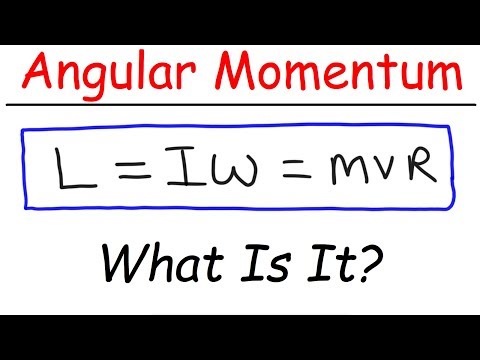
For a spinning object, on the other hand, the angular momentum must be considered as the summation of the quantity mvr for all the particles composing the object.
Q. How angular momentum is conserved?
Rotational collisions conserve angular momentum When objects collide without a net external torque, the angular momentum is constant. The two objects exert equal, but opposite angular impulses upon each other to maintain the total angular momentum of the colliding system.
Table of Contents
- Q. How angular momentum is conserved?
- Q. Is linear and angular momentum conserved?
- Q. What is the difference between orbital angular momentum and spin angular momentum?
- Q. Is kinetic energy constant in uniform circular motion?
- Q. Is there potential energy in circular motion?
- Q. In which accelerated motion is kinetic energy?
- Q. Why kinetic energy is half potential energy?
- Q. How do you find kinetic energy in circular motion?
- Q. What is the kinetic energy of a rotating body?
- Q. What is moment of inertia in terms of angular momentum and kinetic energy?
Q. Is linear and angular momentum conserved?
Angular momentum, like energy and linear momentum, is conserved.
Q. What is the difference between orbital angular momentum and spin angular momentum?
So, spin is an angular momentum, just orbital angular momentum is. Spin is the angular momentum of a particle in the frame where the particle is at rest. If the particle is moving, then there are additional contributions to it’s angular momentum, namely the orbital angular momentum.
Q. Is kinetic energy constant in uniform circular motion?
The kinetic energy in a uniform circular motion is constant. This is true because the speed in a uniform circular motion is constant and kinetic energy depends on the speed of the object as seen the equation of the kinetic energy.
Q. Is there potential energy in circular motion?
Uniform circular motion is a motion in a circular path at constant speed. An object reaches escape speed when the sum of its kinetic energy and its gravitational potential energy is equal to zero.
Q. In which accelerated motion is kinetic energy?
So a change in momentum corresponds to a change in kinetic energy. This is the essence of Newton’s second law: Applying a force to a mass changes the momentum of that mass. An acceleration just represents this change in momentum for an object that has a constant mass.
Q. Why kinetic energy is half potential energy?
Negative kinetic energy equals half the potential energy (−K = ½U). Potential energy equals twice the total energy (U = 2E). Twice the kinetic energy plus the potential energy equals zero (2K + U = 0).
Q. How do you find kinetic energy in circular motion?
Key Points
- Rotational kinetic energy can be expressed as: Erotational=12Iω2 E rotational = 1 2 I ω 2 where ω is the angular velocity and I is the moment of inertia around the axis of rotation.
- The mechanical work applied during rotation is the torque times the rotation angle: W=τθ W = τ θ .
Q. What is the kinetic energy of a rotating body?
We see from this equation that the kinetic energy of a rotating rigid body is directly proportional to the moment of inertia and the square of the angular velocity….Moment of Inertia.
| Rotational | Translational |
|---|---|
| K = 1 2 I ω 2 K = 1 2 I ω 2 | K = 1 2 m v 2 K = 1 2 m v 2 |
Q. What is moment of inertia in terms of angular momentum and kinetic energy?
When an object is rotating about its center of mass, its rotational kinetic energy is K = ½Iω2. Rotational kinetic energy = ½ moment of inertia * (angular speed)2. When the angular velocity of a spinning wheel doubles, its kinetic energy increases by a factor of four.