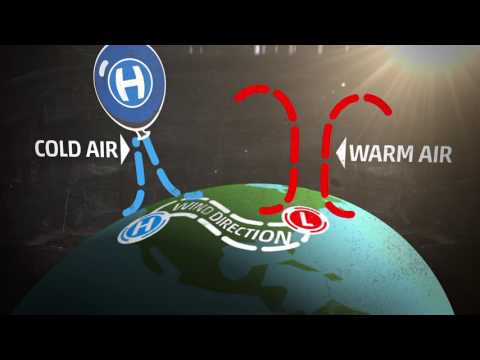
The speed and direction of the wind is governed by three forces; the pressure gradient force (PGF), the Coriolis Force and friction. PGF is the force produced by differences in barometric pressure between two locations and is responsible for the flow of air from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure.
Q. Can Sea breezes occur at night?
The opposite of a sea breeze is a land breeze. While sea breezes occur during the day, land breezes occur at night.
Q. Do valley breezes occur at night?
When the valley floor warms during the day, warm air rises up the slopes of surrounding mountains and hills to create a valley breeze. At night, denser cool air slides down the slopes to settle in the valley, producing a mountain breeze.
Q. How do the sea breezes formed?
Sea breezes occur during hot, summer days because of the unequal heating rates of land and water. During the day, the land surface heats up faster than the water surface. As the warm air over the land is rising, the cooler air over the ocean is flowing over the land surface to replace the rising warm air.
Q. How does wind occur near mountains in the daytime?
description and cause …of such winds, known as mountain winds or breezes, is induced by differential heating or cooling along mountain slopes. During the day, solar heating of the sunlit slopes causes the overlying air to move upslope. These winds are also called anabatic flow.
Q. Is it less wind in a valley?
The flow of air reverses as the sun is going down and at night. This is because the mountain slopes at higher elevations cool quicker than the valleys. The cooler and denser air at higher elevations flows back down the slopes of the mountain and into the valley.
Q. Does wind go up or down a mountain?
Mountain and valley breezes form through a process similar to sea and land breezes. During the day, the sun heats up mountain air rapidly while the valley remains relatively cooler. Convection causes it to rise, causing a valley breeze. At night, the process is reversed.
Q. What causes wind on top of a mountain?
A hill or mountain top will be radiatively warmed by the Sun which in turn heats the air just above it. This creates a lower pressure region into which the air at the bottom of the slope flows, causing the wind.
Q. Do mountains affect wind?
Winds carry moist air over the land. When air reaches the mountain, it rises because the mountains are in the way. As the air rises, it cools, and because cool air can carry less moisture than warm air, there is usually precipitation (rain).
Q. What causes wind on top of hills and mountains quizlet?
Winds created when the atmospheres above the poles cools causing the air to sink and spread out, creating high pressure, causing the air to flow east to west towards the equator at an angle due to the Coriolis effect. Anabatic winds are air currents that blow up hills or mountain slopes that face the sun.
Q. What do you mean by Anabatic wind?
Definition English: Anabatic wind also called upslope wind, local air current that blows up a hill or mountain slope facing the Sun. During the day, the Sun heats such a slope (and the air over it) faster than it does the adjacent atmosphere over a valley or a plain at the same altitude.
Q. What is katabatic and Anabatic wind?
Anabatic Winds are upslope winds driven by warmer surface temperatures on a mountain slope than the surrounding air column. Katabatic winds are downslope winds created when the mountain surface is colder than the surrounding air and creates a down slope wind.
Q. Why do katabatic winds occur at night?
Katabatic wind, also called downslope wind, or gravity wind, wind that blows down a slope because of gravity. It occurs at night, when the highlands radiate heat and are cooled. This process is most pronounced in calm air because winds mix the air and prevent cold pockets from forming.
Q. What is daytime wind called?
An anabatic wind, from the Greek anabatos, verbal of anabainein meaning moving upward, is a warm wind which blows up a steep slope or mountain side, driven by heating of the slope through insolation. It is also known as an upslope flow. These winds typically occur during the daytime in calm sunny weather.
Q. What are the 2 types of breezes?
Breeze
- Wind.
- Sea breeze.
- Land breeze.
- Mountain breeze.
- Glacier breeze.
- Valley breeze.
- Sea and land breeze.