Q. What 3 things can a karyotype tell you?
Karyotypes can reveal changes in chromosome number associated with aneuploid conditions, such as trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). Careful analysis of karyotypes can also reveal more subtle structural changes, such as chromosomal deletions, duplications, translocations, or inversions.
Q. What is a karyotype and why is it important?
“Karyotype” also refers to the actual collection of chromosomes being examined. Examining chromosomes through karyotyping allows your doctor to determine whether there are any abnormalities or structural problems within the chromosomes. Chromosomes are in almost every cell of your body.
Table of Contents
- Q. What 3 things can a karyotype tell you?
- Q. What is a karyotype and why is it important?
- Q. What do karyotypes not show?
- Q. What genetic disorders can be diagnosed using karyotyping?
- Q. What happens if a karyotype test is abnormal?
- Q. What is karyotype test for infertility?
- Q. How expensive is a karyotype test?
- Q. What is a normal female karyotype?
- Q. How much does genetic karyotyping cost?
- Q. Is genetic testing a good idea?
- Q. Does insurance pay for genetic testing?
- Q. How long does genetic testing take?
- Q. Why Genetic testing is bad?
- Q. Is genetic testing expensive?
- Q. What are the pros and cons of genetic testing?
- Q. Why would a doctor order genetic testing?
- Q. Is genetic testing painful?
- Q. What does a genetic test tell you?
- Q. What diseases does genetic testing look for?
- Q. What are the three types of genetic testing?
- Q. Can genetic testing show mental illness?
- Q. What is the hardest mental illness to treat?
- Q. What are the 4 types of mental illness?
- Q. Is there a genetic test for anxiety?
- Q. What is the best anxiety drug?
- Q. Is there a swab test for mental illness?
- Q. How much is genetic testing for mental health?
- Q. Does genetic testing for depression work?
- Q. What mental health disorders are genetic?
- Q. Does genomind really work?
Q. What do karyotypes not show?
Examples of conditions that cannot be detected by karyotyping include: Cystic fibrosis. Tay-Sachs disease. Sickle cell disease.
Q. What genetic disorders can be diagnosed using karyotyping?
The most common things doctors look for with karyotype tests include:
- Down syndrome (trisomy 21). A baby has an extra, or third, chromosome 21.
- Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18). A baby has an extra 18th chromosome.
- Patau syndrome (trisomy 13). A baby has an extra 13th chromosome.
- Klinefelter syndrome .
- Turner syndrome .
Q. What happens if a karyotype test is abnormal?
Abnormal chromosomes can cause a variety of health problems. The symptoms and severity depend on which chromosomes have been affected. Some disorders caused by chromosomal defects include: Down syndrome, a disorder that causes intellectual disabilities and developmental delays.
Q. What is karyotype test for infertility?
Karyotype testing for men and women suffering infertility can provide extremely useful information that helps your doctor to get to the bottom of your problem. Karyotypes can diagnose chromosomal abnormalities, a cause of infertility that is relatively common and underappreciated.
Q. How expensive is a karyotype test?
Results: CMA testing results in more genetic diagnoses at an incremental cost of US $2692 per additional diagnosis compared with karyotyping, which has an average cost per diagnosis of US $11,033.
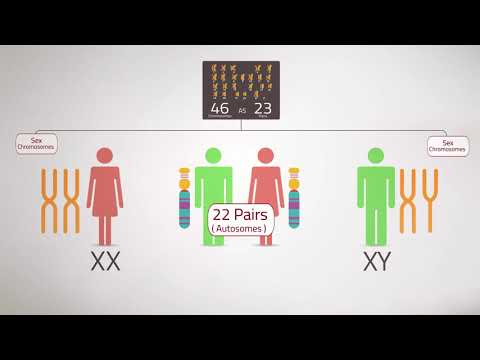
Q. What is a normal female karyotype?
Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. A picture of all 46 chromosomes in their pairs is called a karyotype. A normal female karyotype is written 46, XX, and a normal male karyotype is written 46, XY.
Q. How much does genetic karyotyping cost?
The cost of genetic testing can range from under $100 to more than $2,000, depending on the nature and complexity of the test. The cost increases if more than one test is necessary or if multiple family members must be tested to obtain a meaningful result.
Q. Is genetic testing a good idea?
Genetic testing can reveal changes (mutations) in your genes that may cause illness or disease. Although genetic testing can provide important information for diagnosing, treating and preventing illness, there are limitations.
Q. Does insurance pay for genetic testing?
Most health insurance plans will cover the cost of genetic testing when recommended by a physician. However, all coverage and reimbursement is subject to Medicare, Medicaid, and third-party payer benefit plans.
