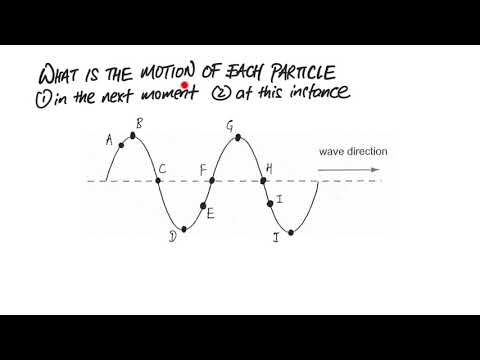
Is the speed of a transverse wave on a string the same as the speed at which a particle on the string moves ? The two speeds, vwave and vparticle, are not the same.
Q. How do you find the speed of a transverse wave?
Key Points
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you find the speed of a transverse wave?
- Q. What is the speed of a transverse wave on the rope?
- Q. What does the speed of a wave on a string depend on?
- Q. Do waves travel faster on thick or thin strings?
- Q. Why does each wave look differently?
- Q. What do the particles in a wave do?
- Q. Do waves transfer matter?
- Q. What are the two types of waves?
- Q. What are 3 things that travel in waves?
- Q. What are the classification of waves?
- Q. What are the 7 types of waves?
- Q. What are the major types of waves?
- Q. What is the most useful electromagnetic wave?
- Q. What are the 7 electromagnetic waves in order?
- Q. What is the correct order of increasing frequency?
- Q. Which type of wave travels the fastest?
- Q. How can you remember the 7 electromagnetic waves?
- Q. Which Colour has lowest frequency?
- Q. Which color has longest wavelength?
- Q. How do you remember the EM waves in order?
- Q. What is the correct order of wavelengths from the longest to the shortest?
- Q. Which two waves lie at the ends of the visible spectrum?
- Q. What electromagnetic waves are used in radar?
- Q. What can electromagnetic waves travel through that mechanical waves Cannot travel through?
- Q. What electromagnetic waves is sometimes called the invisible heat rays?
- Q. At what speed do electromagnetic waves travel?
- Q. What is an example of non ionizing radiation?
- Q. What are two uses for infrared waves?
- The type of wave that occurs in a string is called a transverse wave.
- The period of a wave is indirectly proportional to the frequency of the wave: T=1f T = 1 f .
- The speed of a wave is proportional to the wavelength and indirectly proportional to the period of the wave: v=λT v = λ T .
Q. What is the speed of a transverse wave on the rope?
90 ms−1.
Q. What does the speed of a wave on a string depend on?
Summary. The speed of a wave on a string depends on the linear density of the string and the tension in the string. The linear density is mass per unit length of the string. In general, the speed of a wave depends on the square root of the ratio of the elastic property to the inertial property of the medium.
Q. Do waves travel faster on thick or thin strings?
How does the fundamental vibration frequency compare for the thick versus the thin strings? Since v = √F/µ, where F is the tension and µ is the linear mass density (in kg/m), waves travel faster on the thin strings.
Q. Why does each wave look differently?
Answer: The waves look different because it depends on how fast you move the rope. When you move the rope slowly, bigger but fewer waves will be formed. While when you move the rope fastly, smaller but more waves will be formed.
Q. What do the particles in a wave do?
In a wave phenomenon, energy can move from one location to another, yet the particles of matter in the medium return to their fixed position. A wave transports its energy without transporting matter.
Q. Do waves transfer matter?
It is important to remember that all waves transfer energy but they do not transfer matter . For example, if a ball is placed on the surface of a pond when ripples move across it, the ball will move up and down but not outwards with the wave.
Q. What are the two types of waves?
Waves come in two kinds, longitudinal and transverse. Transverse waves are like those on water, with the surface going up and down, and longitudinal waves are like of those of sound, consisting of alternating compressions and rarefactions in a medium.
Q. What are 3 things that travel in waves?
What are three things that travel in waves? Sound, energy and radio travel in waves.
Q. What are the classification of waves?
One way to categorize waves is on the basis of the direction of movement of the individual particles of the medium relative to the direction that the waves travel. Categorizing waves on this basis leads to three notable categories: transverse waves, longitudinal waves, and surface waves.
Q. What are the 7 types of waves?
The EM spectrum is generally divided into seven regions, in order of decreasing wavelength and increasing energy and frequency. The common designations are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared (IR), visible light, ultraviolet (UV), X-rays and gamma rays.
Q. What are the major types of waves?
There are two basic types of wave motion for mechanical waves: longitudinal waves and transverse waves. The animations below demonstrate both types of wave and illustrate the difference between the motion of the wave and the motion of the particles in the medium through which the wave is travelling.
Q. What is the most useful electromagnetic wave?
visible light
Q. What are the 7 electromagnetic waves in order?
In order from highest to lowest energy, the sections of the EM spectrum are named: gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet radiation, visible light, infrared radiation, and radio waves. Microwaves (like the ones used in microwave ovens) are a subsection of the radio wave segment of the EM spectrum.
Q. What is the correct order of increasing frequency?
Electromagnetic waves of different frequency are called by different names since they have different sources and effects on matter. In order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays.
Q. Which type of wave travels the fastest?
P wave
Q. How can you remember the 7 electromagnetic waves?
The mnemonic for the EM spectrum is Roman Men Invented Very Unusual X-Ray Guns which translates to Radio waves, Microwaves, Infrared wave, visible light, Ultraviolet, X-ray and Gamma rays.
Q. Which Colour has lowest frequency?
red
Q. Which color has longest wavelength?
red light
Q. How do you remember the EM waves in order?
So visible light has a number of colors and from lowest to highest frequency, we have Roy G Biv. So we used this fictional name, Roy G Biv, to be able to memorize the order of visible light from lowest to highest frequency. So we have Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet.
Q. What is the correct order of wavelengths from the longest to the shortest?
The electromagnetic spectrum includes, from longest wavelength to shortest: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, optical, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma-rays.
Q. Which two waves lie at the ends of the visible spectrum?
Based on the electromagnetic spectrum, Infrared and Ultraviolet rays lies at the end of the visible spectrum or visible light.
Q. What electromagnetic waves are used in radar?
radio waves
Q. What can electromagnetic waves travel through that mechanical waves Cannot travel through?
Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. This means that electromagnetic waves can travel not only through air and solid materials, but also through the vacuum of space. This proved that radio waves were a form of light!
Q. What electromagnetic waves is sometimes called the invisible heat rays?
B. Explanation: The electromagnetic waves that are sometimes called heat rays are the waves that are in the spectrum of infrared light. The infrared light waves are commonly associated with heat.
Q. At what speed do electromagnetic waves travel?
Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy that is commonly known as light. Generally speaking, we say that light travels in waves, and all electromagnetic radiation travels at the same speed which is about 3.0 * 108 meters per second through a vacuum.
Q. What is an example of non ionizing radiation?
Non-ionizing radiation includes the spectrum of ultraviolet (UV), visible light, infrared (IR), microwave (MW), radio frequency (RF), and extremely low frequency (ELF). Lasers commonly operate in the UV, visible, and IR frequencies.
Q. What are two uses for infrared waves?
Infrared (IR) light is used by electrical heaters, cookers for cooking food, short-range communications like remote controls, optical fibres, security systems and thermal imaging cameras which detect people in the dark.