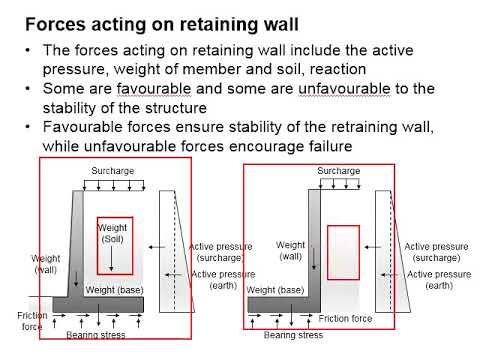
Q. What are the force acting on retaining wall?
The lateral Earth pressure due to earth pressure is the major force acting on the retaining wall .
Q. What kind of forces or pressure does a retaining wall experience?
Depending on the nature of construction, the forces acting on retaining walls are varying. For example, active pressure and at rest pressure can be considered.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the force acting on retaining wall?
- Q. What kind of forces or pressure does a retaining wall experience?
- Q. How much pressure is on a retaining wall?
- Q. How do you calculate slope?
- Q. How do you calculate building slope?
- Q. How do you calculate earth’s pressure?
- Q. How do you calculate the coefficient of active earth pressure?
- Q. How do you calculate hydrostatic pressure in soil?
- Q. What are the 3 slope formulas?
- Q. How do you calculate runway slope?
- Q. How to calculate the force on a slope?
- Q. How is the acceleration of an object on a slope calculated?
- Q. How are loads and forces acting on retaining wall?
- Q. Is the normal force of an object always perpendicular to the slope?
Q. How much pressure is on a retaining wall?
Moist unit weight, a combination of soil, water and air, will generally range from 110 to 130 pounds per cubic foot depending on the soil type. From the equation we can see, as unit weight increases, so does lateral earth pressure. The final variable in the equation, H, is the total height of the retaining wall.
Q. How do you calculate slope?
Calculating the Slope Percentage Convert the rise and run to the same units and then divide the rise by the run. Multiply this number by 100 and you have the percentage slope. For instance, 3″ rise divided by 36″ run = . 083 x 100 = an 8.3% slope.
Q. How do you calculate building slope?
Let us now calculate the slope, run & rise in the 3 different drawings as shown below.
- Slope calculation : Given data : Run = 15m. Rise = 0.5m. Slope = run ÷ rise.
- Run calculation: Given data : Slope = 1: 100. Rise = 0.5m. Run.
- Rise calculation: Given data : Slope or gradient = 1:30. Run = 12m. Rise.
- Rise per meter calculation:
Q. How do you calculate earth’s pressure?
In geotechnical engineering practice, the commonly used procedure for estimating earth pressure on retaining structures is to use the formula p = y h K, where y is the unit weight of backfill material – its value properly adjusted for the design seismic coefficient in the vertical direction, h is the height of the …
Q. How do you calculate the coefficient of active earth pressure?
The principle of determination of active earth pressure is to multiply the effective vertical stress with the lateral pressure coefficient (Ka) and then add the hydrostatic pressure due to water table, if any.
Q. How do you calculate hydrostatic pressure in soil?
Under hydrostatic conditions (no water flow) the pore pressure at a given point is given by the hydrostatic pressure: u = gw . h. It is convenient to think of pore pressure represented by the column of water in an imaginary standpipe; the pressure just outside being equal to that inside.
Q. What are the 3 slope formulas?
There are three major forms of linear equations: point-slope form, standard form, and slope-intercept form.
Q. How do you calculate runway slope?
Divide the difference of the elevations by the length of the runway. For the example, the length of the runway is 3,000 feet. Dividing 30 by 3,000 results in 0.01. Multiply that number by 100 to obtain the slope of the runway.
Q. How to calculate the force on a slope?
•The weight force is resolved into 2 components: omg cosθ perpendicular to plane, and omg sinθ parallel to the plane. •The resultant force ΣF down the slope is given by ΣF = mg sinθ − F f where F f is friction •The resultant force ΣF perpendicular to the slope is zero, hence: mgcosθ = F N
Q. How is the acceleration of an object on a slope calculated?
Mechanics index The acceleration of an object down a slope due to gravity and under friction is calculated by resolving the forces parallel and normal to the slope. If the component of the gravitational force down the slope is greater than the maximum frictional force, then it will slide.
Q. How are loads and forces acting on retaining wall?
Loads and Forces Acting on Retaining Wall. There are various types of loads and forces acting on retaining wall, which are: Lateral earth pressure. Surcharge loads. Axial loads. Wind on projecting stem. Impact forces. Seismic earth pressure.
Q. Is the normal force of an object always perpendicular to the slope?
The normal force of an object placed on a sloping surface is always perpendicular to the surface. Another vital feature is that just as we can analyse the horizontal and vertical components of the motion of an object separately, we can look at components parallel to and perpendicular to the surface of a sloping surface as well.