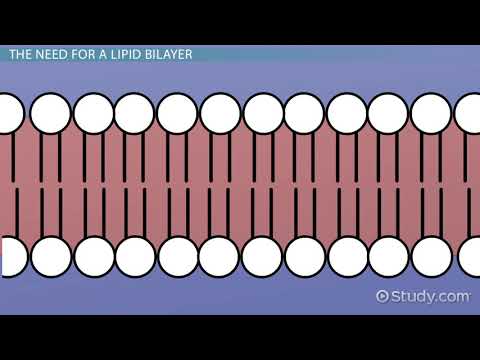
Q. What are the advantages of phospholipid bilayer in maintaining fluidity?
Fluidity of phospholipid bilayer allows the membrane to stretch under stress and to reseal if disrupted, and permits lipid and protein molecules to move sideways.
Q. What are advantages of cell membrane?
The plasma membrane, or the cell membrane, provides protection for a cell. It also provides a fixed environment inside the cell, and that membrane has several different functions. One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the advantages of phospholipid bilayer in maintaining fluidity?
- Q. What are advantages of cell membrane?
- Q. How is compartmentalization an advantage?
- Q. What advantages does compartmentalization provide to a large and complex cell?
- Q. What is compartmentalization of cell and why is it important?
- Q. What advantages are there in having the interior of the cell divided into a number of compartments?
- Q. Do structures lack membranes?
- Q. How do membranes compartmentalize a cell?
- Q. What is the significance of membrane compartmentalization in eukaryotes?
- Q. What are the major differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Q. How is compartmentalization an advantage?
Compartmentalization increases the efficiency of many subcellular processes by concentrating the required components to a confined space within the cell.
Q. What advantages does compartmentalization provide to a large and complex cell?
-Compartmentalization allows the cell to have centralized locations to carry out specific processes which speeds up reactions, uses less energy and may protect other parts of the cell from dangerous products and byproducts produced in the reaction.
Q. What is compartmentalization of cell and why is it important?
Compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells is largely about efficiency. Separating the cell into different parts allows for the creation of specific microenvironments within a cell. That way, each organelle can have all the advantages it needs to perform to the best of its ability.
Q. What advantages are there in having the interior of the cell divided into a number of compartments?
What advantages are there in having the interior of the cell divided into a numberof compartments such as the nucleus, the ER, lysosomes, and so on? The advantages it has are protection and organization. Protection because the plasma membrane protects organelles from outside from the factors outside the environment.
Q. Do structures lack membranes?
Cell Structures : Example Question #5 They lack membrane-bound organelles (such as mitochondria) and contain a nucleoid region instead of a membrane-bound nucleus.
Q. How do membranes compartmentalize a cell?
Cellular organelles separated from the cytoplasm by dedicated lipid membranes are the most obvious form of compartmentalization. Membranes assemble via hydrophobic interactions of lipids without the need for attractive interactions between neighboring components.
Q. What is the significance of membrane compartmentalization in eukaryotes?
Compartmentalization of metabolic processes makes eukaryotic cells very efficient and allows them to increase in size. Within the nucleus, are the molecules of DNA, the macromolecules that carry all the genetic and hereditary information of the cell.
Q. What are the major differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. The nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information.