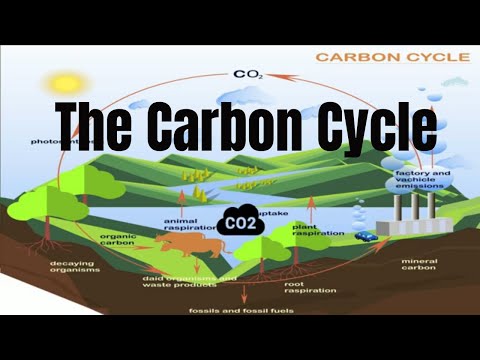
The three key processes and the conversions are shown in the table below. Carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration and combustion. Carbon dioxide is absorbed by producers to make glucose in photosynthesis. Animals feed on the plant passing the carbon compounds along the food chain.
Q. What is the role of combustion in the carbon cycle?
Combustion But a by-product of combustion is that it releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. And too much CO2 increases the greenhouse effect. Because we deplete our oil reserves adding CO2 into the air daily, it affects the carbon cycle with an imbalance of oxygen and carbon.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the role of combustion in the carbon cycle?
- Q. What are the two main processes of the carbon cycle?
- Q. What is carbon cycle with diagram?
- Q. What is the first step of the carbon cycle?
- Q. What is an example of carbon cycle?
- Q. What is the most important step in the carbon cycle?
- Q. What is carbon 9th cycle?
- Q. What are the 5 major carbon reservoirs?
- Q. What if carbon did not exist?
- Q. What is the importance of carbon cycle class 9?
- Q. What are the advantages of carbon cycle?
- Q. What are the biggest causes of CO2 emissions?
Q. What are the two main processes of the carbon cycle?
In the natural carbon cycle, there are two main processes which occur: photosynthesis and metabolism. During photosynthesis, plants use carbon dioxide and produce oxygen.
Q. What is carbon cycle with diagram?
Key Points on Carbon Cycle Carbon cycle explains the movement of carbon between the earth’s biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere. Carbon atoms are then released as carbon dioxide when organisms respire. The formation of fossil fuels and sedimentary rocks contribute to the carbon cycle for very long periods.
Q. What is the first step of the carbon cycle?
Stage one: Carbon enters the atmosphere by – respiration in organisms (e.g. animals breathing) – combustion (e.g. burning of fossil fuels/ wood) – decomposition and decay (microorganisms respiration) Stage two: Carbon Dioxide is absorbed by producers in photosynthesis.
Q. What is an example of carbon cycle?
For example, in the food chain, plants move carbon from the atmosphere into the biosphere through photosynthesis. Animals that eat plants digest the sugar molecules to get energy for their bodies. Respiration, excretion, and decomposition release the carbon back into the atmosphere or soil, continuing the cycle.
Q. What is the most important step in the carbon cycle?
During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide and sunlight to create fuel—glucose and other sugars—for building plant structures. This process forms the foundation of the fast (biological) carbon cycle.
Q. What is carbon 9th cycle?
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon moves from the atmosphere into the Earth and its organisms and then back again. Movement of carbon from the atmosphere to the oceans: The oceans, and other water bodies, soak up about a quarter of the carbon dioxide to form carbonates.
Q. What are the 5 major carbon reservoirs?
Carbon is stored on our planet in the following major sinks (1) as organic molecules in living and dead organisms found in the biosphere; (2) as the gas carbon dioxide in the atmosphere; (3) as organic matter in soils; (4) in the lithosphere as fossil fuels and sedimentary rock deposits such as limestone, dolomite and …
Q. What if carbon did not exist?
Both carbohydrates and carbon dioxide contain carbon. When carbon cycles, it also does so through non-living things. The amount of carbon does not change; we can’t get more. If carbon did not cycle through various forms, there would not be any available for living things, and life would not be possible.
Q. What is the importance of carbon cycle class 9?
The carbon cycle is important in ecosystems because it moves carbon, a life-sustaining element, from the atmosphere and oceans into organisms and back again to the atmosphere and oceans.
Q. What are the advantages of carbon cycle?
Supporting the natural carbon cycle and reducing methane gas emissions into the atmosphere. Creating a sustainable alternative to land application of waste. Reducing nutrient runoff. Reducing pathogens and promoting biosecurity.
Q. What are the biggest causes of CO2 emissions?
Since the Industrial Revolution, human sources of carbon dioxide emissions have been growing. Human activities such as the burning of oil, coal and gas, as well as deforestation are the primary cause of the increased carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere.