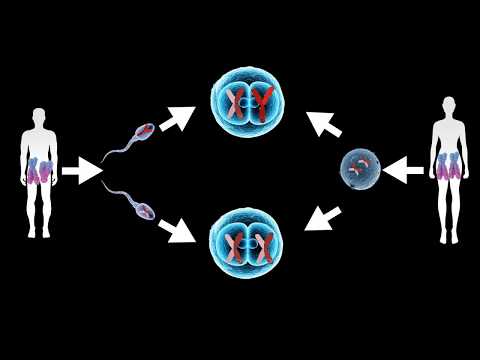
Q. What are the factors that determine the sex of an individual?
In humans, sex is determined by sex chromosomes (XX females, XY males). The X and Y chromosomes harbor dramatically different numbers and sets of genes (about 1,000 genes on the X and only a few dozen genes on the Y), yet they originated from ordinary autosomes during the early evolution of mammals (Figure 1).
Q. Who decides the sex of the baby?
A child’s gender (male or female) is determined by the chromosome that the male parent contributes. Females have XX sex chromosomes. Males have XY sex chromosomes. A male infant results if the male contributes his Y chromosome while a female infant results if he contributes his X chromosome.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the factors that determine the sex of an individual?
- Q. Who decides the sex of the baby?
- Q. How can you tell if its a boy or girl by heartbeat?
- Q. How can you tell gender by placenta?
- Q. Can a posterior placenta cause back pain?
- Q. Is back pain worse with anterior placenta?
- Q. Is a posterior baby more likely to be overdue?
- Q. Are posterior births more painful?
- Q. How do I know if my baby turned posterior?
Q. How can you tell if its a boy or girl by heartbeat?
You may have heard that your baby’s heart rate can predict their sex as early as the first trimester. If it’s over 140 bpm, you’re having a baby girl. Below 140 bpm, you’re carrying a boy. The truth is, your baby’s heart will likely start beating sometime around week 6 of your pregnancy.
Q. How can you tell gender by placenta?
If the placenta is developing on the left side, the sex is female. If it is developing on the right, the sex is male. Unfortunately, Ramzi’s method has not been confirmed in any additional studies. There are no outward signs of sex until about 9 weeks of pregnancy.
Q. Can a posterior placenta cause back pain?
Placental Location and Back Pain A posterior (back) location of the placenta (the tissue that provides nourishment to the fetus) is known to cause back pain in some pregnant women. In these cases, the placenta is located near the posterior wall of the uterus.
Q. Is back pain worse with anterior placenta?
When a baby is back-to-back, labour can be more painful, longer and the likelihood of needing a caesarean increases. Your midwife will be able to monitor the position of your baby. Anterior placenta mums tend to experience lower back pain during pregnancy.
Q. Is a posterior baby more likely to be overdue?
This means that it is harder for labour to start naturally, so posterior babies are more likely to be overdue. When labour does start, there is often increased back pain, irregular contractions and slower dilation of the cervix, which cause a longer labour as the contractions rotate the baby to a better position.
Q. Are posterior births more painful?
No. Back labor – the intense lower back pain that many women feel during labor – was long thought to be more likely when the baby is facing up. But research using ultrasound (much more accurate than a clinical exam, especially in the first stage of labor) suggests that this assumption is probably wrong.
Q. How do I know if my baby turned posterior?
Your baby may be head down if you can:
- feel their head low down in your belly.
- feel their bottom or legs above your belly button.
- feel larger movements — bottom or legs — higher up toward your rib cage.
- feel smaller movements — hands or elbows — low down in your pelvis.