The basis of early classification were simple morphological characters to classify in trees herbs and sherbs and animals to which had red blood and those that did not. This classification was given by Aristotle.
Q. What are the basis of classification of five kingdom classification?
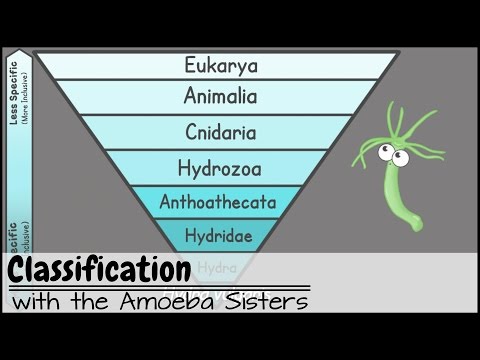
On what basis are the living organisms divided in the five-kingdom classification? The living organisms are divided into five different kingdoms – Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia, and Monera on the basis of their characteristics such as cell structure, mode of nutrition, mode of reproduction and body organization.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the basis of classification of five kingdom classification?
- Q. What is called biological classification?
- Q. What was the earliest classification system called?
- Q. Who proposed 2 kingdom classification?
- Q. What are the two systems of classification?
- Q. What are 3 differences between bacteria and archaea?
- Q. What are the two main domains?
- Q. Which pair of domains is most closely related?
Q. What is called biological classification?
Biological classification is the process by which scientists group living organisms. Organisms are classified based on how similar they are. Historically, similarity was determined by examining the physical characteristics of an organism but modern classification uses a variety of techniques including genetic analysis.
Q. What was the earliest classification system called?
Great Chain of Being
Q. Who proposed 2 kingdom classification?
Summary
| Linnaeus 1735 | Haeckel 1866 | Copeland 1938 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 kingdoms | 3 kingdoms | 4 kingdoms |
| (not treated) | Protista | Monera |
| Protista | ||
| Vegetabilia | Plantae | Plantae |
Q. What are the two systems of classification?
Two Kingdoms Classification: In his Systema Naturae, first published in 1735, Carolus Linnaeus distinguished two kingdoms of living things: Animalia for animals and Plantae (Vegetabilia) for plants. He classified all living organisms into two kingdoms – on the basis of nutrition and locomotion (mobility).
Q. What are 3 differences between bacteria and archaea?
Responses will vary. A possible answer is: Bacteria contain peptidoglycan in the cell wall; archaea do not. The cell membrane in bacteria is a lipid bilayer; in archaea, it can be a lipid bilayer or a monolayer. Bacteria contain fatty acids on the cell membrane, whereas archaea contain phytanyl.
Q. What are the two main domains?
For many biologists, Darwin’s dream was realised on the grandest scale when, in 1990, Carl Woese and colleagues proposed that all cellular life could be placed into one of three separate fundamental groups or ‘domains’ – the Bacteria, the Archaea and the Eukarya, based upon sequence comparisons of small subunit (SSU) …
Q. Which pair of domains is most closely related?
Which pair of organisms are most closely related? Organisms 2 and 3 are most closely related because they have the same family name.