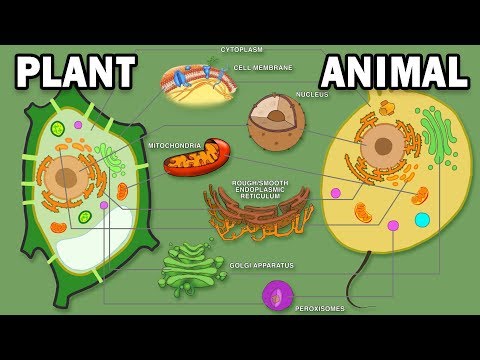
Q. Is Centrioles found in plant or animal cells?
Centrioles are paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope. Centrioles play a role in organizing microtubules that serve as the cell’s skeletal system. They help determine the locations of the nucleus and other organelles within the cell.
Q. Do plant cells contain centrosomes?
Chromosomes, microtubules and kinetochores all contribute to spindle morphogenesis and have important roles during mitosis. A unique property of flowering plant cells is that they entirely lack centrosomes, which in animals have a major role in spindle formation.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is Centrioles found in plant or animal cells?
- Q. Do plant cells contain centrosomes?
- Q. How do plant cells divide?
- Q. How do plants multiply?
- Q. Do plants multiply?
- Q. How do you get a plant to grow roots?
- Q. How do plants reproduce for kids?
- Q. How do plants have babies?
- Q. How do insects help a plant to reproduce for kids?
- Q. What do plants use to make their own food?
- Q. Do plants prepare food?
- Q. What part of a plant makes the most food?
- Q. Is the structure where a plant makes food?
- Q. Can plants grow underwater?
- Q. What are the three puzzle pieces that a plant needs to grow?
- Q. Do plant cells have Kinetochores?
- Q. How do plant cells divide without Centrioles?
- Q. What is the function of centrioles in plant cells?
- Q. Do plants have parent cells?
- Q. Do plant cells duplicate?
- Q. What is a plant cell division called?
- Q. How do plant cells do cytokinesis?
- Q. Do plant cells have cytokinesis?
- Q. What happens in cytokinesis in plant cells?
- Q. What is cytokinesis called in plant cells?
- Q. What is formed in plant cells to begin cytokinesis?
- Q. Why is cytokinesis different in plant cells?
- Q. How are Karyokinesis and cytokinesis connected in plants?
- Q. Does Karyokinesis occur in plants?
- Q. How does Karyokinesis occur in plant cells?
- Q. What is the importance of cell division in plants?
- Q. What is the importance of mitosis in plants?
- Q. What are the 4 reasons cells divide?
- Q. How is cell division responsible for growth?
- Q. Why do cells divide instead of growing larger?
Q. How do plant cells divide?
Plant cells divide in two by constructing a new cell wall (cell plate) between daughter nuclei after mitosis. Golgi-derived vesicles are transported to the equator of a cytoskeletal structure called a phragmoplast, where they fuse together to form the cell plate.
Q. How do plants multiply?
Pollen is carried from a male part to a female part by wind, insects or other animals (a process called pollination), where it releases male gametes that fertilise the female gametes in the ovules. The ovules develop into seeds from which new plants will grow.
Q. Do plants multiply?
You can multiply plants by seeds, cuttings, root division, and layering. To make cuttings from stems, select a stem that is 4 to 6 inches in length. Make a slanting cut completely through the stem and directly beneath a leaf joint.
Q. How do you get a plant to grow roots?
Let’s get started
- Identify the location where you will snip your cutting from the main plant.
- Carefully cut just below the node with a clean sharp knife or scissors.
- Place the cutting in a clean glass.
- Change out the water every 3-5 days with fresh room temperature water.
- Wait and watch as your roots grow!
Q. How do plants reproduce for kids?
Some plants can reproduce asexually (asexual plant reproduction requires only one parent cell that splits into two). However, most plants need pollen or spores to make new plants. This second process is called sexual plant reproduction.
Q. How do plants have babies?
The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. During fertilization, the male and female germ cells of the pollen unite to form a zygote. A zygote then transforms into an embryo, which eventually becomes a seed. The seed then germinates into a new plant.
Q. How do insects help a plant to reproduce for kids?
However, most plants need bees and other insects to pollinate from one plant to the next. When a bee, or other insect lands on a flower, small particles of pollen stick to its legs. As the bee flies to the next plant, it transfers the pollen over with it. Plants rely on bees and other insects to make this happen.
Q. What do plants use to make their own food?
The process by which land plants produce their own food using sunlight and carbon dioxide is known as photosynthesis (Figure 1). While carbon dioxide is absorbed by the leaves, the sunlight is captured by a chemical molecule in the plant, called chlorophyll (Chl).
Q. Do plants prepare food?
Plants are called producers because they make – or produce – their own food. They convert these ingredients into food by using energy from sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis, which means ‘making out of light’. The foods are called glucose and starch.
Q. What part of a plant makes the most food?
leaves
Q. Is the structure where a plant makes food?
Plants make food in their leaves. The leaves contain a pigment called chlorophyll, which colors the leaves green. Chlorophyll can make food the plant can use from carbon dioxide, water, nutrients, and energy from sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis.
