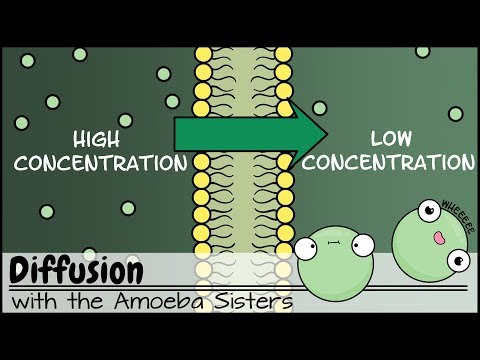
The greater the difference in concentration, the quicker the rate of diffusion. The higher the temperature, the more kinetic energy the particles will have, so they will move and mix more quickly. The greater the surface area, the faster the rate of diffusion.
Q. What are 2 types of diffusion?
Diffusion can be classified into two main types: Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are 2 types of diffusion?
- Q. Why does simple diffusion happen?
- Q. Does simple diffusion use energy?
- Q. Which type of movement occurs when sodium pump is used?
- Q. What is the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion quizlet?
- Q. What do simple and facilitated diffusion have in common?
- Q. What is the process of diffusion quizlet?
- Q. What occurs during diffusion?
- Q. What happens during diffusion *?
- Q. What happens during diffusion in biology?
- Q. What is mean by diffusion in biology?
- Q. What is the importance of diffusion in biology?
- Q. What is the role of diffusion in nutrition?
Q. Why does simple diffusion happen?
The kinetic energy of the molecules results in random motion, causing diffusion. In simple diffusion, this process proceeds without the aid of a transport protein. it is the random motion of the molecules that causes them to move from an area of high concentration to an area with a lower concentration.
Q. Does simple diffusion use energy?
A. Simple diffusion does not require energy: facilitated diffusion requires a source of ATP. Simple diffusion can only move material in the direction of a concentration gradient; facilitated diffusion moves materials with and against a concentration gradient.
Q. Which type of movement occurs when sodium pump is used?
The sodium-potassium pump carries out a form of active transport—that is, its pumping of ions against their gradients requires the addition of energy from an outside source.
Q. What is the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion quizlet?
What is the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion? Diffusion is the driving force behind the movement of many substances across the cell membrane. Facilitated diffusion is where molecules cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels.
Q. What do simple and facilitated diffusion have in common?
Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are similar in that both involve movement down the concentration gradient. The difference is how the substance gets through the cell membrane. Charged or polar molecules that cannot fit between the phospholipids generally enter and leave cells through facilitated diffusion.
Q. What is the process of diffusion quizlet?
Diffusion is the net flow of molecules (or ions) from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration until they are spread out evenly. (i.e down a concentration gradient). It is a passive process therefore it does not require any energy. Small molecules diffuse faster than large molecules.
Q. What occurs during diffusion?
Diffusion occurs when particles spread. They move from a region where they are in high concentration to a region where they are in low concentration. Diffusion happens when the particles are free to move. This is true in gases and for particles dissolved in solutions – but diffusion does not occur in solids.
Q. What happens during diffusion *?
The concentration of a solution is the mass of solute in a given volume of solution, or mass/volume. As a result, the particles tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated, a process known as diffusion (dih-FYOO-zhun).
Q. What happens during diffusion in biology?
Diffusion is the movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Diffusion happens in liquids and gases because their particles move randomly from place to place. Diffusion is an important process for living things; it is how substances move in and out of cells.
Q. What is mean by diffusion in biology?
“Diffusion is a physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration”
Q. What is the importance of diffusion in biology?
Diffusion is important to cells because it allows them to gain the useful substances they require to obtain energy and grow, and lets them get rid of waste products.
Q. What is the role of diffusion in nutrition?
Diffusion is important to organisms because it is the process by which useful molecules enter the body cells and waste products are removed. Digested food molecules (amino acids, glucose) move down a concentration gradient from the intestine to the blood.