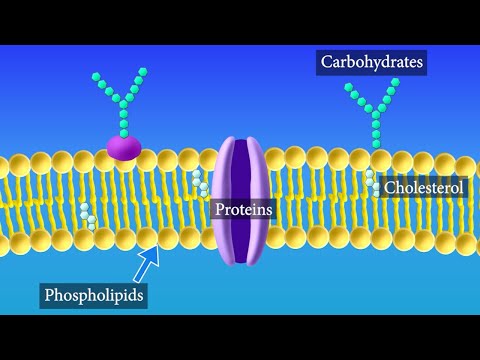
Q. Is the cell membrane composed of carbohydrates and proteins?
The plasma membrane is made up primarily of a bilayer of phospholipids with embedded proteins, carbohydrates, glycolipids, and glycoproteins, and, in animal cells, cholesterol.
Q. How do carbohydrates contribute to the cell membrane?
Carbohydrates covalently linked to proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids) are also a part of cell membranes, and function as adhesion and address loci for cells. The Fluid Mosaic Model describes membranes as a fluid lipid bilayer with floating proteins and carbohydrates.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is the cell membrane composed of carbohydrates and proteins?
- Q. How do carbohydrates contribute to the cell membrane?
- Q. What is fluidity of cell membrane?
- Q. What is the importance of cell membrane fluidity?
- Q. Why do cells regulate their membrane fluidity?
- Q. How does the cell membrane maintain fluidity?
- Q. What are two ways that a bubble is like a membrane?
- Q. Why is cell membrane called fluid mosaic?
Q. What is fluidity of cell membrane?
In biology, membrane fluidity refers to the viscosity of the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane or a synthetic lipid membrane. Lipid packing can influence the fluidity of the membrane. The absence of double bonds decreases fluidity, making the membrane very strong and stacked tightly.
Q. What is the importance of cell membrane fluidity?
Fluidity is important for many reasons: 1. it allows membrane proteins rapidly in the plane of bilayer. 2. It permits membrane lipids and proteins to diffuse from sites where they are inserted into bilayer after their synthesis.
Q. Why do cells regulate their membrane fluidity?
Why do cells regulate their membrane fluidity? Membrane fluidity can be regulated by cells by changing the lipid composition of the membrane. This is important for allowing proteins to move within the membrane, from their place of insertion to the location where they function.
Q. How does the cell membrane maintain fluidity?
If saturated fatty acids are compressed by decreasing temperatures, they press in on each other, making a dense and fairly rigid membrane. If unsaturated fatty acids are compressed, the “kinks” in their tails push adjacent phospholipid molecules away, which helps maintain fluidity in the membrane.
Q. What are two ways that a bubble is like a membrane?
Bubbles make a great stand in for cell membranes. They’re fluid, flexible, and can self-repair. Bubbles and cell membranes are alike because their parts are so similar. If you could zoom down on a cell membrane, you’d see that much of the membrane is a double layer of little molecules called phospholipids.
Q. Why is cell membrane called fluid mosaic?
It is sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic because it has many types of molecules which float along the lipids due to the many types of molecules that make up the cell membrane. The liquid part is the lipid bilayer which floats along the lipids due to the many types of molecules that make up the cell.