Q. Can plants grow underwater?
Submerged plants grow fully immersed in water and get their nutrients from the water through their leaves, not their roots like other plants. Plants that grow completely under water provide shelter for fish, oxygen to the water, and filter out pollutants.
Q. What are the three puzzle pieces that a plant needs to grow?
In order for a plant to grow, it needs three very important puzzle pieces: water, carbon dioxide, and light. Plants use their roots to take in water from the ground.
Centrioles are paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope. Centrioles play a role in organizing microtubules that serve as the cell’s skeletal system.
Q. Do plant cells have Kinetochores?
A small group of kinetochore proteins (CENP-A, CENP-B and CENP-C) are distinguished by their localization to kinetochores throughout the cell cycle and interaction with DNA. As a highly conserved protein20, CENP-A is probably present in plants, although a true plant homolog has yet to be confirmed.
Q. How do plant cells divide without Centrioles?
Plant cells lack centrioles, however, they are still able to form a mitotic spindle from the centrosome region of the cell just outside of the nuclear envelope. They go through the stages of mitotic division as do animal cells-prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, followed by cytokinesis.
Q. What is the function of centrioles in plant cells?
The main function of centrioles is to produce cilia during interphase and the aster and the spindle during cell division.
Q. Do plants have parent cells?
The parent plants have male and female sex cells, called gametes. The genetic material from the male and female gametes combines to produce offspring. This process is called fertilization. Seeds produced through fertilization contain genetic material from both parents.
Q. Do plant cells duplicate?
Plant cells that reproduce by mitosis make identical copies of themselves to sustain the local population.
Q. What is a plant cell division called?
Cytoplasmic division or Cytokinesis separates the original cell, its organelles and its contents into two more or less equal halves. While all types of eukaryotic cells undergo this process, the details are different in animal and plant cells.
Q. How do plant cells do cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis in plant cells involves plants using spindle structures called phragmoplasts to carry vesicles of the cell wall material such as cellulose to the new cell plate. After the plate divides the plant cells into two daughter cells, the plasma membrane seals off and fully separates the two new cells.
Q. Do plant cells have cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis occurs in mitosis and meiosis for both plant and animal cells.
Q. What happens in cytokinesis in plant cells?
Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division in eukaryotes as well as prokaryotes. During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm splits in two and the cell divides. In plant cells, a cell plate forms along the equator of the parent cell. Then, a new cell membrane and cell wall form along each side of the cell plate.
Q. What is cytokinesis called in plant cells?
Cytokinesis, or “cell motion,” is the second main stage of the mitotic phase during which cell division is completed via the physical separation of the cytoplasmic components into two daughter cells.
Q. What is formed in plant cells to begin cytokinesis?
cell plate
Q. Why is cytokinesis different in plant cells?
The cells that have been undergoing cell division through mitosis are now separated, and each cell is an individual cell with a complete set of DNA; however, cytokinesis is different between plant cells and animal cells. The reason for this is that plant cells have a cell wall in addition to their cell membrane.
Q. How are Karyokinesis and cytokinesis connected in plants?
Related Biology Terms Karyokinesis – The separation of chromosomes, separate from the division of the cell. Plasmodesmata – Sections of plant cells that remain connected to other cells, sometimes formed during cytokinesis.
Q. Does Karyokinesis occur in plants?
As described for various plants, the sexual life cycle, i.e. the transformation of a diploid sporophyte generation into a haploid gametophyte, is a result of meiotic division, consisting of karyokinesis and cytokinesis as well as the no less important process of chondriokinesis.
Q. How does Karyokinesis occur in plant cells?
The division of the cell is initiated by division of the nucleus i.e. Karyokinesis followed by division of cytoplasm i.e. Cytokinesis. The stages of karyokinesis are – prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase (Fig. 2.4).
Q. What is the importance of cell division in plants?
Cell division serves as a means of reproduction in unicellular organisms through binary fission. In multicellular organisms, cell division aids in the formation of gametes, which are cells that combine with others to form sexually produced offspring.
Q. What is the importance of mitosis in plants?
Through the process of mitosis, cell division takes place, thereby ensuring the multiplication of cells for growth and development in plants. This means mitosis is responsible for the growth of plant leaves, roots, and stem among other parts.
Q. What are the 4 reasons cells divide?
Terms in this set (4)
- Food, Waste, and Gas Exchange. They need to maintain a workable ratio of surface area to volume to allow an efficient transfer of materials in and out of the cell.
- Growth. In order for an organism to grow, they must divide so they can get larger.
- Repair.
- Reproduction.
Q. How is cell division responsible for growth?
‘Cell division’ is the process in which a ‘cell’ divides into ‘two’ or more cells. This process is known as mitosis that allows for continuous construction and repair of the cells of the body thereby facilitating growth.
Q. Why do cells divide instead of growing larger?
Cells are limited in size because the outside (the cell membrane) must transport the food and oxygen to the parts inside. As a cell gets bigger, the outside is unable to keep up with the inside, because the inside grows a faster rate than the outside.