Q. Is a dome and anticline?
Dome, in geology, any large or elliptical structure formed by the fractureless upwarping of rock strata. It is a type of anticline that lacks clear-cut elongation and that slopes outward in all directions from the highest point.
Q. What do domes and anticlines have in common?
A dome is similar to an anticline, but instead of an axis it has a single point at the center. The strata all dip away from the center point and the oldest rock is at the center. In map view, the strata form concentric circles – a bull’s eye pattern – around the center point.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is a dome and anticline?
- Q. What do domes and anticlines have in common?
- Q. What is the difference between a basin and dome structure?
- Q. What do anticlines form?
- Q. Where are anticlines found?
- Q. Where do anticlines occur?
- Q. Why is oil found in anticlines?
- Q. What does Monocline mean?
- Q. What are the two main types of folds?
- Q. What is the bending of rock layers due to stress called?
- Q. What happens when rocks are applied with stress?
- Q. What do you call the definition in rock layers where there is a change in shape without breaking?
- Q. Why do you think some rock layers are missing from the sequence in some outcrops?
- Q. What is the sinking of rock layers?
- Q. Is an upward fold in a rock is called a plateau?
- Q. What is upward arching rock layer?
- Q. Where is the oldest layer of an anticline fold located?
Q. What is the difference between a basin and dome structure?
Domes and basins are structures with approximately circular or slightly elongate, closed outcrop patterns. Domes are convex upward; basins are concave upward.
Q. What do anticlines form?
Sedimentation and Oil/Gas Formation An anticline is a structural trap formed by the folding of rock strata into an arch-like shape. The rock layers in an anticlinal trap were originally laid down horizontally and then earth movement caused it to fold into an arch-like shape called an anticline.
Q. Where are anticlines found?
most common structural traps are anticlines, upfolds of strata that appear as inverted V-shaped regions on the horizontal planes of geologic maps. About 80 percent of the world’s petroleum has been found in anticlinal traps. Most anticlines were produced by lateral pressure, but some have resulted from the draping and…
Q. Where do anticlines occur?
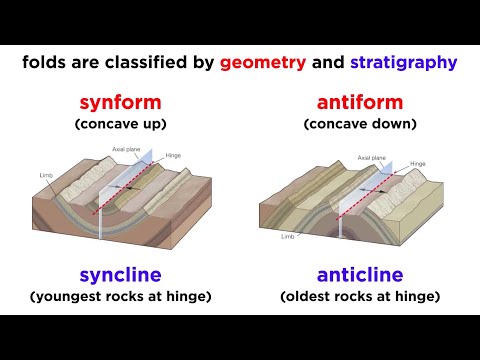
Anticlines and synclines are the up and down folds that usually occur together and are caused by compressional stress. Anticlines are folds in which each half of the fold dips away from the crest. Synclines are folds in which each half of the fold dips toward the trough of the fold.
Q. Why is oil found in anticlines?
Impermeable rock beds, often referred to as seals or cap rock, trap hydrocarbons in the anticline peak. This causes oil and natural gas to build up in the pore spaces of the reservoir rock at the core of the arch. Generally speaking, the largest oilfields occur in anticlines containing sedimentary rock.
Q. What does Monocline mean?
A monocline (or, rarely, a monoform) is a step-like fold in rock strata consisting of a zone of steeper dip within an otherwise horizontal or gently-dipping sequence.
Q. What are the two main types of folds?
A) Types of folds There are three basic types of folds (1) anticlines, (2) synclines and (3) monoclines.
Q. What is the bending of rock layers due to stress called?
Folding. The bending of rock layers due to stress in the Earth’s crust. Fault.
Q. What happens when rocks are applied with stress?
If more stress is applied to the rock, it bends and flows. It does not return to its original shape. Near the surface, if the stress continues, the rock will fracture (rupture) and break. With increasing stress, the rock undergoes: (1) elastic deformation, (2) plastic deformation, and (3) fracture.
Q. What do you call the definition in rock layers where there is a change in shape without breaking?
Figure 10.7: Rocks are defined as brittle or ductile on the basis of the way they are deformed by forces. In ductile deformation, a gradually increasing force will cause the rock to undergo smooth and continuous plastic deformation. The rock will contort and change shape without fracturing.
Q. Why do you think some rock layers are missing from the sequence in some outcrops?
Explain why some rock layers can be missing from the sequence in some outcrops. They were weathered and eroded or never deposited. reconstruct a sequence of events? We de not need to walk, dig, or identify layers or fossils.
Q. What is the sinking of rock layers?
Subsidence
Q. Is an upward fold in a rock is called a plateau?
Answer. an upward fold in rock formed by compression of Earth’s crust is known as syncline and a downward fold in rock formed by compression in Earth’s crust is called plateau.
Q. What is upward arching rock layer?
The answer is “anticline”. Rock layers in compression react comparably into up-arched (which is convex upward) folds called anticlines and down-arched, which is concave descending) folds known as synclines.
Q. Where is the oldest layer of an anticline fold located?
An anticline is a fold in which the oldest layer is in the center of the fold. Anticlines are commonly arch shaped. A syncline is a fold in which the youngest layer is in the center of the fold.