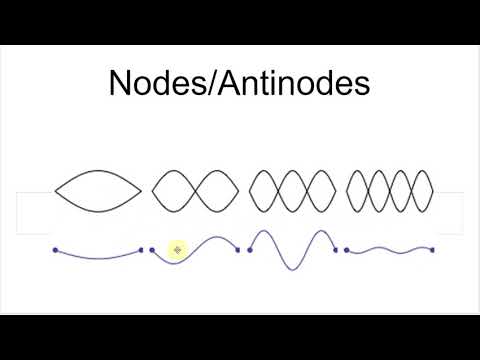
A node is where the amplitude of the wave is zero. Antinodes are where the amplitude (positive of negative) is a maximum, halfway between two adjacent nodes. A standing wave pattern always consists of an alternating pattern of nodes and antinodes.
Q. What is the difference between two consecutive nodes?
Hence we can say that the phase difference between the particles vibrating between two consecutive nodes is zero.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the difference between two consecutive nodes?
- Q. What is the least distance between two consecutive nodes?
- Q. How is a node formed?
- Q. What does node mean?
- Q. What is node with example?
- Q. What is difference between Node and Server?
- Q. Is a switch a node?
- Q. What is a node identifier called?
- Q. Is a node the same as a router?
- Q. Is a host a node?
- Q. What is difference between host and server?
- Q. Is a router a host?
- Q. What is host with example?
- Q. What are types of host?
- Q. What do you understand by the host?
- Q. What do you understand by host very short answer?
- Q. What is the host of disease?
- Q. What are the three major factors of the epidemiologic triangle?
Q. What is the least distance between two consecutive nodes?
In a stationary wave, the distance between two successive nodes(anti-nodes) is one half wavelength. Therefore, the distance between a node and the immediate next anti-node is one fourth of a wavelength.
Q. How is a node formed?
The nodes are produced at locations where destructive interference occurs. For instance, nodes form at locations where a crest of one wave meets a trough of a second wave; or a half-crest of one wave meets a half-trough of a second wave; or a quarter-crest of one wave meets a quarter-trough of a second wave; etc.
Q. What does node mean?
A node is a point, especially in the form of lump or swelling, where one thing joins another. Cut them off cleanly through the stem just below the node. nerve nodes. Synonyms: nodule, growth, swelling, knot More Synonyms of node.
Q. What is node with example?
Any system or device connected to a network is also called a node. For example, if a network connects a file server, five computers, and two printers, there are eight nodes on the network. Each device on the network has a network address, such as a MAC address, which uniquely identifies each device.
Q. What is difference between Node and Server?
Differences between node and server: A node is simply a device in networking with an IP address which helps us in connectivity with other nodes. A node cannot be a server. A node cannot fulfill the clients demand. Node contains less information than server.
Q. Is a switch a node?
A node is any physical device within a network of other tools that’s able to send, receive, or forward information. Modems, switches, hubs, bridges, servers, and printers are also nodes, as are other devices that connect over Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
Q. What is a node identifier called?
A “Node ID,” is a way to conveniently identify nodes within the confines of a single file.
Q. Is a node the same as a router?
In your question, router and switch are nodes, while a camera and printer can be considered as hosts. Hosts are computers whereas nodes are all devices that have network addresses assigned. So, a router is not a host but is a node.
Q. Is a host a node?
A host is a node that participates in user applications, either as a server, client, or both. A server is a type of host that offers resources to the other hosts. Typically a server accepts connections from clients who request a service function. Every network host is a node, but not every network node is a host.
Q. What is difference between host and server?
Host: This is a device such as a computer that connects to a network. Server: This is a piece of hardware or software that provides services to other devices or programs in the network.
Q. Is a router a host?
A host is a computer, connected to other computers for which it provides data or services over a network. Likewise, your router can be a host to other routers. But a host must have an assigned IP address. Therefore, modems, hubs, and switches are not considered hosts because they do not have assigned IP addresses.
Q. What is host with example?
Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner.
Q. What are types of host?
Types of hosts
- accidental host. a host that shelters an organism which does not usually parasitize that host.
- incidental host (a.k.a. dead-end host) a host that shelters an organism but is unable to transmit the organism to a different host.
- primary host (a.k.a. definitive/final host)
- reservoir host.
Q. What do you understand by the host?
The noun host refers to a person who receives and entertains guests. But hosting also has an ickier side: In biology, a host is an animal, plant or person that provides a home for another organism — like a parasite. Host also functions as a noun, meaning a multitude, horde, or great number.
Q. What do you understand by host very short answer?
The biological definition of a host is an organism that harbors another organism, inside or near their body, in a symbiotic relationship. A parasite is an organism that depends on another for food, shelter, and basic needs, to the detriment of its host; this is why it’s called a parasitic relationship.
Q. What is the host of disease?
Host refers to the human who can get the disease. A variety of factors intrinsic to the host, sometimes called risk factors, can influence an individual’s exposure, susceptibility, or response to a causative agent.
Q. What are the three major factors of the epidemiologic triangle?
The epidemiologic triangle is made up of three parts: agent, host and environment.