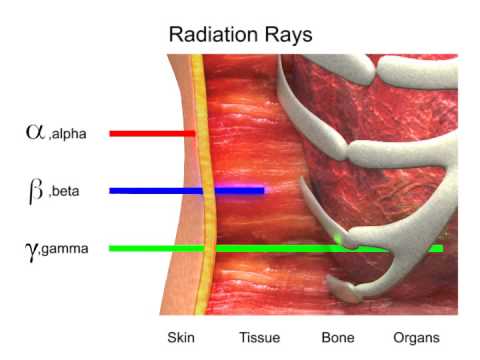
Alpha particles are the most harmful internal hazard as compared with gamma rays and beta particles. Radioactive materials that emit alpha and beta particles are most harmful when swallowed, inhaled, absorbed, or injected. Gamma rays are the most harmful external hazard.
Q. Which of the following types of radiation gives off a stream of negative particles?
beta particles
Table of Contents
- Q. Which of the following types of radiation gives off a stream of negative particles?
- Q. What is Alpha Beta and Gamma radiation?
- Q. Are alpha and beta rays electromagnetic?
- Q. Which of the following is the best example of radiation?
- Q. What are some examples of radiation heat transfer?
- Q. What are common sources of radiation?
- Q. What are 3 sources of radiation?
- Q. What are 3 examples of natural sources of radiation humans are exposed to?
- Q. What is the biggest source of radiation?
- Q. What is a natural source of radiation?
- Q. What household items give off radiation?
- Q. Is radon gas a natural source of radiation?
- Q. What are 5 sources of background radiation?
- Q. What three things can you do to protect yourself from radiation?
- Q. What are the four basic types of radiation packaging?
- Q. What is UN2910?
- Q. What is a Type B package?
- Q. What is a Type C package?
- Q. What materials are best for protecting against beta particles?
- Q. What is package type?
Q. What is Alpha Beta and Gamma radiation?
Alpha radiation is the name for the emission of an alpha particle in fact an helium nuclei, beta radiation is the emission of electrons or positrons , and gamma radiation is the term used for the emission of energetic photons.
Q. Are alpha and beta rays electromagnetic?
Familiar types of electromagnetic radiation include sunlight (cosmic radiation), x-rays, radar, and radio waves. This less-familiar form of radiation includes alpha particles, beta particles, and neutrons, as explained below.
Q. Which of the following is the best example of radiation?
Examples of Everyday Radiation
- Visible light.
- Infrared light.
- Near ultraviolet light.
- Microwaves.
- Low frequency waves.
- Radio waves.
- Waves produced by mobile phones.
- A campfire’s heat.
Q. What are some examples of radiation heat transfer?
Heat transfer by radiation occurs when microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, or another form of electromagnetic radiation is emitted or absorbed. An obvious example is the warming of the Earth by the Sun. A less obvious example is thermal radiation from the human body.
Q. What are common sources of radiation?
The majority of background radiation occurs naturally from minerals and a small fraction comes from man-made elements. Naturally occurring radioactive minerals in the ground, soil, and water produce background radiation. The human body even contains some of these naturally-occurring radioactive minerals.
Q. What are 3 sources of radiation?
Natural background radiation comes from the following three sources:
- Cosmic Radiation.
- Terrestrial Radiation.
- Internal Radiation.
Q. What are 3 examples of natural sources of radiation humans are exposed to?
The major isotopes of concern for terrestrial radiation are uranium and the decay products of uranium, such as thorium, radium, and radon. In addition to the cosmic and terrestrial sources, all people also have radioactive potassium-40, carbon- 14, lead-210, and other isotopes inside their bodies from birth.
Q. What is the biggest source of radiation?
radon
Q. What is a natural source of radiation?
Natural sources Natural sources of background radiation include: cosmic rays – radiation that reaches the Earth from space. rocks and soil – some rocks are radioactive and give off radioactive radon gas. living things – plants absorb radioactive materials from the soil and these pass up the food chain.
Q. What household items give off radiation?
What kinds of consumer products contain radioactive materials?
- Smoke detectors: most smoke detectors available for home use contain americium-241, a radioactive element.
- Clocks and watches: some luminous watches and clocks contain a small quantity of hydrogen-3 (tritium) or promethium-147.
Q. Is radon gas a natural source of radiation?
Radon is a colourless, odourless radioactive gas. It is formed by the radioactive decay of the small amounts of uranium that occur naturally in all rocks and soils.
Q. What are 5 sources of background radiation?
Most background radiation comes from natural sources, including the ground, the air, building materials and food. Radiation is also found in the cosmic rays from space. Some rocks contain radioactive substances that produce a radioactive gas called radon.
Q. What three things can you do to protect yourself from radiation?
Staying inside will reduce your exposure to radiation.
- Close windows and doors.
- Take a shower or wipe exposed parts of your body with a damp cloth.
- Drink bottled water and eat food in sealed containers.
Q. What are the four basic types of radiation packaging?
Four types of packages will be discussed; Excepted packaging, Industrial packaging, Type A packaging and Type B packaging. Consideration for the mode of transporting radioactive material will be discussed.
Q. What is UN2910?
The type of radioactive shipment that needs to be made is based on the activity (Curie content) and radiation levels of the material being shipped. The UN Number is UN2910 and the hazard class is Class 7 (Radioactive).
Q. What is a Type B package?
Type B packages are used to transport materials with high levels of radioactivity, such as spent fuel from nuclear power plants. These large, heavy packages provide shielding against the radiation. The size of the Type B packages can range from small containers to those weighing over 100 tons.
Q. What is a Type C package?
Type C Packaging. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has developed packaging requirements for the transport of radioactive material in large quantities and/or with high radioactivity. This packaging is known as Type C. “Package” means packaging with its radioactive contents as presented for transport.
Q. What materials are best for protecting against beta particles?
Beta particles (electrons) are more penetrating, but still can be absorbed by a few mm of aluminium. However, in cases where high-energy beta particles are emitted, shielding must be accomplished with low atomic weight materials, e.g. plastic, wood, water, or acrylic glass (Plexiglas, Lucite).
Q. What is package type?
There are three major types of paper packaging: corrugated boxes, boxboard or paperboard cartons, and paper bags and sacks. Corrugated Boxes: Corrugated boxes are commonly used to carry heavier products such as appliances, electronic goods, wine, fruit and vegetables.