Unequal heating of Earth, atmospheric convection currents, rotation of the earth, Coriolis effect, earth’s orbit on a tilted axis, and the circulation of ocean waters at the surface and deep ocean. What happens to the air pressure as you move from the troposphere to the exosphere?
Q. What will happen if the Earth is bigger than its current size?
First, if the Earth is bigger that its current size, it would also gain a stronger magnetic field and greater gravitational pull because of the additional mass, and this is a bad news for us, because lifting an object would be so much difficult than ever before due to the increased pull of gravity.
Table of Contents
- Q. What will happen if the Earth is bigger than its current size?
- Q. How does the sun’s uneven heating of Earth drive weather?
- Q. What does uneven heating of the earth create?
- Q. How does uneven heating of Earth affect weather?
- Q. What are some effects of unequal heating?
- Q. Does the Earth heat up evenly?
- Q. How does the uneven heating of Earth Create Global Winds?
- Q. What are the 4 types of wind patterns?
- Q. What are the 3 major wind belts?
- Q. Which best describes the Coriolis effect?
- Q. How do you interpret a weather map symbol for wind direction?
- Q. What is the major cause of winds?
- Q. Which wind direction is the warmest?
- Q. Why is East Wind bad?
- Q. Why is our weather so hard to predict?
- Q. Which wind direction is the coldest?
- Q. Is a westerly wind coming from the west?
- Q. What is the most common wind direction?
- Q. What wind speed tells us?
- Q. What wind speed is dangerous for houses?
- Q. What is the fastest wind in the universe?
- Q. What wind speed is dangerous?
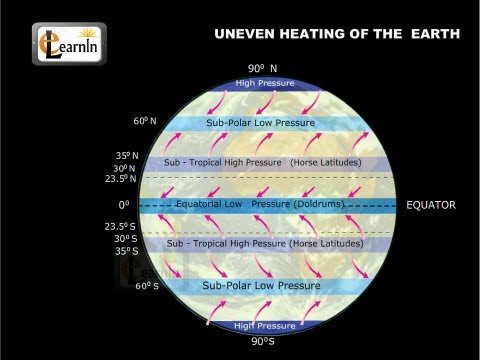
Q. How does the sun’s uneven heating of Earth drive weather?
The Sun heats Earth’s surface unevenly, driving global weather patterns that carry heat and humidity around the world. Differences in air pressure result in wind, causing air masses with different temperature and humidity to move. Clouds and powerful storms can form at a frontal boundary, where two air masses meet.
Q. What does uneven heating of the earth create?
Usually when we talk about uneven heating of the Earth’s surface we are discussing convection. The uneven heating results in some of the atmosphere to be warmer than other parts and changes in volume and pressure which result in updrafts and can cause thunderstorms and other violent weather.
Q. How does uneven heating of Earth affect weather?
The uneven heating causes temperature differences, which in turn cause air currents (wind) to develop, which then move heat from where there is more heat (higher temperatures) to where there is less heat (lower temperatures). The atmosphere thus becomes a giant “heat engine”, continuously driven by the sun.
Q. What are some effects of unequal heating?
Unequal heating of the earth’s surface causes temperature differences which cause pressure differences. Lower temperatures (heavy air) cause higher air pressure. Wind direction is described as where the wind is coming from. For example a northerly wind blows from the north to the south.
Q. Does the Earth heat up evenly?
The Sun doesn’t heat the Earth evenly. Because the Earth is a sphere, the Sun heats equatorial regions more than polar regions. The atmosphere and ocean work non-stop to even out solar heating imbalances through evaporation of surface water, convection, rainfall, winds, and ocean circulation.
Q. How does the uneven heating of Earth Create Global Winds?
Large global wind systems are created by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface. Warm air rises at the equator and moves toward the poles. At the poles, the cooler air sinks and moves back toward the equator.
Q. What are the 4 types of wind patterns?
The four major wind systems are the Polar and Tropical Easterlies, the Prevailing Westerlies and the Intertropical Convergence Zone. These are also wind belts. There are three other types of wind belts, also. They are called Trade Winds, Doldrums, and Horse Latitudes.
Q. What are the 3 major wind belts?
There are three prevailing wind belts associated with these cells: the trade winds, the prevailing westerlies, and the polar easterlies (Fig. 3.10).
Q. Which best describes the Coriolis effect?
The Coriolis effect describes the pattern of deflection taken by objects not firmly connected to the ground as they travel long distances around Earth. The Coriolis effect is responsible for many large-scale weather patterns. Specifically, Earth rotates faster at the Equator than it does at the poles.
Q. How do you interpret a weather map symbol for wind direction?
The symbol highlighted in yellow (in the diagram above) is known as a “Wind Barb”. The wind barb indicates the wind direction and wind speed. Wind barbs point in the direction “from” which the wind is blowing. In the case of the diagram below, the orientation of the wind barb indicates winds from the Northeast.
Q. What is the major cause of winds?
The wind is caused by differences in atmospheric pressure which is mainly caused by temperature difference. When a difference in atmospheric pressure exists, air moves from the higher to the lower pressure area, resulting in winds of various speeds.
Q. Which wind direction is the warmest?
In general, winds from the west or southwest are associated with overcast, wet weather. Winds from the south and southeast mainly occur in summer and these bring warm, dry weather. However, southerly winds can sometimes bring hot, thundery weather.
Q. Why is East Wind bad?
In Chapters 10 and 14 of Exodus, Moses summons the east wind to bring the locusts that plague Egypt and to part the Red Sea so that the Children of Israel can escape Pharaoh’s armies. Several other references exist, most associating the east wind with destruction. Often, this is destruction of the wicked by God.
Q. Why is our weather so hard to predict?
Well, their ability to predict the weather is limited by three factors: the amount of available data; the time available to analyze it; and. the complexity of weather events.
Q. Which wind direction is the coldest?
Easterly winds can bring very cold spells of weather, in fact it is winds from the east that produce our coldest weather.
Q. Is a westerly wind coming from the west?
Wind Strength To describe the strength of wind, weather reports often use words like Light Wind, Strong Wind, and Gale. Easterly winds blow from the east, while westerly winds blow from the west.
Q. What is the most common wind direction?
Prevailing winds are winds that blow from a single direction over a specific area of the Earth. Areas where prevailing winds meet are called convergence zones. Generally, prevailing winds blow east-west rather than north-south. This happens because Earth’s rotation generates what is known as the Coriolis effect.
Q. What wind speed tells us?
Wind speed describes how fast the air is moving past a certain point. Wind direction describes the direction on a compass from which the wind emanates, for instance, from the North or from the West.
Q. What wind speed is dangerous for houses?
50-75 mph
Q. What is the fastest wind in the universe?
Astronomers have discovered the fastest ultraviolet winds ever recorded in the Universe, swirling around a supermassive black hole at speeds of up to 200 million km/h (125 million mph). “We’re talking wind speeds of 20 percent the speed of light,” says one of the team, Jesse Rogerson from York University in Canada.
Q. What wind speed is dangerous?
Damaging winds are classified as those exceeding 50-60 mph.