A seismograph, or seismometer, is an instrument used to detect and record earthquakes. Generally, it consists of a mass attached to a fixed base. During an earthquake, the base moves and the mass does not. The motion of the base with respect to the mass is commonly transformed into an electrical voltage.
Q. What information do geologists gain from analyzing seismograph data?
Geologists first study data from seismographs, this shows what kinds of seismic waves the earthquake produced and how strong they were-it also helps geologists infer how much movement occurred along the fault and the strength of the rocks that broke when the fault slipped-they use all this info to rate the quake on the …
Table of Contents
- Q. What information do geologists gain from analyzing seismograph data?
- Q. What information can geologists gain by analyzing seismographs from different locations on Earth the direction of motion of tectonic plates the approximate time of the next earthquake the location and strength of the earthquake the cost of damage an earthquake causes?
- Q. Which type of information can scientists collect using a seismograph?
- Q. What is a earthquake scientist called?
- Q. Which device is used to measure earthquakes?
- Q. What is a safe distance from a fault line?
- Q. How are earthquakes detected?
- Q. What are the three types of seismographs?
- Q. What is the atomic bomb equivalent to a 7.0 earthquake?
- Q. Where do most earthquakes happen?
- Q. What is seismologist?
- Q. Who is the most famous seismologist?
- Q. Is being a seismologist dangerous?
- Q. What are 3 things a seismologist does?
- Q. What is it like to be a seismologist?
- Q. What qualifications do I need to be a seismologist?
- Q. What is a Seismologists salary?
- Q. How many years does it take to become a seismologist?
- Q. What is the difference between a geologist and a seismologist?
- Q. Which type of wave caused by an earthquake does the most above ground damage?
- Q. Is Seismology a branch of geophysics?
- Q. What other professions would use seismic data?
- Q. What is the most significant discovery of scientist because of earthquake?
- Q. Who is known as the father of seismology?
- Q. What are the branches of geophysics?
- Q. What is the point of seismology?
- Q. How do seismometers affect people’s lives?
- Q. How important facts about an earthquake are measured?
Q. What information can geologists gain by analyzing seismographs from different locations on Earth the direction of motion of tectonic plates the approximate time of the next earthquake the location and strength of the earthquake the cost of damage an earthquake causes?
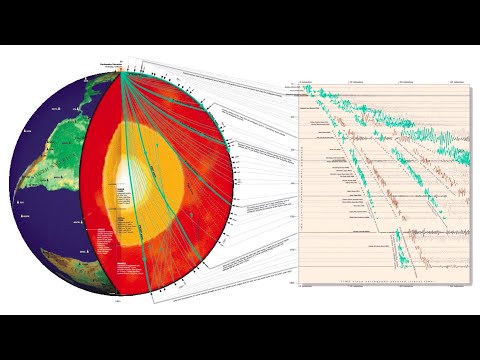
the answer is: Seismologist use the seismic waves produced by an earthquake to locate the epicenter. Because P waves travel through the earth at different speeds than S waves, seismologist can determine the distance from their station that an earthquake has occurred.
Q. Which type of information can scientists collect using a seismograph?
How Are Earthquakes Studied? Seismologists study earthquakes by going out and looking at the damage caused by the earthquakes and by using seismographs. A seismograph is an instrument that records the shaking of the earth’s surface caused by seismic waves.
Q. What is a earthquake scientist called?
Seismology ( /saɪzˈmɒlədʒi/; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (seismós) meaning “earthquake” and -λογία (-logía) meaning “study of”) is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology.
Q. Which device is used to measure earthquakes?
Seismographs
Q. What is a safe distance from a fault line?
Phivolcs now recommends avoiding construction within 5 meters on each side of a fault trace, or a total width of 10 meters. We may call this the ideal “10-meter wide no-build zone” in the vicinity of a fault.
Q. How are earthquakes detected?
How do we measure earthquakes? Earthquakes are measured using instruments called seismometers, that detect the vibrations caused by seismic waves as they travel through the crust. Seismic waves can be both natural (from earthquakes) or caused by human activity (explosions).
Q. What are the three types of seismographs?
To overcome this problem, modern seismograph stations have three separate instruments to record horizontal waves – (1) one to record the north-south waves, (2) another to record east-west waves, and (3) a vertical one in which a weight resting on a spring tends to stand still and record vertical ground motions.
Q. What is the atomic bomb equivalent to a 7.0 earthquake?
More examples
| Approximate Richter Magnitude number | Seismic energy equivalent: Amount of TNT |
|---|---|
| 7.0 | 32 megatons |
| 7.1 | 50 megatons |
| 7.5 | 178 megatons |
| 7.8 | 600 megatons |
Q. Where do most earthquakes happen?
Where do earthquakes occur?
