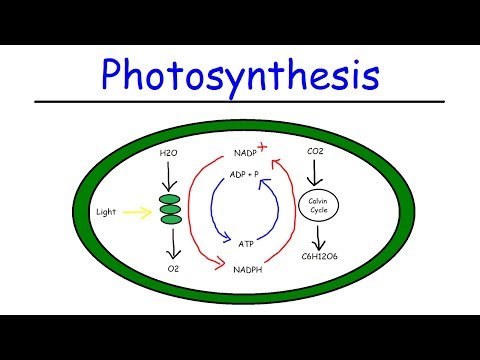
During these initial reactions, water is used and oxygen is released. The energy from sunlight is converted into a small amount of ATP and an energy carrier called NADPH. Together with carbon dioxide, these are used to make glucose (sugar) through a process called the Calvin Cycle.
Q. What is the end result of the Calvin cycle quizlet?
The end product of the Calvin Cycle is a 3-C GP3 molecule and two 3-C G3P molecules must combine to create one 6-C glucose which is two spins around the Calvin Cycle.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the end result of the Calvin cycle quizlet?
- Q. Which is not a product of the light reaction?
- Q. What sugar is produced by the Calvin cycle?
- Q. What does the Calvin cycle need help from in order to make sugar?
- Q. Why is it important to regenerate RuBP in the Calvin cycle?
- Q. What does Rubisco do simple?
- Q. What is the most abundant protein in the human body?
- Q. Where can Rubisco be found?
Q. Which is not a product of the light reaction?
NADH
Q. What sugar is produced by the Calvin cycle?
The reactions of the Calvin cycle add carbon (from carbon dioxide in the atmosphere) to a simple five-carbon molecule called RuBP. These reactions use chemical energy from NADPH and ATP that were produced in the light reactions. The final product of the Calvin cycle is glucose.
Q. What does the Calvin cycle need help from in order to make sugar?
Illustration. The Calvin cycle is a process that plants and algae use to turn carbon dioxide from the air into sugar, the food autotrophs need to grow.
Q. Why is it important to regenerate RuBP in the Calvin cycle?
The remaining G3P molecules regenerate RuBP, which enables the system to prepare for the carbon-fixation step. ATP is also used in the regeneration of RuBP. In stage 2, the organic molecule is reduced. In stage 3, RuBP, the molecule that starts the cycle, is regenerated so that the cycle can continue.
Q. What does Rubisco do simple?
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase, better known as RuBisCO, is an enzyme that catalyzes the first major step of carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle. RuBisCO splits 6-C molecules into two equal parts.
Q. What is the most abundant protein in the human body?
collagen
Q. Where can Rubisco be found?
Form I Rubisco, found in green algae and vascular plants, is a hexadecamer composed of 8 large subunits (RbcL), encoded by the chloroplast genome and 8 small, nuclear-encoded subunits (RbcS).