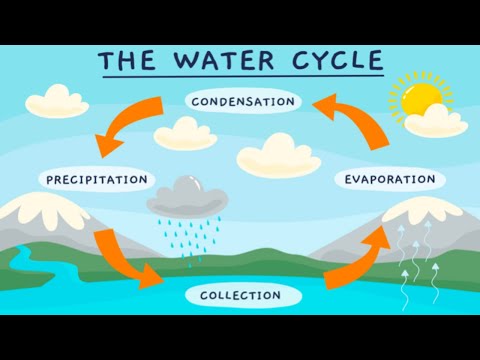
It can be studied by starting at any of the following processes: evaporation, condensation, precipitation, interception, infiltration, percolation, transpiration, runoff, and storage.
Q. Which statement best describes the role of animals in the water and carbon cycles?
Explanation: Animals play a huge role in water cycle and carbon cycle. The process by which animals get energy is cellular respiration. Cellular respiration can be defined as the process by which the food that we eat is broken and energy is transformed in the form of Adenosine triphosphate.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which statement best describes the role of animals in the water and carbon cycles?
- Q. What is transpiration in the water cycle?
- Q. What does the plastic wrap with ice cubes represents?
- Q. What does the plastic wrap represent in this experiment?
- Q. What did you observe on the underside of the plastic wrap?
- Q. What is it called when water vapor condenses?
- Q. What happens when water vapor is cooled?
Q. What is transpiration in the water cycle?
Transpiration: The release of water from plant leaves Plants put down roots into the soil to draw water and nutrients up into the stems and leaves. Some of this water is returned to the air by transpiration.
Q. What does the plastic wrap with ice cubes represents?
Lastly, place one or two ice cubes on top of your plastic wrap, right over the small bowl or cup. This represents the cooler sky / atmosphere, where condensation like clouds and rain form. 6.
Q. What does the plastic wrap represent in this experiment?
In the experiment, the beakers represented the earth’s atmosphere, the plastic wrap represented the greenhouse gases trapping in the air and the lamps acted as the sun, to heat up the beakers.
Q. What did you observe on the underside of the plastic wrap?
The plastic wrap of the covered cup acts like the atmosphere, and traps the water vapor. In a real cloud, the water vapor cools back into liquid water. In the covered cup, the air can only hold so much vapor, and the vapor condenses back to liquid water forming a “rain cloud” on the plastic wrap.
Q. What is it called when water vapor condenses?
Condensation is the change of water from its gaseous form (water vapor) into liquid water. Condensation generally occurs in the atmosphere when warm air rises, cools and looses its capacity to hold water vapor. As a result, excess water vapor condenses to form cloud droplets.
Q. What happens when water vapor is cooled?
When water vapor in the atmosphere loses heat and cools down, condensation happens. As the water vapor cools down and condenses, it attaches to small particles of dust floating in the atmosphere, forming tiny liquid water droplets. When condensation occurs on the ground, it forms dew.