If the load is 380 amps or less, then you can use a 500 MCM. If the load is 381 amps or higher, you cannot use a 500 MCM. If you have not calculated the load, and you plan to use a 400 amp overcurrent device to protect a 400 amp panel, then a 500 MCM will not be sufficient.
Q. How many amps can 3 0 Wire carry?
Related Resources
Table of Contents
- Q. How many amps can 3 0 Wire carry?
- Q. What size copper wire is good for 150 amps?
- Q. What size wire do I need for 150 amp service?
- Q. How many ground rods do I need for a 200 amp service?
- Q. Can I use rebar as a grounding rod?
- Q. Why are 2 ground rods required?
- Q. Does ground rod wire need to be in conduit?
- Q. Are ground rods necessary?
- Q. What is the minimum depth for a ground rod?
- Q. How do you get a ground rod out of the ground?
- Q. Does a grounding rod have to be copper?
- Q. Can grounding rods be under concrete?
- Q. Can you have too many ground rods?
- Q. Do all houses have grounding rods?
- Q. How do you tell if your house is grounded?
- Q. How much does it cost to install a ground rod?
- Q. Can you test a ground rod with a multimeter?
- Q. How many ohms is a good ground?
- Q. How do I know if my ground rod is bad?
- Q. How do you test a grounding system?
- Q. Can you install a ground rod horizontally?
- Q. Does a grounding rod have to be 8 feet?
- Q. How many grounding rods do I need?
| Size | Temperature Rating of Copper Conductor | |
|---|---|---|
| (AWG or kcmil) | 60°C (140°F) | 75°C (167°F) |
| 1/0 AWG | 125 | 150 |
| 2/0 AWG | 145 | 175 |
| 3/0 AWG | 165 | 200 |
Q. What size copper wire is good for 150 amps?
Wire Size and Amp Ratings
| Wire Size | 75°C (167°F) | |
|---|---|---|
| AWG | (mm²) | Copper |
| 2 | (33.6) | 115 |
| 1 | (42.4) | 130 |
| 1/0 | (53.5) | 150 |
Q. What size wire do I need for 150 amp service?
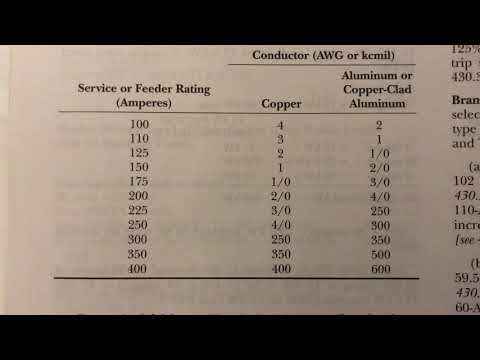
| SERVICE ENTRANCE CONDUCTORS SIZE AND RATING | ||
|---|---|---|
| Service or Feeder Rating | Copper Conductors | Aluminum or Copper-Clad Aluminum |
| 100 Amps | #4 AWG | #2 AWG |
| 125 Amps | #2 AWG | #1/0 AWG |
| 150 Amps | #1 AWG | #2/0 AWG |
Q. How many ground rods do I need for a 200 amp service?
4 grounding electrode
Q. Can I use rebar as a grounding rod?
Proper Grounding Rod In most cases, pipe or rebar can be used. The grounding rod needs to be made of galvanized steel and also needs to be at least four feet in length for best results.
Q. Why are 2 ground rods required?
Suppose you drive the first ground rod for a system. If it has a ground resistance of 25 ohms or more, 250.56 of the 2005 NEC requires you to drive a second rod. Ground rods spaced less than two rod-lengths apart will interfere with each other because their effective resistance areas will overlap (Fig.
Q. Does ground rod wire need to be in conduit?
Bare naked ground conductor is perfect fine in certain space. The reason the CODE requires the ground conductor to be inside the conduit is for protecting the conductor from being damaged by any mechanical means e.g., gardener weed whacker. In fact, you can use PVC to house the ground conductor.
