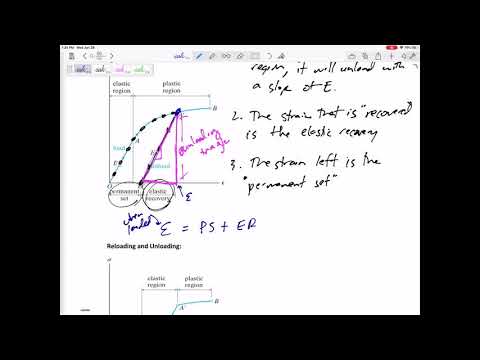
Q. Is the stress beyond which the material will not return to its original shape when unloaded but will retain a permanent deformation?
The elastic limit is the stress value beyond which the material no longer behaves elastically but becomes permanently deformed.
Q. What is elastic and plastic deformation?
When energy goes into changing the shape of some material and it stays changed, that is said to be plastic deformation. When the material goes back to its original form, that’s elastic deformation. Mechanical energy is lost whenever an object undergoes plastic deformation.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is the stress beyond which the material will not return to its original shape when unloaded but will retain a permanent deformation?
- Q. What is elastic and plastic deformation?
- Q. What occurs to a plastic solid after an applied force is removed?
- Q. Why do wires return to their original shape after being bent?
- Q. How can we return them to their original shape?
- Q. Which material returns to original shape after bending?
- Q. How can we return alloys to their original shape?
- Q. Does steel have memory?
- Q. Can SMA be used to control and prevent fire?
- Q. How do atoms naturally arrange themselves?
- Q. Can atoms create themselves?
- Q. Why is nitinol called a smart alloy?
- Q. Why are shape memory alloys useful?
- Q. What is shape memory used for?
- Q. Why smart materials are used?
- Q. What are examples of smart materials?
- Q. What is the special characteristic of shape memory alloy?
- Q. How does shape memory alloys work?
- Q. What are the properties of shape memory polymers?
- Q. Does plastic have a memory?
- Q. What type of materials are formed when monomers join together?
- Q. What is a polymer definition?
- Q. What is an example of a biological polymer?
- Q. What is a polymer give an example?
- Q. What are the uses of polymer?
- Q. What are the advantages of polymer?
- Q. What are the two main types of polymers?
Q. What occurs to a plastic solid after an applied force is removed?
The body exhibiting elasticity regains its shape or size after the removal of the external force. The body exhibiting plasticity retains its new shape or size after the removal of the external force. There is a temporary change in dimensions of the body on the application of the deforming force.
Q. Why do wires return to their original shape after being bent?
When you first start treatment with braces, your teeth are crooked. The wire that attaches to your braces must be able to return to its original shape when it is deformed or bent. The force that returns the wire to its original shape is what moves your teeth.
Q. How can we return them to their original shape?
Something that is elastic can return to its original shape after being stretched or compressed. This property is called elasticity. As you stretch or compress an elastic material like a bungee cord, it resists the change in shape.
Q. Which material returns to original shape after bending?
Elastic
Q. How can we return alloys to their original shape?
Shape-memory materials behave differently. They’re strong, lightweight alloys (generally, mixtures of two or metals) with a very special property. They can be “programmed” to remember their original shape, so if you bend or squeeze them you can get that original shape back again just by heating them.
Q. Does steel have memory?
It is the reversible diffusionless transition between these two phases that results in special properties. While martensite can be formed from austenite by rapidly cooling carbon-steel, this process is not reversible, so steel does not have shape-memory properties.
Q. Can SMA be used to control and prevent fire?
Can SMA be used to control and prevent fire? Explanation: SMA is mainly used to control and prevent fire to a large extent. For example, an SMA is placed in a fire safety valve, when a fire occurs, due to the change in temperature the SMA changes its shape and shuts off the fire.
Q. How do atoms naturally arrange themselves?
This attraction between chemical particles is called cohesion. The shape and size of the chemical particles determines how they arrange themselves in the crystaline structure. The orderly pattern of chemical particles gives a minerala geometric shape called a crystal.
