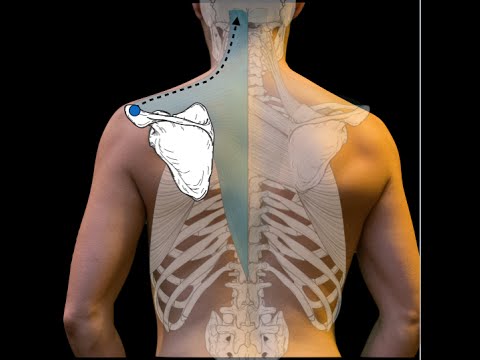
Q. What are the 2 main superficial back muscles?
Superficial Back Muscles
- Trapezius.
- Latissimus dorsi.
- Levator scapulae.
- Rhomboid major.
- Rhomboid minor.
- Quiz.
- References.
Q. Which muscle is the most superficial of the posterior upper back and neck?
Trapezius muscle location It extends laterally to the spine of the shoulder blades and attaches to the collarbone, ribs, and ligamentum nuchae muscle on the back of the neck.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the 2 main superficial back muscles?
- Q. Which muscle is the most superficial of the posterior upper back and neck?
- Q. What are the muscles in the upper back called?
- Q. Is rhomboid major deep or superficial?
- Q. How long does it take for a rhomboid muscle to heal?
- Q. Is rhomboid pain permanent?
- Q. What exercises work the rhomboids?
- Q. How do you release tension between shoulder blades?
- Q. Can anxiety cause pain between shoulder blades?
- Q. What causes pain between the shoulder blades?
- Q. Why does my upper back and neck hurt all the time?
- Q. Why is my upper back always tight?
- Q. What does lung pain feel like in the back?
- Q. What does a pinched lung feel like?
- Q. Where is pleurisy pain located?
Q. What are the muscles in the upper back called?
There is a set of muscles in the upper back (called the thoracic area) called the spinalis thoracis. The iliocostalis muscles are furthest from the spine.
Q. Is rhomboid major deep or superficial?
Located inferior to levator scapulae and superior to rhomboid major, it acts together with the latter to keep the scapula pressed against the thoracic wall. It lies deep to trapezius but superficial to the long spinal muscles.
Q. How long does it take for a rhomboid muscle to heal?
The amount of time it takes to recover from rhomboid muscle pain will depend on how severe the strain is. Most mild strains will heal within three weeks. More serious strains can take several months to heal. It’s important to avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting during recovery.
Q. Is rhomboid pain permanent?
A mild rhomboid injury might get better within a few days. More serious injuries can take weeks — or even months — to fully heal. To prevent future episodes of rhomboid pain: Always warm up for at least 5 to 10 minutes before you exercise or play sports, and stretch for a few minutes afterward.
Q. What exercises work the rhomboids?
These five exercises help strengthen the rhomboid muscles and improve your posture.
- Prone lateral raise. Lie flat on your stomach on a mat or bench.
- Front raise thumbs up. Lie down on your stomach on a mat or bench with your forehead resting down.
- Scapular retraction.
- Rear delt flys.
- Scapular wall slides.
Q. How do you release tension between shoulder blades?
Shoulder blade squeeze
- Sit or stand up tall with your arms at your sides.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed and down, not shrugged.
- Squeeze your shoulder blades together. Hold for 6 seconds, then relax.
- Repeat 8 to 12 times.
Q. Can anxiety cause pain between shoulder blades?
When we experience high levels of anxiety or stress, our body’s natural reaction is to tense up. When this happens consistently over a long period of time, it can lead to muscle tension, which can cause stiffness, tightness, aching, and pain in your neck and shoulders.
Q. What causes pain between the shoulder blades?
The most common cause of pain between the shoulder blades is a muscle strain. This can result from poor posture (especially leaning forward with prolonged sitting or standing), excess lifting, activities that involve twisting such as golf or tennis or even sleeping on a poor mattress.
Q. Why does my upper back and neck hurt all the time?
Upper back and neck pain are often due to poor posture and muscle strain. People who are diligent in correcting and maintaining their posture will likely experience a reduction in pain. Anyone who cannot get relief with home treatments should seek the help of a medical professional.
Q. Why is my upper back always tight?
Your shoulders may feel tight and stiff as the result of stress, tension, and overuse. Tight shoulders can be also caused by sitting for extended periods, incorrect sleeping positions, and injuries. Poor posture and improper alignment of your body can also play a part.
Q. What does lung pain feel like in the back?
Lung cancer related back pain may be generalized like a muscle ache or sharp like a pinched nerve. People with adrenal gland involvement may sometimes complain of “kidney pain” on one side of their back, or describe a feeling like they’ve just been “kidney punched.”
Q. What does a pinched lung feel like?
A collapsed lung feels like a sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens on breathing or with deep inspiration. This is referred to as “pleuritic” because it comes from irritation of nerve endings in the pleura (inner lining of the rib wall).
Q. Where is pleurisy pain located?
Pleurisy is inflammation of the sheet-like layers that cover the lungs (the pleura). The most common symptom of pleurisy is a sharp chest pain when breathing deeply. Sometimes the pain is also felt in the shoulder.