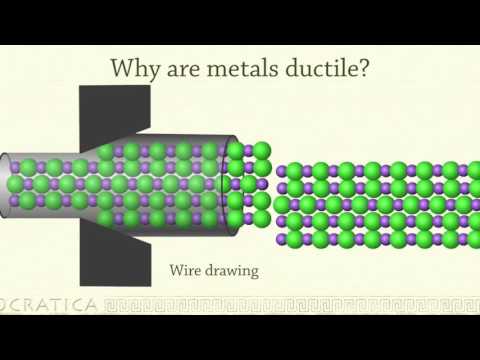
Q. Is sodium a ductile?
Sodium is classified as an “Alkali Metal” and located in Group 1 elements of the Periodic Table. Alkali metals are soft, malleable, ductile, and are good conductors of heat and electricity.
Q. Is Salt malleable and ductile?
Ionic compounds only conduct electricity when they are molten or dissolved in water. Metals and salts have different properties because in a metal valence electrons are not attached to any one atom; in a salt they are. Metals are malleable and ductile. Ionic compounds are brittle.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is sodium a ductile?
- Q. Is Salt malleable and ductile?
- Q. Why isn’t salt malleable or ductile?
- Q. Is table salt brittle or malleable?
- Q. Why is k2o brittle?
- Q. Why salts are brittle?
- Q. Are ionic bonds ductile?
- Q. Are metals brittle?
- Q. Why is metal not brittle?
- Q. Which metal is least brittle?
- Q. Is metal ductile or brittle?
- Q. Which metal is most ductile?
- Q. Why is steel so ductile?
- Q. What metal is ductile?
- Q. What is the least ductile metal?
- Q. Is Aluminium more ductile than steel?
- Q. Is titanium a ductile?
- Q. What’s the hardest metal on earth?
- Q. Is titanium alloy stronger than titanium?
- Q. What is the best grade titanium?
- Q. Is there a metal harder than titanium?
- Q. What is the strongest metal alloy in the world?
- Q. What is the rarest metal on earth?
- Q. Is Silver rarer than gold?
- Q. Is Silver stronger than steel?
Q. Why isn’t salt malleable or ductile?
Bharat Jajoo, 12th Grade Physics student from India. Two properties: Ductility and malleability. Metals are malleable and ductile while salts aren’t. This is because of the ability of the atoms to roll over each other into new positions without breaking the metallic bond.
Q. Is table salt brittle or malleable?
Table salt is an ionic compound and is brittle.
Q. Why is k2o brittle?
Na and K have same number of valence electrons and thus shows same oxidation state. Na and K both belong to group 1 and are brittle in nature. One can easily cut them into pieces.
Q. Why salts are brittle?
Ionic solids are very hard and brittle. Hard due to the strong bonds. Brittle since when distorted like charged ions move closer to each other and the strong electrostatic repulsions shatter the crystal. Ionic solids cannot conduct electricity.
Q. Are ionic bonds ductile?
In ionic compounds, electrons are tightly held by the ions, and the ions cannot move translationally relative to each other. This explains many properties of ionic solids. They are hard and brittle, they are not malleable or ductile (i.e. cannot be shaped without cracking/breaking), and they do not conduct electricity.
Q. Are metals brittle?
Unlike most metals, nearly all ceramics are brittle at room temperature; i.e., when subjected to tension, they fail suddenly, with little or no plastic deformation prior to fracture. Metals, on the other hand, are ductile (that is, they deform and bend when subjected to…
Q. Why is metal not brittle?
Because the delocalised electrons are free to move. These delocalised electrons are free to move throughout the giant metallic lattice, so as one layer of metal ions slides over another, the electrons can move too keeping the whole structure bonded together.
Q. Which metal is least brittle?
silicon carbide
Q. Is metal ductile or brittle?
7.6: Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
| Metallic Elements | |
|---|---|
| Malleable and ductile (flexible) as solids | Brittle, hard or soft |
| Conduct heat and electricity | Poor conductors |
| Metallic oxides are basic, ionic | Nonmetallic oxides are acidic, covalent |
| Form cations in aqueous solution | Form anions, oxyanions in aqueous solution |
Q. Which metal is most ductile?
platinum
Q. Why is steel so ductile?
These steels are ductile because they can switch from one crystal structure to another, which uses up energy that would otherwise cause damage. Many steel components such as car body parts are made up of lots of tiny areas that alternate between two different crystal structures.
Q. What metal is ductile?
A ductile substance can be drawn into a wire. Examples: Most metals are good examples of ductile materials, including gold, silver, copper, erbium, terbium, and samarium. Examples of metals that are not very ductile include tungsten and high-carbon steel. Nonmetals are not generally ductile.
Q. What is the least ductile metal?
Originally Answered: Which metal is malleable but not ductile? It is Zinc as it can be made into thin plates on hammering but can not be drawn into thin wires. Thus Zinc is malleable but not ductile.
Q. Is Aluminium more ductile than steel?
Most recent answer Mild Steel is having a ductility of nearly 50% as compared to Aluminum, however the formability of the materials also plays a pivotal role in determining the materials for its design.
Q. Is titanium a ductile?
Physical properties Titanium metal is brittle when cold and can break apart easily at room temperature. At higher temperatures, it becomes malleable and ductile.
Q. What’s the hardest metal on earth?
The Hardest Metals in the World
- Tungsten (1960–2450 MPa) Tungsten is one of the hardest metals you will find in nature.
- Iridium (1670 MPa)
- Steel.
- Osmium (3920–4000 MPa)
- Chromium (687-6500 MPa)
- Titanium (716 to 2770 MPa)
Q. Is titanium alloy stronger than titanium?
When alloyed with Ti, the resulting titanium alloy is significantly stronger than commercially pure titanium while retaining comparable stiffness and thermal characteristics. As mentioned, Grade 5 has properties similar to human bones which makes it the popular choice for orthopedic medical devices.
Q. What is the best grade titanium?
Grade 4 titanium
Q. Is there a metal harder than titanium?
Extra-hard alloys Its tensile strength to density ratio is the highest among all metals, beating tungsten, which, however, scores higher than titanium on the Mohs scale. As a natural metal with the highest tensile strength, tungsten is often combined with steel and other metals to achieve even stronger alloys.
Q. What is the strongest metal alloy in the world?
Steel
Q. What is the rarest metal on earth?
francium
Q. Is Silver rarer than gold?
Most studies agree gold is overall the more rare of the two metals; however, above ground silver is actually more rare than gold. To date, over 1.5 million tonnes of silver have been mined.
Q. Is Silver stronger than steel?
Steel is more durable than sterling silver, resisting high pressure and scratching. The metal is much more difficult to break or otherwise irreparably damage. However, sterling silver is more ductile.