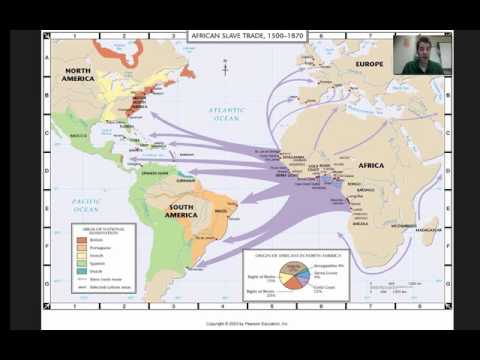
What is the intervening obstacle faced by migrants today? Local diversity in government and politics-Migrant needs a passport to legally emigrate from a country and a visa to legally immigrate to a new country. Migrants need a_________ to legally emigrate from a country.
Q. What are two examples of physical intervening obstacles?
Intervening obstacles are factors that cause migrants challenges or prevent them from reaching their goal. Examples of intervening obstacles include mountains, forests, deserts, cities and bodies of water.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are two examples of physical intervening obstacles?
- Q. What is an intervening obstacle in human geography?
- Q. What does intervening obstacles mean?
- Q. What are 2 examples of push factors?
- Q. Which of the following is an example of push factor?
- Q. What is a push factor that might cause immigration?
- Q. What are three push factors?
- Q. What is the push and pull method?
- Q. What is a push or pull called?
- Q. What are the two major types of force?
- Q. What are the common forces?
- Q. What are two types of frictions?
- Q. What is force and its type?
- Q. What are the three common forces?
- Q. What can a force change?
Q. What is an intervening obstacle in human geography?
An intervening obstacle is an environmental or cultural feature that hinders migration. Some Migrants will leave their destination, encounter an intervening OBSTACLE and be forced to return to their origin.
Q. What does intervening obstacles mean?
INTERVENING OBSTACLES. An intervening obstacle is a environmental or cultural feature that hinders migration.
Q. What are 2 examples of push factors?
A “push factor” is something that encourages an individual to migrate away from a certain place. Natural disasters, political revolutions, civil war, and economic stagnation are all reasons why people might want to migrate away from a certain area.
Q. Which of the following is an example of push factor?
6) Push Factor: Economic Displacement Caused by Environmental, Technological and Demographic Change: Economic hardship has been a powerful “push” factor for many groups. The Irish potato famine of 1845-47 is a good example.
Q. What is a push factor that might cause immigration?
Push factors “push” people away from their home and include things like war. Pull factors “pull” people to a new home and include things like better opportunities. The reasons people migrate are usually economic, political, cultural, or environmental.
Q. What are three push factors?
Push factors may include conflict, drought, famine, or extreme religious activity. Poor economic activity and lack of job opportunities are also strong push factors for migration.
Q. What is the push and pull method?
The original meaning of push and pull, as used in operations management, logistics and supply chain management. In the pull system production orders begin upon inventory reaching a certain level, while on the push system production begins based on demand (forecasted or actual demand).
Q. What is a push or pull called?
A push or a pull on an object is called a force.
Q. What are the two major types of force?
Basically, there are two main types of forces, contact forces, and non-contact forces.
Q. What are the common forces?
These forces include normal force, tension, friction, and spring force.
Q. What are two types of frictions?
There are two main types of friction, static friction and kinetic friction. Static friction operates between two surfaces that aren’t moving relative to each other, while kinetic friction acts between objects in motion.
Q. What is force and its type?
Force is a physical cause that can change the state of motion or the dimensions of an object. There are two types of forces based on their applications: Contact Force. Non-Contact Force.
Q. What are the three common forces?
Action at a distance, such as the gravitational force of Earth on the Moon, is explained by the existence of a force field rather than by “physical contact.” The four basic forces are the gravitational force, the electromagnetic force, the weak nuclear force, and the strong nuclear force.
Q. What can a force change?
A force can speed up or slow down an object. A force can change the direction in which an object is moving. A bigger force on an object will produce a bigger change in the motion. A heavier object requires a larger force than a lighter object in order to undergo the same change in motion.