Q. How long does genetic testing take?
It takes about 1 week to get the results. A positive cell-free DNA test result should be followed by a diagnostic test with amniocentesis or CVS. What do the different results of prenatal screening tests mean?
Q. Why Genetic testing is bad?
Some disadvantages, or risks, that come from genetic testing can include: Testing may increase your stress and anxiety. Results in some cases may return inconclusive or uncertain. Negative impact on family and personal relationships.
Q. Is genetic testing expensive?
For patients not covered by health insurance, genetic testing cost ranges from less than $300-$3,000 or more, depending on the individual, the type of test and the comprehensiveness of the test.
Q. What are the pros and cons of genetic testing?
Pros of Genetic Testing
- Treatment of Disease.
- Lifestyle Changes for Disease Prevention.
- Stress Release from Lack of Genetic Variants.
- A Negative Test Could Mask Additional Causes.
- A Positive Test Could Unnecessarily Increase Stress.
- Genetic Purgatory.
- Cost.
- Privacy Concerns.
Q. Why would a doctor order genetic testing?
Genetic testing is useful in many areas of medicine and can change the medical care you or your family member receives. For example, genetic testing can provide a diagnosis for a genetic condition such as Fragile X or information about your risk to develop cancer. There are many different kinds of genetic tests.
Q. Is genetic testing painful?
In our DNA Myths video series, Helix scientists take on common misconceptions about genetics. A DNA test isn’t painful at all. No needles, no blood! Believe it or not, all it takes to get your DNA sequenced with Helix is our DNA kit—which you can get by shopping products in the Helix Store—and a little saliva.
Q. What does a genetic test tell you?
Genetic testing is a type of medical test that identifies changes in chromosomes, genes, or proteins. The results of a genetic test can confirm or rule out a suspected genetic condition or help determine a person’s chance of developing or passing on a genetic disorder.
Q. What diseases does genetic testing look for?
7 Diseases You Can Learn About from a Genetic Test
- Intro. (Image credit: Danil Chepko | Dreamstime)
- Breast and ovarian cancer.
- Celiac disease.
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
- Bipolar disorder.
- Obesity.
- Parkinson’s disease.
- Psoriasis.
Q. What are the three types of genetic testing?
The following information describes the three main types of genetic testing: chromosome studies, DNA studies, and biochemical genetic studies. Tests for cancer susceptibility genes are usually done by DNA studies.
Q. Can genetic testing show mental illness?
Can Genetic Testing Help Predict My Risk of Developing a Mental Disorder? The short answer to this question is no. Currently, genetic tests cannot accurately predict your risk of developing a mental disorder.
Q. What is the hardest mental illness to treat?
Borderline personality disorder has historically been viewed as difficult to treat.
Q. What are the 4 types of mental illness?
Summary
- Anxiety disorders, including panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and phobias.
- Depression, bipolar disorder, and other mood disorders.
- Eating disorders.
- Personality disorders.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder.
- Psychotic disorders, including schizophrenia.
Q. Is there a genetic test for anxiety?
The GeneSight Psychotropic test analyzes how your genes may affect your outcomes with medications commonly prescribed to treat depression, anxiety, ADHD, and other mental health conditions.
Q. What is the best anxiety drug?
The most prominent of anti-anxiety drugs for the purpose of immediate relief are those known as benzodiazepines; among them are alprazolam (Xanax), clonazepam (Klonopin), chlordiazepoxide (Librium), diazepam (Valium), and lorazepam (Ativan).
Q. Is there a swab test for mental illness?
You can be tested in your doctor’s office by taking a swab on the inside of your cheek, which is completely painless. The results usually takes 3 to 5 days to process.
Q. How much is genetic testing for mental health?
(Myriad says 95% of patients pay less than $330 for their test, the cost remaining after insurance and possible financial assistance; Genomind says most privately insured customers pay no more than $325.)
Q. Does genetic testing for depression work?
Genetic Tests for Depression Treatment Aren’t Effective, Experts Say. Dozens of companies invite consumers to spit in a tube to determine which antidepressant is right for them. There’s little evidence that these tests work.
Q. What mental health disorders are genetic?
Scientists have long recognized that many psychiatric disorders tend to run in families, suggesting potential genetic roots. Such disorders include autism, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), bipolar disorder, major depression and schizophrenia.
Q. Does genomind really work?
Genomind did an unblinded study of its 10-gene panel in 2013, with 685 patients and a variety of diagnoses. The study showed that 91% of patients with 2 or more prior treatment failures had clinically measurable improvement, but the study was limited by having no treatment-as-usual comparison group.