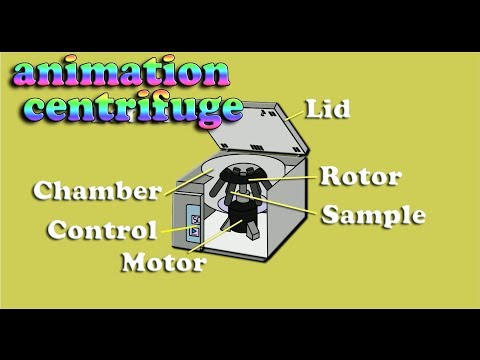
Basic centrifuge components include an electric motor, a shaft and rotor heads on which the centrifuge head turns, and a motor- drive assembly. If the centrifuge is refrigerated, a compressor and associated components are included. The entire system is housed within a chamber.
Q. Which best describes the function of a centrifuge?
A laboratory centrifuge is used for the separation of fluids, gas or liquid, based on density. The centrifugal force created by the spinning the vessel containing the material pushes the materials outside of the vessel, thus, separating dissolved particles from undissolved particles.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which best describes the function of a centrifuge?
- Q. What are the features of centrifuge?
- Q. How do you choose a centrifuge?
- Q. What is the principle and application of centrifugation?
- Q. What are the different types of centrifuge?
- Q. What are the two types of centrifugation?
- Q. What is centrifuge and its type?
- Q. Where is centrifugation used?
- Q. What is centrifugation with example?
- Q. What happens after centrifugation?
- Q. What is the ideal centrifugation time and RPM?
- Q. At what speed do you centrifuge blood?
- Q. Why is it important to centrifuge blood?
- Q. Why does a centrifuge separate blood?
- Q. What blood tube colors are for which test?
- Q. What is Pearl top tube used for?
- Q. What color tube is used for syphilis?
- Q. What is the principle of centrifugation?
- Q. Why is centrifugation important?
- Q. What are two applications of centrifugation?
- Q. What are the two applications of crystallization?
- Q. What are the three application of centrifugation?
- Q. What are the types of centrifugation?
- Q. What is the principle of centrifugation Class 9?
- Q. What are the applications of centrifugation Class 9?
- Q. What are the applications of crystallization Class 9?
- Q. What are the main components of the blood?
- Q. Why is serum red?
- Q. How platelets are separated from blood?
Q. What are the features of centrifuge?
Product Features
- High Performance. Easy-to-use touch screen displays. Programmable acceleration and deceleration.
- Refrigerated Models. Offset heat generated by friction with a refrigerated centrifuge.
- Reliable. Efficient, zero-maintenance brushless induction motors.
- Environmentally Friendly. Low energy consumption.
Q. How do you choose a centrifuge?
Tips for Selecting a Centrifuge
- RPMs are important, but G-Force is even better.
- Flexibility is key.
- Factor in available space in your lab.
- Make life easy on yourself and your labmates.
- Take advantage of industry tools.
Q. What is the principle and application of centrifugation?
Centrifugation is a technique of separating substances which involves the application of centrifugal force. The particles are separated from a solution according to their size, shape, density, the viscosity of the medium and rotor speed.
Q. What are the different types of centrifuge?
They are:
- Small Bench Centrifuges:
- Large Capacity Refrigerated Centrifuges:
- High Speed Refrigerated Centrifuges:
- Ultra Centrifuges:
- Fixed Angle Rotors:
- Vertical Tube Rotors:
- Zonal Rotors:
- Elutriator Rotors:
Q. What are the two types of centrifugation?
Centrifugation Techniques There are two types of centrifugal techniques for separating particles: differential centrifugation and density gradient centrifugation.
Q. What is centrifuge and its type?
A centrifuge is a device used to separate components of a mixture on the basis of their size, density, the viscosity of the medium, and the rotor speed. There are different types of centrifuge used for the separation of different molecules, but they all work on the principle of sedimentation.
Q. Where is centrifugation used?
Centrifugation is the process where a mixture is separated through spinning. It is used to separate skim milk from whole milk, water from your clothes, and blood cells from your blood plasma.
Q. What is centrifugation with example?
Some common examples of centrifugation include: The extraction of fat from milk in order to produce skimmed milk. The removal of water from moist lettuce with the help of a salad spinner. The Spin-drying of water in washing machines in order to remove water from the clothing.
Q. What happens after centrifugation?
After an initial centrifugation, the pellet, containing the largest components, is separated from the remaining suspension (known as the supernatant) which contains the smaller components.
Q. What is the ideal centrifugation time and RPM?
In general, the recommended centrifuge speed for chemistry testing is 3500 rpm for ten minutes; for coagulation testing, the spin speed is 3500 rpm for seven minutes.
