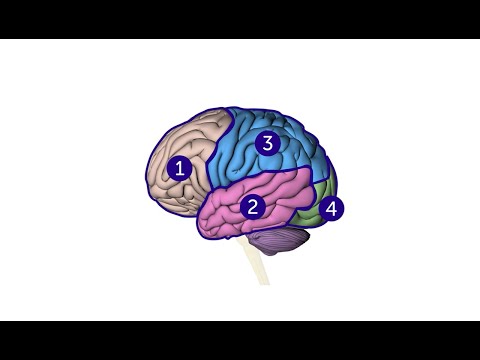
Each hemisphere has four sections, called lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital. Each lobe controls specific functions. For example, the frontal lobe controls personality, decision-making and reasoning, while the temporal lobe controls, memory, speech, and sense of smell.
Q. What are the four 4 specific structures structural mechanisms that protect the brain?
The brain is protected by the skull (cranium), cerebrospinal fluid and 3 protective membranes (Meninges). The spinal cord is protected similarly but with vertebrae instead of the cranium.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the four 4 specific structures structural mechanisms that protect the brain?
- Q. What are the 4 lobes of the cerebral cortex and their functions?
- Q. Where are the 4 lobes of the brain located?
- Q. What is considered a heavy smoker?
- Q. Does 1 cigarette a month affect you?
- Q. Is one cigarette a week bad?
- Q. How bad is 2 cigarettes a day?
- Q. Is 2 to 3 cigarettes a day bad?
- Q. Which cigarette is not harmful?
- Q. Does smoking take years off your life?
- Q. Does watching TV shorten your lifespan?
- Q. Does sadness shorten your lifespan?
- Q. What happens when u cry too much?
- Q. Does PTSD shorten your life?
- Q. Does chronic pain shorten life expectancy?
- Q. What are the long term effects of chronic pain?
- Q. What is best medication for chronic pain?
Q. What are the 4 lobes of the cerebral cortex and their functions?
Each side of your brain contains four lobes. The frontal lobe is important for cognitive functions and control of voluntary movement or activity. The parietal lobe processes information about temperature, taste, touch and movement, while the occipital lobe is primarily responsible for vision.
Q. Where are the 4 lobes of the brain located?
The four lobes of the brain are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes (Figure 2). The frontal lobe is located in the forward part of the brain, extending back to a fissure known as the central sulcus.
Q. What is considered a heavy smoker?
Background: Heavy smokers (those who smoke greater than or equal to 25 or more cigarettes a day) are a subgroup who place themselves and others at risk for harmful health consequences and also are those least likely to achieve cessation. Results: Heavy smokers constituted 26.7% of all cigarette smokers.
Q. Does 1 cigarette a month affect you?
Study: A Cigarette A Month Can Get A Kid Hooked Occasional smoking among middle-schoolers can lead to tobacco addiction, according to a study in the journal Pediatrics. Of the young people in the study who said they had inhaled from a cigarette, nearly two-thirds said they smoked at least once a month.
Q. Is one cigarette a week bad?
Simon Chapman, Emeritus Professor in the School of Public Health at the University of Sydney said: “Smoking a small number of cigarettes, say less than four a day or once a week does elevate your risk [of health problems].
Q. How bad is 2 cigarettes a day?
Even Smoking ‘Just’ One or Two Cigarettes a Day Increases Your Risk of Lung Disease. A new study shows even light smokers can develop deadly lung diseases such as emphysema and COPD. Pulmonologist Humberto Choi, MD, explains the findings.
Q. Is 2 to 3 cigarettes a day bad?
“We know that smoking just one to four cigarettes a day doubles your risk of dying from heart disease,” he says. “And heavy smokers who reduce their smoking by half still have a very high risk of early death.” ‘Light’ cigarettes are safer. MYTH.
Q. Which cigarette is not harmful?
Of all the herbal cigarettes available in the market, Mea Ame’s Organic Smokes is one of the leading brands. Packaged in a rustic wooden box, the cigarettes are marketed as a ‘safer’ way of smoking. “We have worked with Ayurveda doctors to create our cigarettes.
Q. Does smoking take years off your life?
The amount of life expectancy lost for each pack of cigarettes smoked is 28 minutes, and the years of life expectancy a typical smoker loses is 25 years. Every cigarette a man smokes reduces his life by 11 minutes.
Q. Does watching TV shorten your lifespan?
Every single hour of television watched after age 25 was associated with a 22-minute reduction in average life expectancy. Researchers say their calculations show that an adult who spends an average of six hours per day watching TV can expect to live 4.8 years fewer than someone who does not watch TV.
Q. Does sadness shorten your lifespan?
It’s long been believed people with major depression and some other serious mental illnesses tend to live shorter lives than others—and die more quickly than expected when they develop illnesses such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Q. What happens when u cry too much?
If you cry a lot, you may feel self-conscious. It may feel like people are taking you less seriously when they see you cry, or you may feel weak (which isn’t really true). But if you cry a lot, it may mean you’re having difficulty dealing with your stress.
Q. Does PTSD shorten your life?
Some people who develop PTSD and chronic pain also experience depression and alcohol and prescription medication misuse. Chronic PTSD has been shown to increase the risk of having a variety of health issues and decreased life expectancy.
Q. Does chronic pain shorten life expectancy?
Thus, while the pain-free life expectancy of males and females across ages is about equal, females live more years with pain, and with more severe pain. As males and females age, life expectancy decreases. But, proportion of life expected with pain does not change.
Q. What are the long term effects of chronic pain?
Results: A review of recent literature examining the neurobiology and pathophysiology of chronic pain reveals that this highly prevalent condition negatively impacts multiple aspects of patient health, including sleep, cognitive processes and brain function, mood/mental health, cardiovascular health, sexual function.
Q. What is best medication for chronic pain?
Acetaminophen is usually recommended as a first line treatment for mild to moderate pain, such as from a skin injury, headache or musculoskeletal condition. Acetaminophen is often prescribed to help manage osteoarthritis and back pain. It may also be combined with opioids to reduce the amount of opioid needed.