Q. Are ground rods necessary?
A fundamental component of safety and protection for your business and/or home’s electrical system is proper grounding. For this reason, one or more ground rods are required on your property by the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local building codes.
Q. What is the minimum depth for a ground rod?
8 feet
Q. How do you get a ground rod out of the ground?
Get an old bumper jack and attach a chain to it and the grounding rod. Then just use the jack to lift it out. That’ll work or if there is enough of the rod above the ground use a large pipe wrench with a hydraulic bottle jack under it. The pipe wrench will lock around the pipe and not slip like a chain usually does.
Q. Does a grounding rod have to be copper?
If the facility being grounded has a life expectancy of less than 15 years, a galvanized ground rod is appropriate and will provide the most cost-effective solution. For installations with a longer service life, copper-bonded ground rods are the best fit.
Q. Can grounding rods be under concrete?
(A) Accessibility. All mechanical elements used to terminate a grounding electrode conductor or bonding jumper to a grounding electrode shall be accessible. Exception No. 1: An encased or buried connection to a concrete-encased, driven, or buried grounding electrode shall not be required to be accessible.
Q. Can you have too many ground rods?
Is it possible to have TOO MANY ground rods that creates problems?? No Bob you can put in as many as you can afford, but there is a point where it does no good. For simplicity follow this rule for ground rods spacing should be equal to the length of the rod. So if you are using 8 foot rods space them at 8 feet.
Q. Do all houses have grounding rods?
Household electrical systems are required by the National Electrical Code (NEC) to have a grounded system connected to earth ground via a ground rod. The Ground Rod is usually located very close to your main electrical service panel. Since 1990 it has been general practice to install two ground rods for safety.
Q. How do you tell if your house is grounded?
The major indication of a grounded home is three prong outlets instead of two. A three-prong outlet usually has a “U-shaped slot” which serves as the grounding component in the outlet.
Q. How much does it cost to install a ground rod?
8′ ground rods cost about $11 apiece – 10′ if required in your area about $15 each. The grounding wire, assuming #4 bare copper wire, about $1.20/LF, 4 clamps at $5 ea – so assuming about 10′ run to each rod, then about $66-74 materials – say maybe $80-90 with markup.
Q. Can you test a ground rod with a multimeter?
To ensure your home is safe, you should always test your ground rod resistance. You can do this at home using a multimeter.It is a handheld testing tool that is mostly used to take voltage readings. Advanced digital multimeters can take ampere and ohms (resistance) readings.
Q. How many ohms is a good ground?
5.0 ohms
Q. How do I know if my ground rod is bad?
Check the resistance reading on the meter. Your clamp-on ground tester will have a screen that will show you a numeric reading. The lower the number on the meter, the better your grounding rod is working. In general, a reading under 25 ohms means that your ground rod has a good connection to the earth.
Q. How do you test a grounding system?
Ground Testing Techniques
- Soil Resistivity Test. This is the most commonly used method used for testing newly-installed grounding systems.
- Fall-of-Potential. The fall-of-potential method is typically used for testing individual grounding stakes or grounding systems as a whole.
- Stakeless.
- Selective.
Q. Can you install a ground rod horizontally?
Step 2 – Install the Ground Rod Horizontally If you hit a rock trench before you can hammer the rod down all eight feet, then you can simply install it horizontally. Shovel out a strip of the earth at least 2 1/2 feet deep and long enough to accommodate the entire grounding rod (at least 8 feet).
Q. Does a grounding rod have to be 8 feet?
The only legal ground rod must be installed a minimum of 8-foot in the ground. The length of rod and pipe electrodes is located at 250.52(A)(5) in the 2017 National Electric Code (NEC).
Q. How many grounding rods do I need?
The requirement is 2 rods spaced at least six feet apart unless you can prove one rod will turn less than 25 ohms resistance. That is all the requirement is. Run all the extras you want, the requirement for rods is two unless there is less than 25 ohms on one rod.