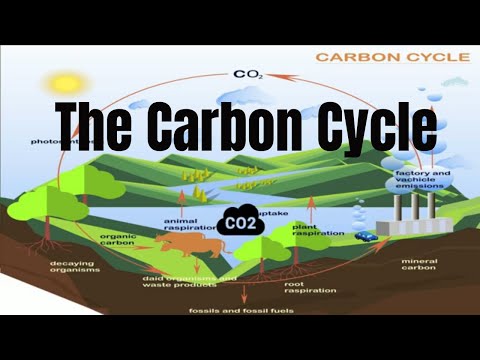
Q. What are the 5 parts of the carbon cycle?
The Carbon Cycle
- Carbon moves from the atmosphere to plants.
- Carbon moves from plants to animals.
- Carbon moves from plants and animals to soils.
- Carbon moves from living things to the atmosphere.
- Carbon moves from fossil fuels to the atmosphere when fuels are burned.
- Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the oceans.
Q. How does carbon get into the atmosphere?
Atmospheric carbon dioxide comes from two primary sources—natural and human activities. Human activities that lead to carbon dioxide emissions come primarily from energy production, including burning coal, oil, or natural gas. …
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the 5 parts of the carbon cycle?
- Q. How does carbon get into the atmosphere?
- Q. How many ways can carbon enter the atmosphere?
- Q. What are the 6 steps of the carbon cycle?
- Q. What are the 4 steps of carbon cycle?
- Q. What part of the carbon cycle takes the longest?
- Q. What are the 7 places carbon is stored?
- Q. Where is most of the carbon on Earth stored?
- Q. Why is releasing carbon dioxide bad?
- Q. What human activities produce carbon dioxide?
- Q. What is the largest source of CO2 emissions globally?
- Q. Do cows emit more pollution than cars?
- Q. Do cows contribute to global warming?
- Q. Why are cows bad for the environment?
- Q. What’s the worst thing for the environment?
- Q. Does killing animals cause global warming?
- Q. Are cows bad for the planet?
- Q. Why cows should not be killed?
- Q. Do cows actually fart?
- Q. How much do cows fart a day?
Q. How many ways can carbon enter the atmosphere?
Cellular Respiration, burning coal, wood, gasoline, turn the Carbon-based molecules back into Carbon Dioxide and water. These Oxidation reactions return the Carbon Dioxide to the atmosphere.
Q. What are the 6 steps of the carbon cycle?
this process is driven by the six processes of: photosynthesis, respiration, exchange, sedimentation and burial, extraction, and combustion.
Q. What are the 4 steps of carbon cycle?
Photosynthesis, Decomposition, Respiration and Combustion. Carbon cycles from the atmosphere into plants and living things.
Q. What part of the carbon cycle takes the longest?
fossil fuels
Q. What are the 7 places carbon is stored?
Carbon is stored on our planet in the following major sinks (1) as organic molecules in living and dead organisms found in the biosphere; (2) as the gas carbon dioxide in the atmosphere; (3) as organic matter in soils; (4) in the lithosphere as fossil fuels and sedimentary rock deposits such as limestone, dolomite and …
Q. Where is most of the carbon on Earth stored?
On Earth, most carbon is stored in rocks and sediments, while the rest is located in the ocean, atmosphere, and in living organisms. These are the reservoirs, or sinks, through which carbon cycles.
Q. Why is releasing carbon dioxide bad?
The major threat from increased CO2 is the greenhouse effect. As a greenhouse gas, excessive CO2 creates a cover that traps the sun’s heat energy in the atmospheric bubble, warming the planet and the oceans. An increase in CO2 plays havoc with the Earth’s climates by causing changes in weather patterns.
Q. What human activities produce carbon dioxide?
Carbon dioxide (CO2). A minor but very important component of the atmosphere, carbon dioxide is released through natural processes such as respiration and volcano eruptions and through human activities such as deforestation, land use changes, and burning fossil fuels.
Q. What is the largest source of CO2 emissions globally?
Energy consumption
Q. Do cows emit more pollution than cars?
Do cows pollute more than cars? Statistically, yes. Researchers say that cows produce, on average, about 100 to 200 liters (26 to 53 gallons) of methane per day through belching. Some even raise the figure up to 500 liters (about 132 gallons) of methane in one day.
Q. Do cows contribute to global warming?
Cattle are the No. 1 agricultural source of greenhouse gases worldwide. Methane from cattle is shorter lived than carbon dioxide but 28 times more potent in warming the atmosphere, said Mitloehner, a professor and air quality specialist in the Department of Animal Science.
Q. Why are cows bad for the environment?
The bad news: Their burps are a real problem. Cows are ruminants, meaning that microbes in their multichambered stomachs help them digest by fermenting their food. This process produces the powerful greenhouse gas methane, which gets released into the atmosphere when they burp. Here, again, cows are a major culprit.
Q. What’s the worst thing for the environment?
21 Habits That Are Bad for the Environment
- Driving too much.
- Buying fast fashion.
- Throwing out items in good condition.
- Buying single-use items.
- Drinking bottled water.
- Using tampons and pads.
- Using utilities at 6:00 pm.
- Using pesticides and weed killers.
Q. Does killing animals cause global warming?
When it comes to climate change, animal agriculture is a leading culprit. It’s simple, really: Those crops and water are used to bulk up animals for slaughter. The animals emit noxious levels of CO2, methane gas, and excrement that pollute our air and waterways.
Q. Are cows bad for the planet?
Cows release methane gas into the atmosphere — a pollutant that’s considered 25 times more harmful to the environment than CO2.
Q. Why cows should not be killed?
In many areas in the world, cows are cultivated in large numbers for just beef and that has catastrophic environmental impacts on total land used for grazing, greenhouse emissions and water usage and effects on polluting aquatic ecosystems. We don’t want to bring that type of culture into India.
Q. Do cows actually fart?
From London, Rabaiotti said methane emissions from cattle are belch-focused because the gas is produced near the start of their digestive system and comes up when they regurgitate their food to chew the cud. And for the record, says this authority on the animal kingdom’s ruder moments, “Yes, cows do fart.”
Q. How much do cows fart a day?
Methane is subsequently expelled through the cow’s front end – through burping – or through the cow’s backdoor – via farting. A cow burps and farts between 160 to 320 litres of methane per day.