- The world’s greatest earthquake belt, the circum-Pacific seismic belt, is found along the rim of the Pacific Ocean, where about 81 percent of our planet’s largest earthquakes occur.
- The Alpide earthquake belt extends from Java to Sumatra through the Himalayas, the Mediterranean, and out into the Atlantic.
Q. What is seismologist?
Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and related phenomena, such as volcanic eruptions. Seismologists also apply what they learn from studying the Earth’s structure and other geological events, such as tsunamis, for commercial and other purposes, such as detecting nuclear explosions.
Q. Who is the most famous seismologist?
Charles F. Richter, American physicist and seismologist who developed the Richter scale for measuring earthquake magnitude. Born on an Ohio farm, Richter moved with his mother to Los Angeles in 1916.
Q. Is being a seismologist dangerous?
Hiking in areas where the ground tends to shake and/or spew lava isn’t exactly the safest thing to be doing. Seismologists who work for oil and mining companies don’t exactly have risk-free work environments either. Explosions, equipment malfunctions, toxic chemicals—this stuff can kill you.
Q. What are 3 things a seismologist does?
Seismologists study earthquakes and their results, like tsunamis, and landslides. They may also monitor active volcanoes for tremors and signs of an impending eruption. They use seismographs and computer equipment to collect and analyze data on seismic events.
Q. What is it like to be a seismologist?
Seismologists study and collect data about vibrations that occur in the Earth’s interior, such as earthquakes and tsunamis. Seismologists, like other geoscientists, study the Earth’s structure, composition and processes, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Q. What qualifications do I need to be a seismologist?
You can do a degree or postgraduate qualification in: geology. geography. Earth science….You’ll usually need:
- 5 GCSEs at grades 9 to 4 (A* to C), or equivalent, including English, maths and science.
- 2 or 3 A levels, or equivalent, including a science, for a degree.
- a degree in a relevant subject for postgraduate study.
Q. What is a Seismologists salary?
$89,597 per year
Q. How many years does it take to become a seismologist?
Entry-level positions in seismology require a bachelor’s degree or higher in geophysics or a related area, and more advanced roles may require a master’s degree or a doctorate. For positions in the petroleum industry, a bachelor’s degree is often sufficient, although a master’s degree could be beneficial.
Q. What is the difference between a geologist and a seismologist?
The difference between these two careers lies in their approach. Seismologists look at waves of energy beneath the earth’s surface, whereas geologists look at the structure and makeup of minerals and ancient rock formations.
Q. Which type of wave caused by an earthquake does the most above ground damage?
S waves
Q. Is Seismology a branch of geophysics?
Seismology, scientific discipline that is concerned with the study of earthquakes and of the propagation of seismic waves within the Earth. A branch of geophysics, it has provided much information about the composition and state of the planet’s interior.
Q. What other professions would use seismic data?
If you want to do seismic research or find a university position, you’ll need a Doctorate degree. Seismologists can find work with universities, laboratories, observatories, research firms, environmental consulting firms, oil and gas companies, governments, insurance companies, or engineering companies.
Q. What is the most significant discovery of scientist because of earthquake?
1850 – Seismic waves discovered Robert Mallet realised that most earthquake damage is due to moving waves caused by a sudden land movement, named seismic waves. When an earthquake occurs shockwaves of energy, called seismic waves, are released from the earthquake focus.
Q. Who is known as the father of seismology?
John Milne
Q. What are the branches of geophysics?
While there are many divisions of geophysics such as oceanography, atmospheric physics, climatology, and planetary geophysics, this brochure describes three of the most popular branches of geophysics: Petroleum Geophysics. Environmental Geophysics. Mining Geophysics.
Q. What is the point of seismology?
Seismology is the science of earthquakes to study the causes and effects of minute pulsation to most catastrophic natural phenomenon inside the earth.
Q. How do seismometers affect people’s lives?
Seismographs can detect quakes that are too small for humans to feel. During an earthquake, ground-shaking seismic waves radiate outward from the quake source, called the epicenter. These measurements allow scientists to estimate the distance, direction, magnitude, and the type of earthquake that just occurred.
Q. How important facts about an earthquake are measured?
Scientists use seismic waves to measure how big an earthquake is. They use a device called a seismograph to measure the size of the waves. To tell the strength of an earthquake scientists use a scale called the Moment Magnitude Scale or MMS (it used to be called the Richter scale).