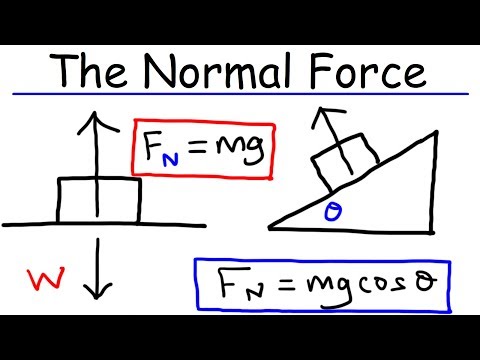
Many forces do come from objects being in contact with each other. The normal force is usually symbolized by N . In many cases the normal force is simply equal to the weight of an object, but that’s only when the normal force is the only thing counteracting the weight.
Q. What are the two kinds of forces?
There are 2 types of forces, contact forces and act at a distance force. Every day you are using forces. Force is basically push and pull. When you push and pull you are applying a force to an object.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the two kinds of forces?
- Q. What are the units of normal force?
- Q. How is force equal to weight?
- Q. What is normal force and weight?
- Q. Do scales read normal force?
- Q. What force does a weighing scale measure?
- Q. What forces can act on an object without touching it?
- Q. How many forces are there?
- Q. Which is the strongest attractive force?
- Q. What is force of Class 8?
- Q. What is distance in Science Grade 8?
- Q. What type of force is compression?
- Q. What is a load placed on a structure?
- Q. What are two types of load on a structure?
- Q. What is an example of a live load?
- Q. How do you calculate structure load?
Q. What are the units of normal force?
The unit for the normal force is ‘N’ (Newton). The normal force is a typical example of the Newton’s third law of motion. If one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of equal magnitude and opposite direction on the first object (action equals reaction).
Q. How is force equal to weight?
The weight of an object is defined as the force of gravity on the object and may be calculated as the mass times the acceleration of gravity, w = mg. Since the weight is a force, its SI unit is the newton.
Q. What is normal force and weight?
The net force must be zero – the normal force balances the weight. It looks like the weight and the normal force are “equal and opposite forces” as in Newton’s Third Law. The weight force is identical – it only depends on the mass of the object and on the acceleration due to gravity – neither of which are changed here.
Q. Do scales read normal force?
A scale measures the force that the scale is exerting on the object; typically this is a normal force, i.e. one that is normal, or perpendicular, to the surface or the scale. Now, very often, this normal force is equal to the weight, because the object is in equilibrium.
Q. What force does a weighing scale measure?
Remember, weight is the force of gravity ( usually earth’s) exerted on an object. When you stand on a bathroom scale, the scale measures the upward support force (N) that it exerts.
Q. What forces can act on an object without touching it?
Magnetism is an example of a non-contact or action-at-a-distance force. These are forces which can act on an object without being in physical contact with it. The force of gravity is another example. Thus, gravity will pull a raindrop down to Earth without any tangible physical link between the Earth and the drop.
Q. How many forces are there?
four
Q. Which is the strongest attractive force?
The strongest intermolecular force is hydrogen bonding, which is a particular subset of dipole-dipole interactions that occur when a hydrogen is in close proximity (bound to) a highly electronegative element (namely oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine).
Q. What is force of Class 8?
A force is the change of state of an object due to external surroundings. Due to forces, an object will either be in a state of motion or will be resting. For example, consider a football placed on the ground motionless. To move the ball in any direction, you will have to apply some forces on the ball.
Q. What is distance in Science Grade 8?
Distance is the length of the route between two points. The SI unit for distance is the meter.
Q. What type of force is compression?
Compression force (or compressive force) occurs when a physical force presses inward on an object, causing it to become compacted. There can also be different results depending on the direction or position on the object that the compressive force is applied.
Q. What is a load placed on a structure?
Internal and external forces act on structural components. An external force is commonly referred to as a structural load; an internal force is a stress. Another way to look at it is action and reaction.
Q. What are two types of load on a structure?
The types of loads acting on structures for buildings and other structures can be broadly classified as vertical loads, horizontal loads and longitudinal loads. The vertical loads consist of dead load, live load and impact load. The horizontal loads comprises of wind load and earthquake load.
Q. What is an example of a live load?
Live loads (also known as applied or imposed loads, or variable actions) may vary over time and often result from the occupancy of a structure. Typical live loads may include; people, the action of wind on an elevation, furniture, vehicles, the weight of the books in a library and so on.
Q. How do you calculate structure load?
How to Beam Load Calculation:
- 300 mm x 600 mm excluding slab.
- Volume of Concrete = 0.30 x 0.60 x 1 =0.18 m³
- Weight of Concrete = 0.18 x 2400 = 432 kg.
- Weight of Steel (2%) in Concrete = 0.18 x 2% x 7850 = 28.26 kg.
- Total Weight of Column = 432 + 28.26 = 460.26 kg/m = 4.51 KN/m.