Q. Can atoms create themselves?
Atoms cannot be created nor destroyed, and they are indestructible; they cannot be broken into smaller parts. This was based on the Law of Conservation of Mass. It was later learned that atoms can break into smaller parts. Chemical reactions involve a separation, combination, or rearrangement of atoms.
Q. Why is nitinol called a smart alloy?
A smart alloy is a smart material that can remember its original shape. The technical name for a smart alloy is a shape memory alloy (SMA). copper-zinc-aluminium and copper-aluminium-nickel. it keeps its new shape until it is heated.
Q. Why are shape memory alloys useful?
v Dental wires: used for braces and dental arch wires, memory alloys maintain their shape since they are at a constant temperature, and because of the super elasticity of the memory metal, the wires retain their original shape after stress has been applied and removed.
Q. What is shape memory used for?
They are used as wires and tubes in applications with hot fluids flowing through them. These materials are ideal as they can retain their shape even in a heated environment. Another application of SMAs is in civil engineering. For example, they have been used in bridge structures.
Q. Why smart materials are used?
With benefits for aerospace, medical, textile, construction, and electronics industries, smart materials improve efficiency and save resources by responding to corrosion, pH changes, water content, temperature, mechanical forces, and much more.
Q. What are examples of smart materials?
TYPES OF SMART MATERIALS
- Piezoelectric materials.
- Shape memory materials.
- Chromoactive materials.
- Magnetorheological materials.
- Photoactive materials.
Q. What is the special characteristic of shape memory alloy?
Shape memory alloys are a unique class of alloys that have ability to ‘remember’ their shape and are able to return to that shape even after being bent. At a low temperature, a SMA can be seemingly plastically deformed, but this ‘plastic’ strain can be recovered by increasing the temperature.
Q. How does shape memory alloys work?
When a shape memory alloy is in its martensitic form, it is easily deformed to a new shape. This process is known as shape memory. The temperature at which the alloy remembers its high temperature form when heated can be adjusted by slight changes in alloy composition and through heat treatment.
Q. What are the properties of shape memory polymers?
Shape-memory polymers (SMPs) are polymeric smart materials that have the ability to return from a deformed state (temporary shape) to their original (permanent) shape induced by an external stimulus (trigger), such as temperature change.
Q. Does plastic have a memory?
Plastic memory is the ability of some plastics to return to their original form when hot. An example of plastic memory is a clear plastic drinking cup returning to a flat disk when heated. The tendency of certain plastics after being deformed to resume their original form when heated.
Q. What type of materials are formed when monomers join together?
Monomers are small molecules which may be joined together in a repeating fashion to form more complex molecules called polymers. Monomers form polymers by forming chemical bonds or binding supramolecularly through a process called polymerization.
Q. What is a polymer definition?
Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called monomers. Polymers make up many of the materials in living organisms, including, for example, proteins, cellulose, and nucleic acids.
Q. What is an example of a biological polymer?
There are four basic kinds of biological macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These polymers are composed of different monomers and serve different functions. Starch is an example of a polysaccharide (many saccharides linked together) and is a form of stored glucose in plants.
Q. What is a polymer give an example?
Polymer is a substance made up of a large number of smaller molecules that link together to form larger molecules. An example of a synthetic polymer is plastic. An example of a natural polymer is rubber.
Q. What are the uses of polymer?
Product made from polymers are all around us: clothing made from synthetic fibers, polyethylene cups, fiberglass, nylon bearings, plastic bags, polymer-based paints, epoxy glue, polyurethane foam cushion, silicone heart valves, and Teflon-coated cookware.
Q. What are the advantages of polymer?
Advantages
- Polymers are more resistant to chemicals than their metal counterparts.
- Polymer parts do not require post-treatment finishing efforts, unlike metal.
- Polymer and composite materials are up to ten times lighter than typical metals.
- Polymer materials handle far better than metals in chemically harsh environments.
Q. What are the two main types of polymers?
Types of polymers
- Natural polymers. Natural polymers are all those found in nature.
- Synthetic polymers. Synthetic or artificial polymers are manufactured in the laboratory and generally have petroleum-derived ingredients.
- Addition polymers.
- Condensing polymers.
- Rearrangement polymers.
- Biodegradable polymers.