Q. At what speed do you centrifuge blood?
Do not centrifuge immediately after drawing blood. Allow the blood to clot in an upright position for at least 30 minutes but not longer than 1 hour before centrifugation. Centrifuge for at least 15 minutes at 2200-2500 RPM within one hour of collection.
Q. Why is it important to centrifuge blood?
Centrifuge Promptly It is important to separate the cellular and liquid portions of a blood specimen as soon as possible when the test requires a sample of serum or plasma. This is because the cells interact with the serum/plasma, altering its chemical composition and affecting test results.
Q. Why does a centrifuge separate blood?
A machine called a centrifuge spins your blood to separate your red blood cells, platelets and plasma. When you give blood, it triggers your spleen to flood your blood stream with stored platelets to try and stop the bleeding.
Q. What blood tube colors are for which test?
The tests each bottle is used for are the same: the purple one is for cell count, the yellow one is for electrolytes, albumin and LDH, the grey one is for glucose, and blood culture bottles can be used for fluid cultures.
Q. What is Pearl top tube used for?
PHLEBOTOMY SERVICES
| STOPPER COLOR | CONTENTS | USES/COMMENTS |
|---|---|---|
| Pearl Top (Plasma Preparation, “PPT”) | Separating gel and (K2)EDTA | Adenovirus PCR Toxoplasma PCR HHV-6 PCR |
| Lavender (“Purple”) | (K2)EDTA | CBC/Diff/Retic/Sed Rate, FK506, Cyclosporin, Platelet Ab, Coombs, Flow Cytometry |
Q. What color tube is used for syphilis?
Obtain 5-10 ml of blood from the patient using standard venipuncture technique. Collect the blood into an anticoagulant free (i.e. “clot”) tube or serum separator tube (SST). Plasma (purple top tube) may be used up to 48 hrs.
Q. What is the principle of centrifugation?
A centrifuge works by using the principle of sedimentation: Under the influence of gravitational force (g-force), substances separate according to their density. Here, particles are concentrated as a pellet at the bottom of the centrifuge tube and separated from the remaining solution, called supernatant.
Q. Why is centrifugation important?
It is one of the most useful and frequently employed techniques in the molecular biology laboratory. Centrifugation is used to collect cells, to precipitate DNA, to purify virus particles, and to distinguish subtle differences in the conformation of molecules.
Q. What are two applications of centrifugation?
Centrifugation is a process where a mixture is separate through spinning according to their size ,shape ,density , viscosity medium and rotor speed. Application; > It helps in separating Milk and cream, when rotated rapidly in circular motion. The cream is forced to on the top, leaving milk at the bottom.
Q. What are the two applications of crystallization?
The most practical usage of crystallization should be salt crystallization and it’s the most cost-effective way to produce salt even at today. Other applications of the tech include compound purification and crystal production.
Q. What are the three application of centrifugation?
Applications of centrifugation: (a) Used in dairies and home to separate cream from milk or butter from cream. (b) Used in washing machines to squeeze out water from clothes. (c) Used in laboratories to separate colloidal particles from their solutions.
Q. What are the types of centrifugation?
Centrifugation Techniques There are two types of centrifugal techniques for separating particles: differential centrifugation and density gradient centrifugation. Density gradient centrifugation can further be divided into rate-zonal and isopycnic centrifugation.
Q. What is the principle of centrifugation Class 9?
Principle of Centrifugation: When a mixture is rotated very fast, the denser particles are forced to go to the bottom of the centrifuge and the lighter particles stay at the top.
Q. What are the applications of centrifugation Class 9?
Application of centrifugation are:
- Used in diagnostic laboratories for blood and urine test.
- Used in dairies and home to separate butter from cream.
- Used in a washing machines to squeeze out water from wet clothes.
Q. What are the applications of crystallization Class 9?
Crystallization is primarily employed as a separation technique in order to obtain pure crystals of a substance from an impure mixture. Another important application of crystallization is its use to obtain pure salt from seawater. Crystallization can also be used to obtain pure alum crystals from an impure alum.
Q. What are the main components of the blood?
Blood is a specialized body fluid. It has four main components: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Blood has many different functions, including: transporting oxygen and nutrients to the lungs and tissues.
Q. Why is serum red?
Hemoglobin is also what makes blood red. So naturally, when red cells burst, it tinges the liquid portion of the blood. That’s because hemoglobin is a liquid protein which dilutes the serum or plasma being tested.
Q. How platelets are separated from blood?
During a platelet donation, whole blood is drawn from one arm into a sterile kit inside a cell separating machine. The machine separates the blood so that only platelets and plasma are collected. The other blood components (red cells and white cells) are returned to the donor via the same arm.