? Explanation: Synchronous time division multiplexing provides constant bandwidth and constant delay.