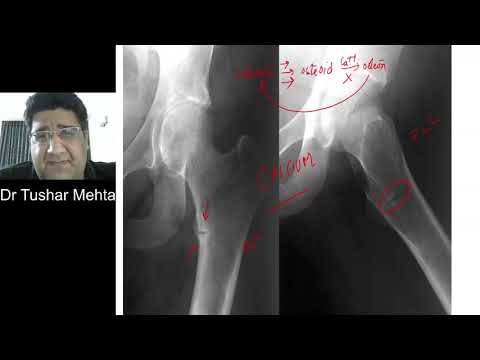
Q. What are looser zones?
Looser zones, also known as cortical infractions, Milkman lines or pseudofractures, are wide, transverse lucencies with sclerotic borders traversing partway through a bone, usually perpendicular to the involved cortex, and are associated most frequently with osteomalacia and rickets.
Q. What pathologic condition is associated with looser zones?
Osteomalacia is the result of impaired mineralization of newly formed osteoid, which leads to characteristic Looser zones.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are looser zones?
- Q. What pathologic condition is associated with looser zones?
- Q. What is pseudofracture?
- Q. What is a banana fracture?
- Q. Can an MRI show osteoporosis?
- Q. What is Milkman syndrome?
- Q. What is a Greenstick fracture?
- Q. Do the bones in your forearm cross?
- Q. Is there a free zone at the MRI?
- Q. What does Zone 2 mean in an MRI?
- Q. What are the ACR safety zones in MRI?
- Q. What are zones 2 and 3 at cismri?
Q. What is pseudofracture?
[soo″do-frak´chur] radiographic appearance of a thickened periosteum and new bone formation over what looks like an incomplete fracture.
Q. What is a banana fracture?
A banana fracture refers to a complete, horizontally orientated pathological fracture seen in deformed bones affected by Paget disease. This term is often used to describe incremental fractures that occur in Paget disease as well, which represent a type of insufficiency fracture.
Q. Can an MRI show osteoporosis?
Other methods rather than DEXA as quantitative computed tomography and quantitative ultrasound also have a role [8]. MRI has a role in detecting osteoporosis that the appearance of bone marrow is determined by its relative amount of protein, fat, water, and cells on MRI pulse sequence.
Q. What is Milkman syndrome?
Medical Definition of Milkman’s syndrome : an abnormal condition marked by porosity of bone and tendency to spontaneous often symmetrical fractures.
Q. What is a Greenstick fracture?
A greenstick fracture occurs when a bone bends and cracks, instead of breaking completely into separate pieces. The fracture looks similar to what happens when you try to break a small, “green” branch on a tree. Most greenstick fractures occur in children younger than 10 years of age.
Q. Do the bones in your forearm cross?
The radius is the forearm bone of the hand. The ulna is the forearm bone of the elbow. The two bones are not just associated at the elbow and wrist joints, but cross attached by a flexible sheet – like the two posts of a canvas stretcher. The motion stops when the radius bone abuts the ulna as the bones cross over.
Q. Is there a free zone at the MRI?
The public is free to move around without being screened. This zone would include the waiting area and hallways outside of the restricted MRI hallways. Zone 2- This zone still has no detectable magnetic field but we do restrict access because it is close to the MRI scanners. Patients, families, and visitors must be escorted into Zone 2.
Q. What does Zone 2 mean in an MRI?
This zone would include the waiting area and hallways outside of the restricted MRI hallways. Zone 2- This zone still has no detectable magnetic field but we do restrict access because it is close to the MRI scanners. Patients, families, and visitors must be escorted into Zone 2.
Q. What are the ACR safety zones in MRI?
What are the ACR Safety Zones? The American College of Radiology has defined four safety zones within MRI facilities. These are denoted Zones I through IV and correspond to levels of increasing magnetic field exposure (and hence potential safety concern). All areas freely accessible to the general public without supervision.
Q. What are zones 2 and 3 at cismri?
Individuals who have been granted access to the CIS beyond the reception area must escort visitors and volunteers into other areas of Zone 2. Restricted area. All visitors and volunteers in Zone 3 must be escorted by authorized personnel at all times while in this zone. Zone 3 contains the MR control area and participant changing area.