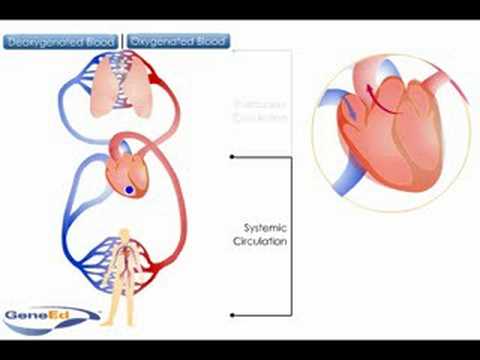
Q. Is pulmonary or systemic circuit bigger?
Systemic and pulmonary circulation transition to the opposite type of circulation when they return blood to the opposite side of the heart. Systemic circulation is a much larger and higher pressure system than pulmonary circulation.
Q. In which circuit does blood become oxygenated?
Blood enters the right atrium and passes through the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs where it becomes oxygenated. The oxygenated blood is brought back to the heart by the pulmonary veins which enter the left atrium.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is pulmonary or systemic circuit bigger?
- Q. In which circuit does blood become oxygenated?
- Q. How does pulmonary and systemic circulation?
- Q. What does systemic circulation do?
- Q. Where is the systemic circuit?
- Q. What foods to avoid if you have pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. What is the life expectancy for pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. What is the best diet for pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. Should I worry about mild pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. What is the treatment for mild pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. What is the main symptom of pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. How serious is mild pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. Can mild pulmonary hypertension go away?
- Q. Does walking help pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. Can you have surgery if you have pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. Can a blood test detect pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. What is considered severe pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. Does CBD help pulmonary hypertension?
- Q. How do you reverse pulmonary hypertension naturally?
- Q. Is Pulmonary Hypertension the same as heart failure?
- Q. Does pulmonary hypertension cause fatigue?
Q. How does pulmonary and systemic circulation?
Pulmonary circulation moves blood between the heart and the lungs. It transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood then flows back to the heart. Systemic circulation moves blood between the heart and the rest of the body.
Q. What does systemic circulation do?
Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle, through the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body. From the tissue capillaries, the deoxygenated blood returns through a system of veins to the right atrium of the heart.
Q. Where is the systemic circuit?
In the systemic circulation, blood travels out of the left ventricle, to the aorta, to every organ and tissue in the body, and then back to the right atrium. The arteries, capillaries, and veins of the systemic circulatory system are the channels through which this long journey takes place.
Q. What foods to avoid if you have pulmonary hypertension?
Limit the ingestion of stimulants like coffee or alcohol, which can provoke blood pressure irregularities. A diet rich in iron, found in red meat and dark, leafy greens, and vitamin C, found in bell peppers, orange, tomatoes and broccoli, can help manage the symptoms of the disease.
Q. What is the life expectancy for pulmonary hypertension?
While there’s no cure for PAH, there are effective ways to manage the disease. The median survival [from time of diagnosis] used to be 2.5 years. Now I’d say most patients are living seven to 10 years, and some are living as long as 20 years.
Q. What is the best diet for pulmonary hypertension?
Try incorporating more red meat, beans, and dark, leafy greens into your diet. Your body will better absorb iron if you include foods rich in vitamin C such as tomatoes, bell peppers, and broccoli.
Q. Should I worry about mild pulmonary hypertension?
Do not worry. Your cardiologist is correct. You do not need treatment for pulmonary hypertension.
Q. What is the treatment for mild pulmonary hypertension?
Treatments for pulmonary arterial hypertension anticoagulant medicines – such as warfarin to help prevent blood clots. diuretics (water tablets) – to remove excess fluid from the body caused by heart failure. oxygen treatment – this involves inhaling air that contains a higher concentration of oxygen than normal.
Q. What is the main symptom of pulmonary hypertension?
Pulmonary hypertension symptoms include: Shortness of breath (dyspnea), initially while exercising and eventually while at rest. Fatigue. Dizziness or fainting spells (syncope)
Q. How serious is mild pulmonary hypertension?
Mildly elevated mean pulmonary artery pressure ≈19 to 24 mm Hg, which is below the traditional threshold of >25 mm Hg used to define pulmonary hypertension (PH), is associated with an increased risk of all‐cause mortality.
Q. Can mild pulmonary hypertension go away?
Pulmonary hypertension cannot be cured, but treatment can reduce the symptoms and help you manage your condition. Pulmonary hypertension usually gets worse over time. Left untreated, it may cause heart failure, which can be fatal, so it’s important treatment is started as soon as possible.
Q. Does walking help pulmonary hypertension?
Some exercises are better for you if you have PAH. Good choices include: Light aerobic activity, like walking or swimming.
Q. Can you have surgery if you have pulmonary hypertension?
In PAH patients with right heart failure and or severe right ventricular dysfunction, it is recommended that any surgery, other than that needed to treat a potentially life-threatening problem, be avoided.
Q. Can a blood test detect pulmonary hypertension?
Your doctor will order tests to help diagnose pulmonary hypertension and determine its cause. Tests for pulmonary hypertension may include: Blood tests. Blood tests can help your doctor determine the cause of pulmonary hypertension or look for signs of complications.
Q. What is considered severe pulmonary hypertension?
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) due to lung disease (World Health Organization (WHO) group 3) is common, but severe PH, arbitrarily defined as mean pulmonary artery pressure ≥35 mmHg is reported in only a small proportion.
Q. Does CBD help pulmonary hypertension?
In conclusion, CBD may be a safe, promising therapeutic or adjuvant therapy agent for the treatment of human pulmonary artery hypertension.
Q. How do you reverse pulmonary hypertension naturally?
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Good for heart health, and may help lower blood pressure.
- L-carnitine. Improves endurance and is good for heart health.
- Magnesium. Helps your heart work better and may help lower blood pressure.
- Potassium.
- Vitamin E and vitamin C.
- Taurine.
Q. Is Pulmonary Hypertension the same as heart failure?
This is called pulmonary hypertension. The heart needs to work harder to force the blood through the vessels against this pressure. Over time, this causes the right side of the heart to become larger. This condition is called right-sided heart failure, or cor pulmonale.
Q. Does pulmonary hypertension cause fatigue?
About pulmonary hypertension It is a serious medical condition as it results in damage to the right-hand side of the heart muscle, making the heart muscle less efficient at pumping blood and oxygen around the body. This leads to symptoms such as: shortness of breath. fatigue (tiredness)