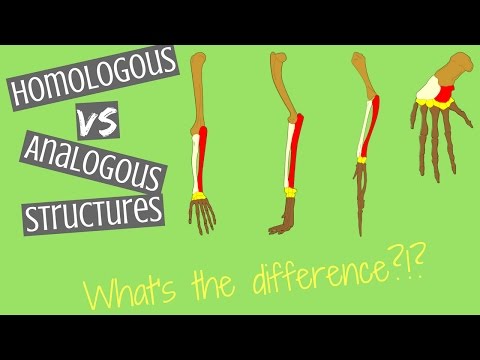
Q. What are structures that are similar in function but different in structure?
Homologous structures are structures that are similar in related organisms because they were inherited from a common ancestor. These structures may or may not have the same function in the descendants. Figure below shows the hands of several different mammals. They all have the same basic pattern of bones.
Q. What has the same evolutionary origin but have different uses?
Features of animals that have similar structure are classified as homologous if they have a common evolutionary origin, even if they have different functions in different animals. These have converged to have the same or comparable function despite differing origins and are known as analogous or homoplastic structures.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are structures that are similar in function but different in structure?
- Q. What has the same evolutionary origin but have different uses?
- Q. What word is used to describe similar structures that evolved from different origins?
- Q. What is homologous and analogous structures?
- Q. What are two homologous structures?
- Q. What is an example of vestigial structures?
- Q. What are two structures that are vestigial?
- Q. What body parts are vestigial?
- Q. How do vestigial structures disappear?
- Q. Why are vestigial structures not removed?
- Q. How is vestigial structures evidence of evolution?
- Q. Why is wisdom teeth vestigial?
- Q. Why is the little toe vestigial?
- Q. What is the oldest age you can get wisdom teeth?
- Q. Are humans losing wisdom teeth?
- Q. Is it rare to have all 4 wisdom teeth?
- Q. Is it rare to have no wisdom teeth?
- Q. What planet takes 7 years to get to?
- Q. Who was the first person to go to Mars?
- Q. How can I send my name to Mars?
Q. What word is used to describe similar structures that evolved from different origins?
Definition. Analogous structures are similar structures that evolved independently in two living organisms to serve the same purpose. The term “analogous structures” comes from the root word “analogy,” which is a device in the English language where two different things on a basis of their similarities.
Q. What is homologous and analogous structures?
Homologous structures share a similar embryonic origin; analogous organs have a similar function. For example, the bones in the front flipper of a whale are homologous to the bones in the human arm. These structures are not analogous. The wings of a butterfly and the wings of a bird are analogous but not homologous.
Q. What are two homologous structures?
The arm of a human, the wing of a bird or a bat, the leg of a dog and the flipper of a dolphin or whale are homologous structures. They are different and have a different purpose, but they are similar and share common traits. They are considered homologous structures because they have a similar underlying anatomy.
Q. What is an example of vestigial structures?
Examples of vestigial structures (also called degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary organs) are the loss of functional wings in island-dwelling birds; the human appendix and vomeronasal organ; and the hindlimbs of the snake and whale.
Q. What are two structures that are vestigial?
Examples of vestigial structures include the human appendix, the pelvic bone of a snake, and the wings of flightless birds. Vestigial structures can become detrimental, but in most cases these structures are harmless; however, these structures, like any other structure, require extra energy and are at risk for disease.
Q. What body parts are vestigial?
7 Vestigial Features of the Human Body
- Palmar Grasp Reflex. inherited reflex.
- Tails. In the sixth week of gestation, the human embryo possesses a tail, complete with several vertebrae.
- Wisdom Teeth. teeth Zoonar/Thinkstock.
- Nictitating Membrane. eye © Sam23/Fotolia.
- Auricular Muscles.
- Palmaris Longus Muscle.
- Pyramidalis Muscle.
Q. How do vestigial structures disappear?
Why do vestigial structures not disappear together? – Quora. Essentially, vestigial structures remain because there is no selection pressure against them.
Q. Why are vestigial structures not removed?
Vestigial structures are not removed by natural selection because natural selection only acts on traits that impact reproductive success.
Q. How is vestigial structures evidence of evolution?
Structures that have lost their use through evolution are called vestigial structures. They provide evidence for evolution because they suggest that an organism changed from using the structure to not using the structure, or using it for a different purpose.
Q. Why is wisdom teeth vestigial?
Wisdom teeth are considered a vestigial organ — no longer useful — because our diet has evolved. Early humans ate a mostly raw diet of foraged plants and hunted animals, which required a lot of rough chewing.
Q. Why is the little toe vestigial?
Pinkie Toes Sure, your pinkie toe is cute, but does it really serve a purpose? As it turns out, science says no, it does not. We don’t use it for balance, walking, or grabbing, and we no longer need it to climb trees as our ancestors once did. Thus, our little toe is vestigial.
Q. What is the oldest age you can get wisdom teeth?
Although it’s preferable to extract the wisdom teeth before age 25, it can still be done later in life. Older adults may require wisdom tooth removal because the tooth has become impacted or infected.
Q. Are humans losing wisdom teeth?
Today, humans may or may not develop the final back molars. Worldwide, it’s estimated that one or more wisdom teeth are absent in about 22 percent of people and become impacted in 24 percent. The flip side: Over half the planet forms normal, functioning wisdom teeth.
Q. Is it rare to have all 4 wisdom teeth?
The number of wisdom teeth varies from person to person Some people get one wisdom tooth, while others have two, three, four, or none at all. While rare, sometimes a person will get more than four wisdom teeth. In this instance, they call the extra teeth supernumerary teeth.
Q. Is it rare to have no wisdom teeth?
About 20-25% of the human population is born with 1 to 3 wisdom teeth, and 35% is born without any wisdom teeth at all.
Q. What planet takes 7 years to get to?
FAQ – Spacecraft
| Spacecraft | Target | Time |
|---|---|---|
| Messenger | Mercury | 6.5 years |
| Cassini | Saturn | 7 years |
| Voyager 1 & 2 | Jupiter; Saturn; Uranus; Neptune | 13,23 months; 3,4 years; 8.5 years; 12 years |
| New Horizons | Pluto | 9.5 years |
Q. Who was the first person to go to Mars?
Astronaut Eli Cologne
Q. How can I send my name to Mars?
All you have to do is head to the mars.nasa.gov website and complete the form. Once your name is approved it will then be etched onto a microchip which is placed aboard the next spacecraft for a mission (which may or not be identified yet). Once approved, you can also print out your very own boarding pass.