It doesnt form hydrogen bonds with other formaldehyde molecules but it can form them with molecules that do have a hydrogen atom bonded to O,N,F like water for example. No, but it will polymerize. It’s a hydrogen bond acceptor. It will hydrogen bond with water.
Q. Can ch3oh form hydrogen bonds?
Only CH₃NH₂ and CH₃OH can have hydrogen bonds between other molecules of the same kind. To have hydrogen bonding, you need an N, O, or F atom in one molecule and an H attached to an N, O, or F atom in another molecule. CH₃OH has an O atom and an O-H bond. It can form hydrogen bonds with other CH₃OH molecules.
Table of Contents
- Q. Can ch3oh form hydrogen bonds?
- Q. Is HF capable of hydrogen bonding?
- Q. Is formaldehyde a hydrogen bond?
- Q. Why is ammonia a hydrogen bond?
- Q. Where are hydrogen bonds found in DNA?
- Q. Which one is not an example of hydrogen bonding?
- Q. How is hydrogen bond used in real life?
- Q. Where is the phosphodiester bond in DNA?
- Q. Are hydrogen bonds in DNA strong or weak?
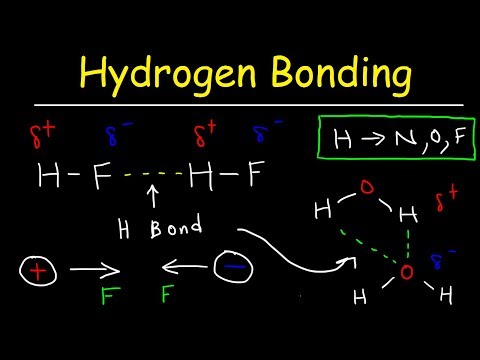
Q. Is HF capable of hydrogen bonding?
Any molecule which has a hydrogen atom attached directly to an oxygen or a nitrogen is capable of hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonds also occur when hydrogen is bonded to fluorine, but the HF group does not appear in other molecules.
Q. Is formaldehyde a hydrogen bond?
No, formaldehyde does not form hydrogen bonds. Looking at the classic example of water, the hydrogen atoms are bonded directly to oxygen. The difference in electronegativity between hydrogen and oxygen is what polarizes the molecule and allows for hydrogen bonding to occur.
Q. Why is ammonia a hydrogen bond?
In the case of ammonia, the amount of hydrogen bonding is limited by the fact that each nitrogen only has one lone pair. That means that on average each ammonia molecule can form one hydrogen bond using its lone pair and one involving one of its δ+ hydrogens. The other hydrogens are wasted.
Q. Where are hydrogen bonds found in DNA?
Covalent bonds exist within each linear strand and strongly bond bases, sugars, and phosphate groups (both within each component and between components). Hydrogen bonds exist between the two strands and form between a base, from one strand and a base from the second strand in complementary pairing.
Q. Which one is not an example of hydrogen bonding?
Liquid ammonia – contains Nitrogen, hence shows H-bonding. Water – contains Oxygen, hence shows H-bonding. Hydrochloric acid – does not contain Oxygen, Nitrogen or Fluorine, does not show hydrogen bonding.
Q. How is hydrogen bond used in real life?
Hydrogen bonding occurs most famously between water molecules. When one molecule of water attracts another the two can bond together; adding more molecules results in more and more water sticking together. This bond is responsible for the crystal structure of ice, which allows it to float.
Q. Where is the phosphodiester bond in DNA?
In DNA and RNA, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3′ carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5′ carbon atom of another, deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. Strong covalent bonds form between the phosphate group and two 5-carbon ring carbohydrates (pentoses) over two ester bonds.
Q. Are hydrogen bonds in DNA strong or weak?
Hydrogen bonds are weak, noncovalent interactions, but the large number of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs in a DNA double helix combine to provide great stability for the structure.